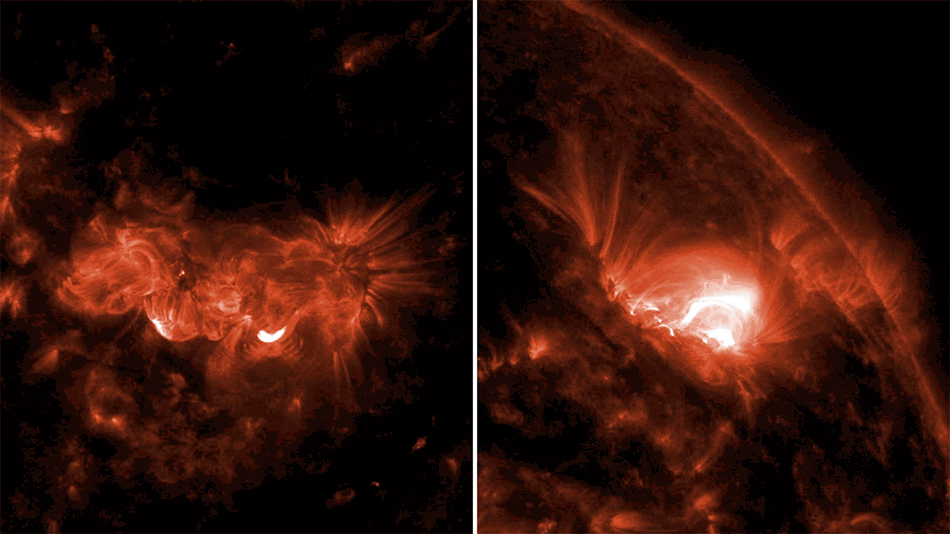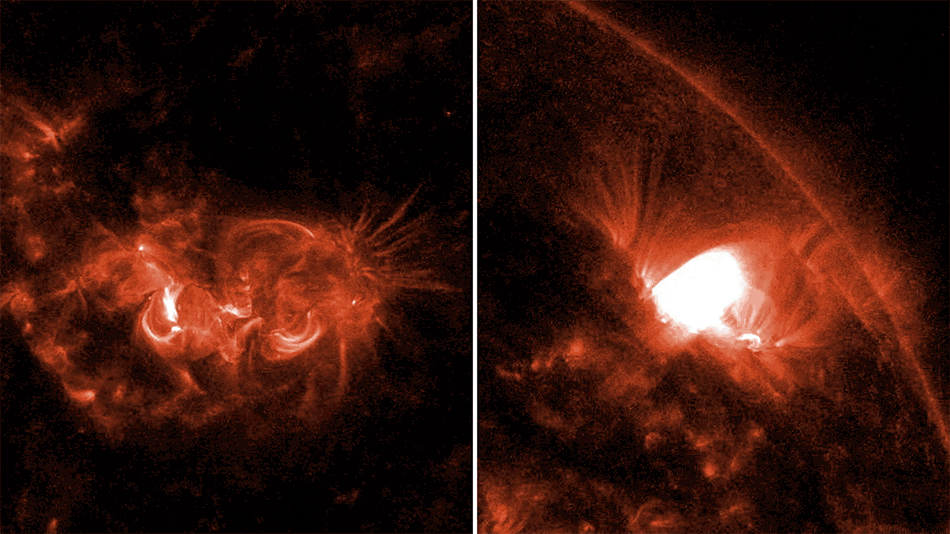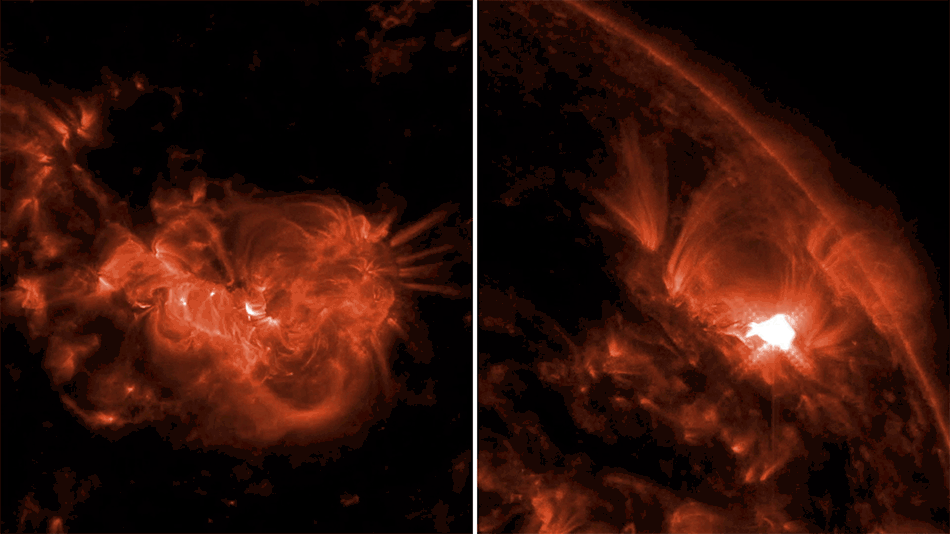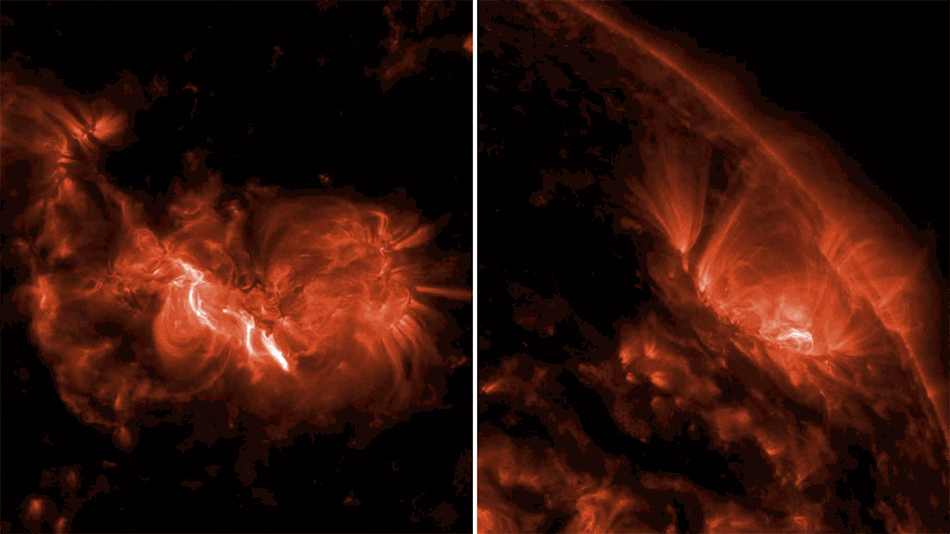
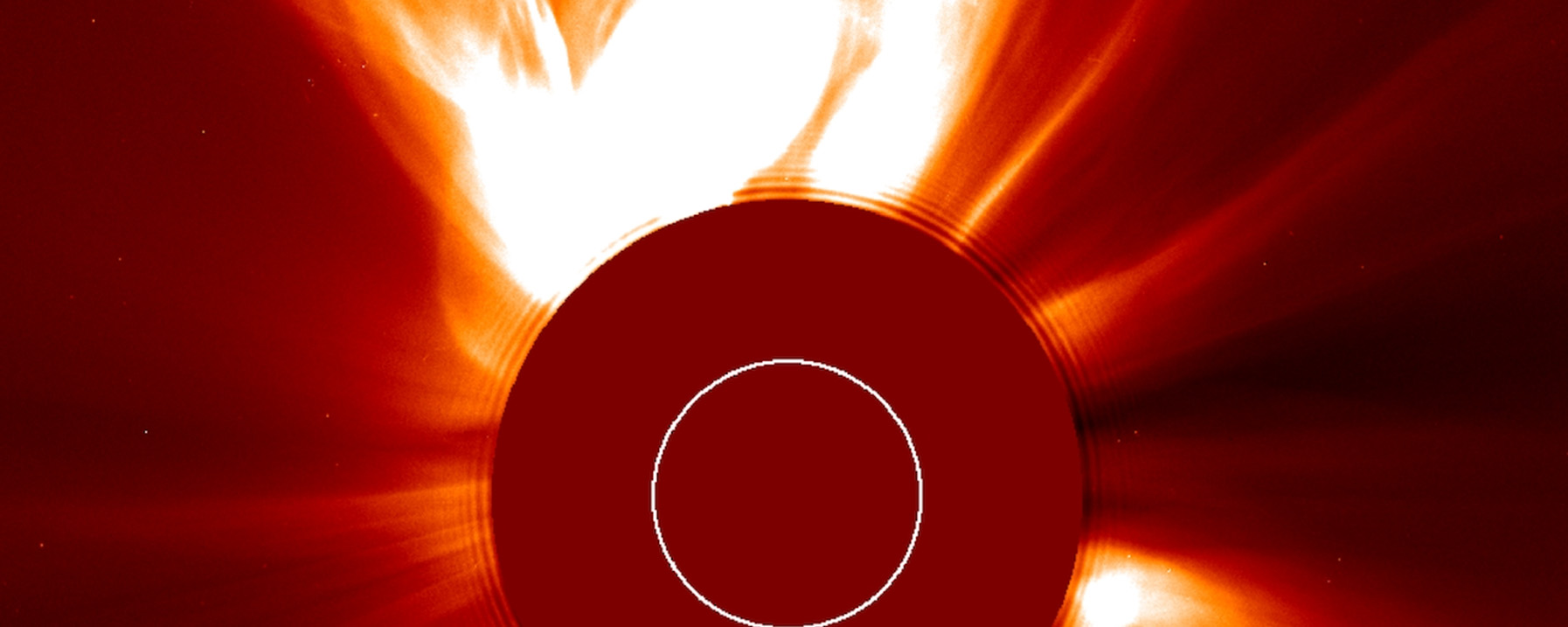
Scientists have used data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the NSF’s Jansky Very Large Array to determine the likely trigger for the most recent supernova in the Milky Way. They applied a new technique that could have implications for understanding other Type Ia supernovas, a class of stellar explosions that scientists use to determine the expansion rate of the Universe.
Astronomers had previously identified G1.9+0.3 as the remnant of the most recent supernova in our Galaxy. It is estimated to have occurred about 110 years ago in a dusty region of the Galaxy that blocked visible light from reaching Earth.
G1.9+0.3 belongs to the Type Ia category, an important class of supernovas exhibiting reliable patterns in their brightness that make them valuable tools for measuring the rate at which the universe is expanding.
“Astronomers use Type Ia supernovas as distance markers across the Universe, which helped us discover that its expansion was accelerating,” said Sayan Chakraborti, who led the study at Harvard University. “If there are any differences in how these supernovas explode and the amount of light they produce, that could have an impact on our understanding of this expansion.”
