With the help of citizen scientists, astronomers have discovered two highly unusual brown dwarfs, balls of gas that are not massive enough to power themselves the way stars do.
Participants in the NASA-funded Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 project helped lead scientists to these bizarre objects, using data from NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) satellite along with all-sky observations collected between 2009 and 2011 under its previous moniker, WISE. Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 is an example of “citizen science,” a collaboration between professional scientists and members of the public.
Scientists call the newly discovered objects “the first extreme T-type subdwarfs.” They weigh about 75 times the mass of Jupiter and clock in at roughly 10 billion years old. These two objects are the most planet-like brown dwarfs yet seen among the Milky Way’s oldest population of stars.
Astronomers hope to use these brown dwarfs to learn more about exoplanets, which are planets outside of our solar system. The same physical processes may form both planets and brown dwarfs.
“These surprising, weird brown dwarfs resemble ancient exoplanets closely enough that they will help us understand the physics of the exoplanets,” said astrophysicist Marc Kuchner, the principal investigator of Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 and the Citizen Science Officer for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. Kuchner is also an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
These two special brown dwarfs have highly unusual compositions. When viewed in particular wavelengths of infrared light, they look like other brown dwarfs, but at others they do not resemble any other stars or planets that have been observed so far.
Scientists were surprised to see they have very little iron, meaning that, like ancient stars, they have not incorporated iron from star births and deaths in their environments. A typical brown dwarf would have as much as 30 times more iron and other metals than these newly discovered objects. One of these brown dwarfs seems to have only about 3% as much iron as our Sun. Scientists expect very old exoplanets would have a low metal content, too.
“A central question in the study of brown dwarfs and exoplanets is how much does planet formation depend on the presence of metals like iron and other elements formed by multiple earlier generations of stars,” Kuchner said. “The fact that these brown dwarfs seem to have formed with such low metal abundances suggests that maybe we should be searching harder for ancient, metal-poor exoplanets, or exoplanets orbiting ancient metal-poor stars.”
A study in The Astrophysical Journal details these discoveries and the potential implications. Six citizen scientists are listed as co-authors of the study.
How volunteers found these extreme brown dwarfs
The study’s lead author, Adam Schneider of Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration in Tempe, first noticed one of the unusual brown dwarfs, called WISE 1810, in 2016, but it was in a crowded area of the sky and was difficult to confirm.
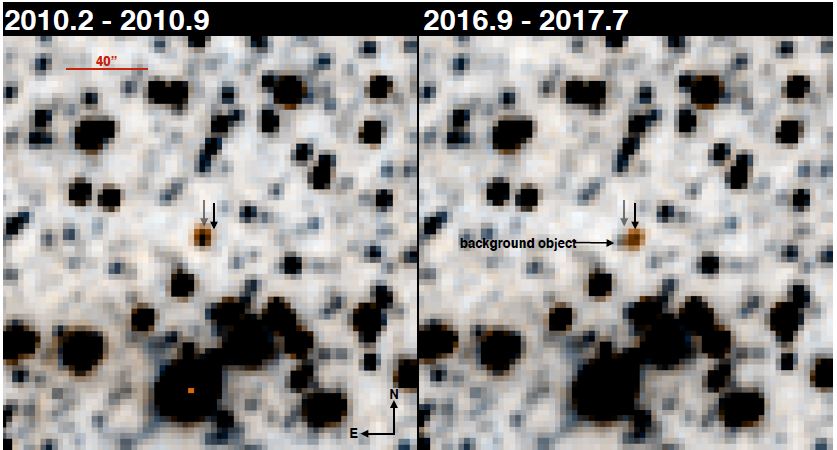
With the help of a tool called WiseView, created by Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 citizen scientist Dan Caselden, Schneider confirmed that the object he had seen years earlier was moving quickly, which is a good indication that an object is a nearby celestial body like a planet or brown dwarf.
“WiseView scrolls through data like a short movie,” Schneider said, “so you can see more easily see if something is moving or not.”
The second unusual brown dwarf, WISE 0414, was discovered by a group of citizen scientists including Backyard Worlds participants Paul Beaulieu, Sam Goodman, William Pendrill, Austin Rothermich, and Arttu Sainio.
The citizen scientists who found WISE 0414 combed through hundreds of images taken by WISE looking for moving objects, which are best detected with the human eye.
“The discovery of these two brown dwarfs shows that science enthusiasts can contribute to the scientific process,” Schneider said. “Through Backyard Worlds, thousands of people can work together to find unusual objects in the solar neighborhood.”
Astronomers followed up to determine their physical properties and confirm that they are indeed brown dwarfs. The discovery of these two unusual brown dwarfs suggests astronomers may be able to find more of these objects in the future.
About Backyard Worlds: Planet 9
The ongoing Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 project lets anyone join the quest to find more mysterious objects in spacecraft data. Citizen scientists using this project have discovered a wealth of astronomical treasures, including more than 1,600 brown dwarfs and the oldest, coldest white dwarf surrounded by a disk of debris.
About 150,000 people have participated so far. Check it out at backyardworlds.org.
About WISE and NEOWISE
The WISE spacecraft was placed in hibernation in February 2011 after completing its primary astrophysics mission, but in late 2013, the spacecraft was reactivated, renamed NEOWISE, and assigned a second mission dedicated to identifying and characterizing the population of near-Earth objects while also providing information about the size and composition of more distant asteroids and comets.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages and operates the NEOWISE mission for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office within the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The principal investigator, Amy Mainzer, is at the University of Arizona. The Space Dynamics Laboratory in Logan, Utah, built the science instrument. Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, built the spacecraft. Science data processing takes place at IPAC at Caltech in Pasadena. Caltech manages JPL for NASA.
JPL managed and operated WISE for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. Edward Wright at UCLA was the principal investigator. The mission was selected competitively under NASA’s Explorers Program managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
For more information about NEOWISE, visit:
For more information about WISE, visit:
Elizabeth Landau
NASA Headquarters
elandau@nasa.gov
202-923-0167
Karin Valentine
Media Relations
School of Earth and Space Exploration
Arizona State University
karin.valentine@asu.edu
480-965-9345