The Jan. 31 full moon is special for three reasons: it’s the third in a series of “supermoons,” when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit — known as perigee — and about 14 percent brighter than usual. It’s also the second full moon of the month, commonly known as a “blue moon.” The super blue moon will pass through Earth’s shadow to give viewers in the right location a total lunar eclipse. While the Moon is in the Earth’s shadow it will take on a reddish tint, known as a “blood moon.”
If you live in the western part of North America, Alaska, and the Hawaiian islands, you might set your alarm early the morning of Wednesday, Jan. 31 for a lunar trifecta: a pre-dawn “super blue blood moon.”
“For the (continental) U.S., the viewing will be best in the West,” said Gordon Johnston, program executive and lunar blogger at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Set your alarm early and go out and take a look.”
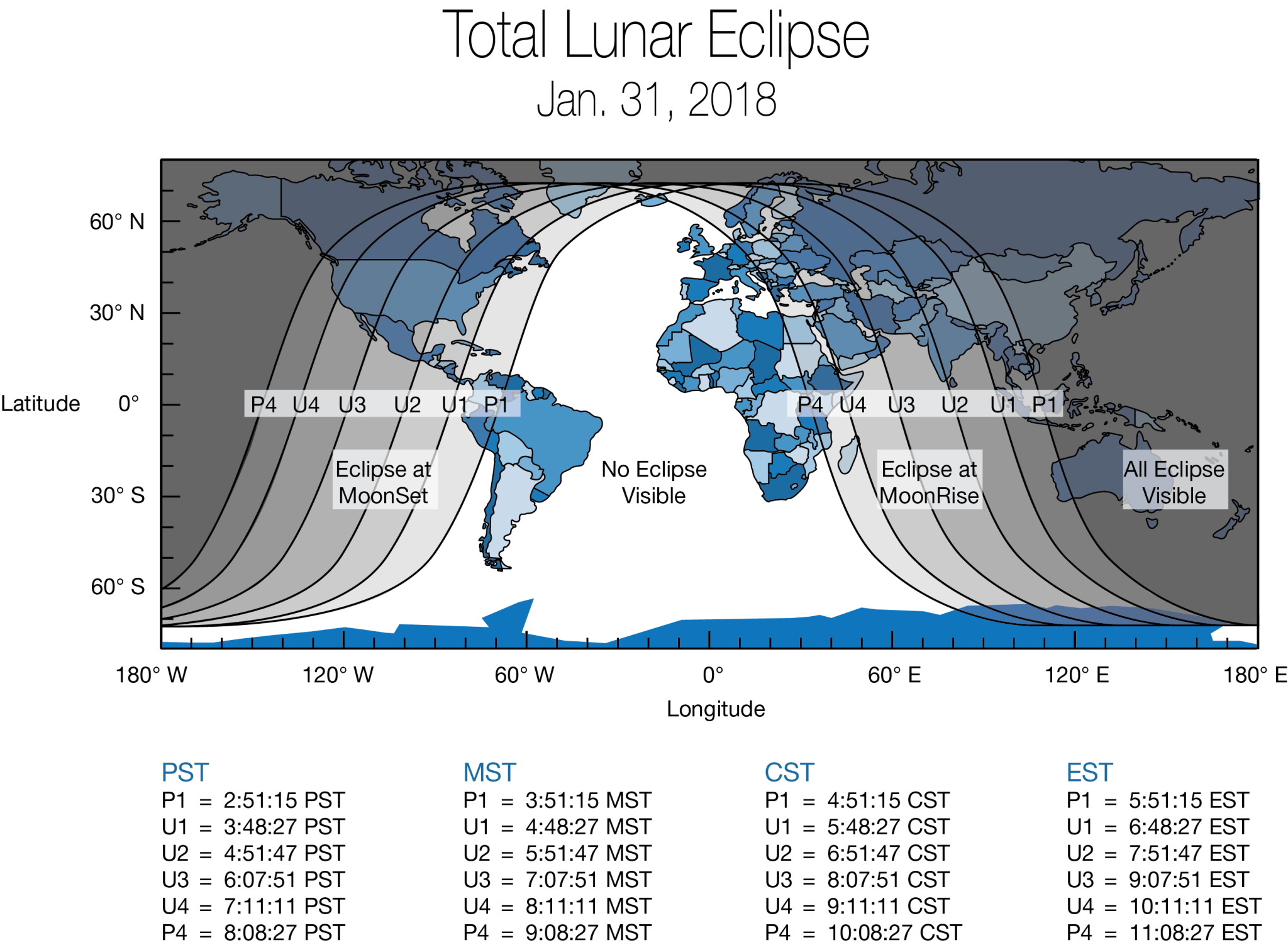
If you live in North America, Alaska, or Hawaii, the eclipse will be visible before sunrise on Jan. 31. For those in the Middle East, Asia, eastern Russia, Australia and New Zealand, the “super blue blood moon” can be seen during moonrise in the evening of the 31st.