Most scientists agree that Type Ia supernovas occur when white dwarfs, the dense remnants of Sun-like stars that have run out of fuel, explode. However, there has been a debate over what triggers these white dwarf explosions. Two primary ideas are the accumulation of material onto a white dwarf from a companion star or the violent merger of two white dwarfs.
The new research with archival Chandra and VLA data examines how the expanding supernova remnant G1.0+0.3 interacts with the gas and dust surrounding the explosion. The resulting radio and X-ray emission provide clues as to the cause of the explosion. In particular, an increase in X-ray and radio brightness of the supernova remnant with time, according to theoretical work by Chakraborti’s team, is expected only if a white dwarf merger took place.
“We observed that the X-ray and radio brightness increased with time, so the data point strongly to a collision between two white dwarfs as being the trigger for the supernova explosion in G1.9+0.3,” said co-author Francesca Childs, also of Harvard.
The result implies that Type Ia supernovas are either all caused by white dwarf collisions, or are caused by a mixture of white dwarf collisions and the mechanism where the white dwarf pulls material from a companion star.
“It is important to identify the trigger mechanism for Type Ia supernovas because if there is more than one cause, then the contribution from each may change over time,” said Harvard’s Alicia Soderberg, another co-author on the study. This means astronomers might have to recalibrate some of the ways we use them as ‘standard candles’ in cosmology.”
The team also derived a new estimate for the age of the supernova remnant of about 110 years, younger than previous estimates of about 150 years.
More progress on understanding the trigger mechanism should come from studying Type Ia supernovas in nearby galaxies, using the increased sensitivity provided by a recent upgrade to the VLA.
A paper describing these results appeared in the March 1st, 2016 issue of The Astrophysical Journal and is available online. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts, controls Chandra’s science and flight operations.
Read More from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
For more Chandra images, multimedia and related materials, visit: