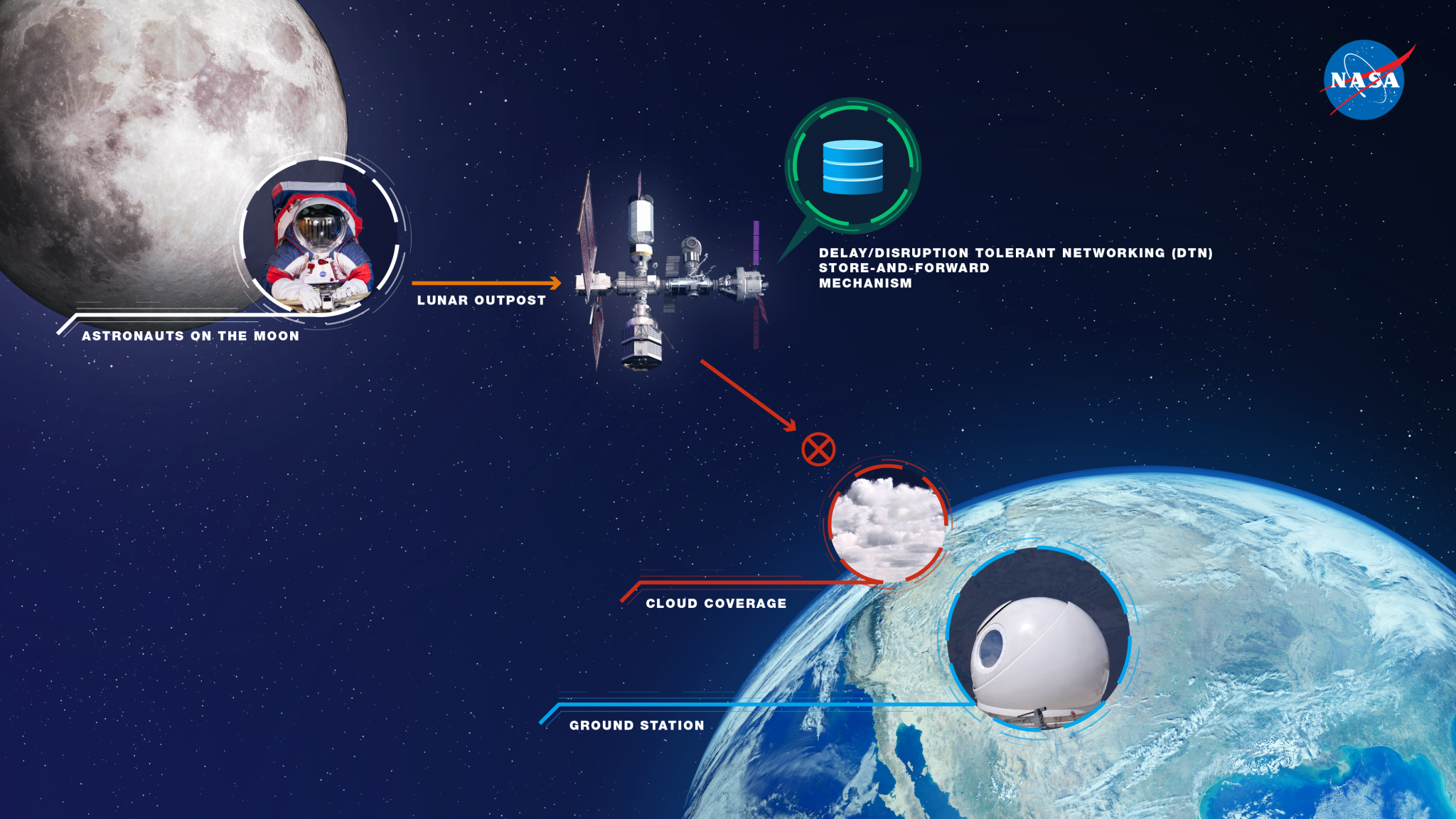
What are the Benefits of using DTN?
Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking (DTN) can benefit all types of missions. It is currently being used on the International Space Station. DTN has also been used by Lunar and deep space missions, successfully demonstrating its utility for complex future missions that include multiple landers and relay orbiters, human exploration efforts involving numerous assets on the Moon and Mars, swarms of spacecraft, and scenarios where all mission assets must communicate with each other.
- LEO – The majority of NASA spacecraft operate in Low Earth Orbit. LEO remote sensing missions that collect high volumes of data could benefit from how DTN deals with data rate mismatches between the spacecraft-to-ground and terrestrial links.
- Planetary relay/Deep space – For the purposes of telecommunications, “deep space” is defined by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) as beginning at a distance of more than 2 million km from Earth. Due to these distances, contacts between deep space missions and Earth are characterized by significant delays. DTN can help maximize the efficiency of these links and help ensure reliable data delivery.
- Hosted Payloads – If an instrument is being hosted by a partner or external entity’s spacecraft, the use of the standardized DTN protocol suite can help the instrument take advantage of DTN’s benefits without resorting to “one-off” customized interfaces to the host’s communications system
- Cis-lunar – Past demonstrations have shown that DTN can facilitate the reliable delivery of data from the Moon back to Earth via optical communications by compensating for any link disruption due to cloud cover
- Human Space Flight – DTN is currently being used on the International Space Station to reliably deliver data not just for scientific payloads but also for systems responsible for the health and safety of the astronauts on board. Those same applications could be applied to a sustained human presence at the Moon
- Sun-Earth Lagrange L1/L2 – DTN can help ensure quick and reliable delivery of data on incoming space weather and solar events from spacecraft at the Sun-Earth Lagrange points
- SmallSats/CubeSats – DTN can reduce risk for smallsats, especially multi-spacecraft constellations, by coordinating and/or automating data delivery from distributed spacecraft in a standardized fashion
- Suborbital – With their relatively low costs and short lifetimes, DTN could help suborbital missions reduce the need to throttle data
What Benefits Does DTN Provide?
DTN enables Science and Exploration
- Increases science data return through interoperability and more efficient link utilization
- Enables communications between and through constellations and swarms of smallsats
- Enables missions that would either be impossible or too difficult/costly
- Facilitates science across distributed platforms
- Monitoring of phenomena by multiple spacecraft
- Delivery of data from distributed instruments to a central processing node
- Communication between diverse space assets across heterogeneous links
- Promotes data relay through Gateway or planned Lunar assets
- Exchange of data with each other and Earth
- From Lunar surface without direct view of Earth
- Increased coverage and capacity
DTN increases autonomy
- Reduces of operational complexity
- Enables responsive mission operations
- Increases scalability
DTN decreases life cycle cost
- Enables reuse
- Increases interoperability
- Facilitates streamlined operations and more efficient use of personnel
Read more:
The Benefits of Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking (DTN) for Future NASA Science Missions
DTN Success Stories
From Antarctic research stations and Earth-observing spacecraft to the International Space Station and missions at the Moon and beyond, NASA has successfully demonstrated Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking (DTN) in a variety of orbits and environments. Each of the demonstrations detailed below was instrumental in the development and maturation of the protocols that enable DTN. The lessons learned continue to guide DTN’s current and future operational use.

- Jones, Ross. “Deep Space Networking experiments on the EPOXI spacecraft.” AIAA Infotech @ Aerospace Conference, 29-31 March 2011. https://trs.jpl.nasa.gov/handle/2014/42087
- Schlesinger, Adam et al. “Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking for the International Space Station (ISS).” https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20160014037.pdf
- Johnson, Sandra et al. “Delay Tolerant Networking on NASA’s Space Communication and Navigation Testbed.” CCSDS DTN Working Group, October 2016. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20170004100.pdf
- Kraft, R. (2012). “NASA, ESA Use Experimental Interplanetary Internet to Test Robot From International Space Station.” NASA Press Release 12-391. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2012/nov/HQ_12-391_DTN.html
- Martin S. & Cardone, M. (2018, 28 February). “METERON Operations Environment – Preparing Data Systems for Robotic Exploration.”*
- Fong, T. (2012) “Human Exploration Telerobotics Project Demonstrates Remote Operation of ‘Smart Spheres’ on Space Station.” Retrieved from https://ti.arc.nasa.gov/news/iss-spheres-demo/
- “Antarctic Selfie’s Journey to Space via Disruption Tolerant Networking.” https://www.nasa.gov/feature/antarctic-selfie-s-journey-to-space-via-disruption-tolerant-networking
- Davis, Faith et al. “Benefits of Delay Tolerant Networking for Earth Science Missions.” https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20120002041.pdf
- Suzuki, K. et al. (2014). “JAXA-NASA Interoperability Demonstration for Application of DTN under Simulated Rain Attenuation.” Retrieved from https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20140010962.pdf
- Israel, D. and Cornwell, D. (2014). “Disruption Tolerant Networking over LLCD’s Optical Links.” IPNSIG Space Technology Innovations Conference.*
- “Disruption Tolerant Networking Experiments with Optical Communications.”














/quantum_physics_bose_einstein_condensate.jpg?w=1024)