“Weather permitting, the West Coast, Alaska and Hawaii will have a spectacular view of totality from start to finish,” said Johnston. “Unfortunately, eclipse viewing will be more challenging in the Eastern time zone. The eclipse begins at 5:51 AM ET, as the Moon is about to set in the western sky, and the sky is getting lighter in the east.”
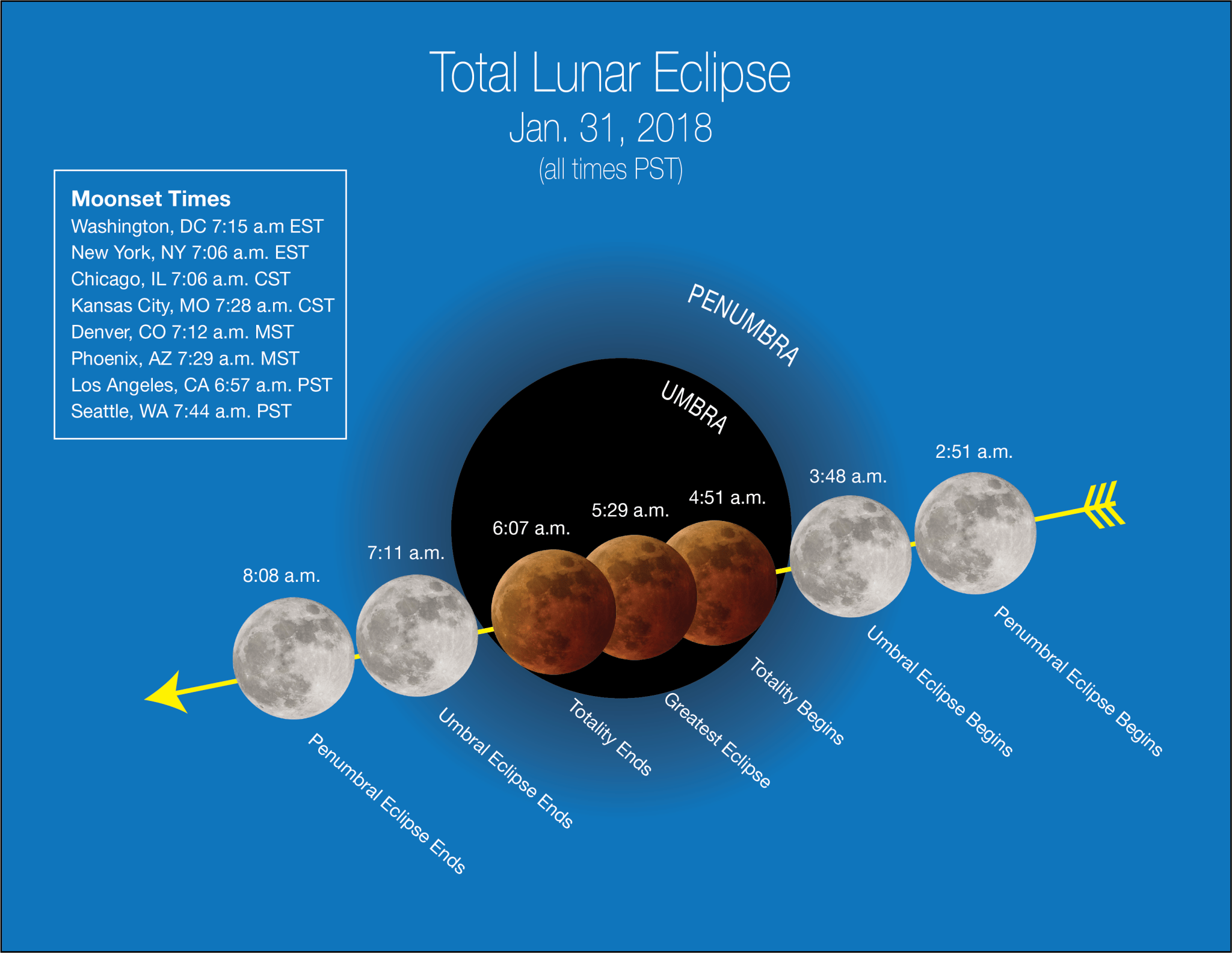
So for viewers in New York or Washington, D.C., the Moon will enter the outer part of Earth’s shadow at 5:51 a.m., but Johnston says it won’t be all that noticeable. The darker part of Earth’s shadow will begin to blanket part of the Moon with a reddish tint at 6:48 a.m. EST, but the Moon will set less than a half-hour later. “So your best opportunity if you live in the East is to head outside about 6:45 a.m. and get to a high place to watch the start of the eclipse—make sure you have a clear line of sight to the horizon in the west-northwest, opposite from where the Sun will rise,” said Johnston.
If you live in the Central time zone, viewing will be better, since the action begins when the Moon is higher in the western sky. At 4:51 a.m. CST the penumbra — or lighter part of Earth’s shadow – will touch the Moon. By about 6:15 a.m. CST the Earth’s reddish shadow will be clearly noticeable on the Moon. The eclipse will be harder to see in the lightening pre-dawn sky, and the Moon will set after 7:00 a.m. as the Sun rises. “So if you live in Kansas City or Chicago, your best viewing will be from about 6:15-6:30 a.m,” said Johnston. “Again, you’ll have more success if you can go to a high place with a clear view to the West.”
In the Rocky Mountain region, the show begins as the umbra touches the edge of the Moon at 4:48 a.m. MST. The peak of the blood moon eclipse is at about 6:30 a.m. local time, and the Moon will set shortly after 7 a.m.
Californians and viewers in western Canada will be treated to the total eclipse phase from start to finish, though the penumbral shadow will pass after the Moon has set. The umbral eclipse begins at 3:48 a.m. Pacific Time. At 4:51 a.m., totality will begin, with best viewing between about 5:00 and 6:00 a.m. local time. The totality phase ends about 6:05 a.m.
Weather permitting, eclipse fans in Hawaii will experience the lunar eclipse from start to finish, as will skywatchers in Alaska, Australia and eastern Asia.
If you miss the Jan. 31 lunar eclipse, you’ll have to wait almost another year for the next opportunity in North America. Johnston said the Jan. 21, 2019 lunar eclipse will be visible throughout all of the U.S. and will be a supermoon, though it won’t be a blue moon.
Credits: NASA 360
Download this video
Johnston has been following and writing about the Moon since 2004, when he and about 20 colleagues at NASA Headquarters would get together after work during the full moon in “celebratory attire”—which for Johnston meant his signature bow tie. Long after the socializing fell by the wayside, Johnston’s monthly blog lives on, with a dedicated following on NASA’s lunar website, moon.nasa.gov.
Said Johnston, “I have always been fascinated by the night sky. Most of what we can see without a telescope are points of light, but the Moon is close enough that we can see it and the features on it, and notice what changes and what stays the same each night.”
To watch a NASA ScienceCast video, A Supermoon Trilogy about the Dec. 3, 2017, Jan. 1, 2018, and Jan. 31, 2018 supermoons, click here.
Love to observe the Moon? It’s easy to make a Moon Phases Calendar and Calculator that will keep all of the dates and times for the year’s phases of the Moon at your fingertips.
Take notes and record your own illustrations of the Moon with a Moon observation journal, ready to download and print at moon.nasa.gov.