Mission to the International Space Station
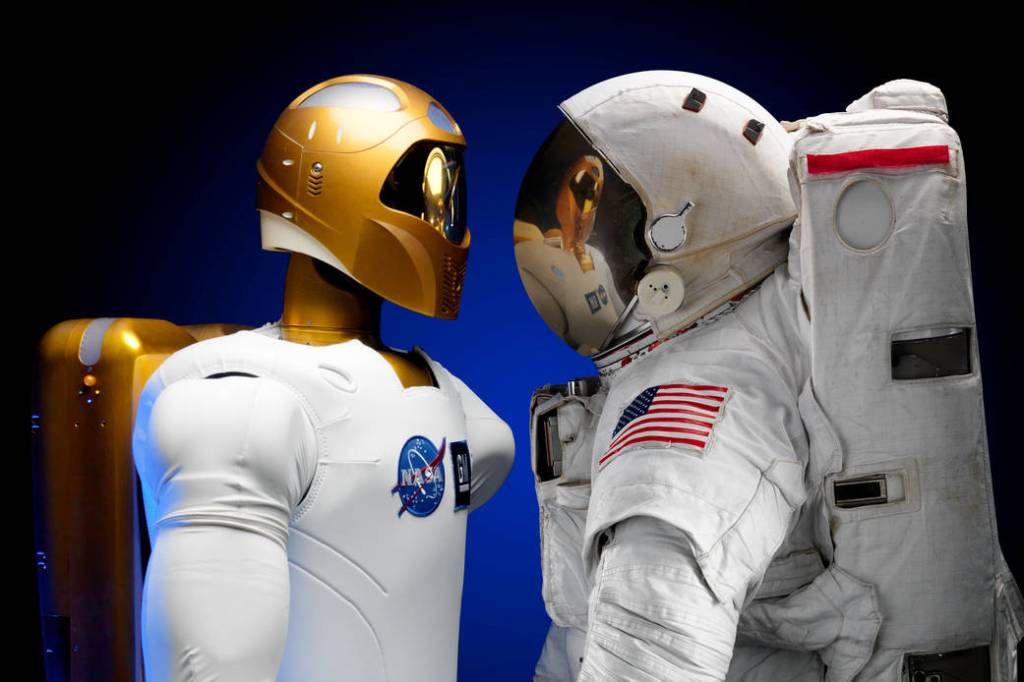
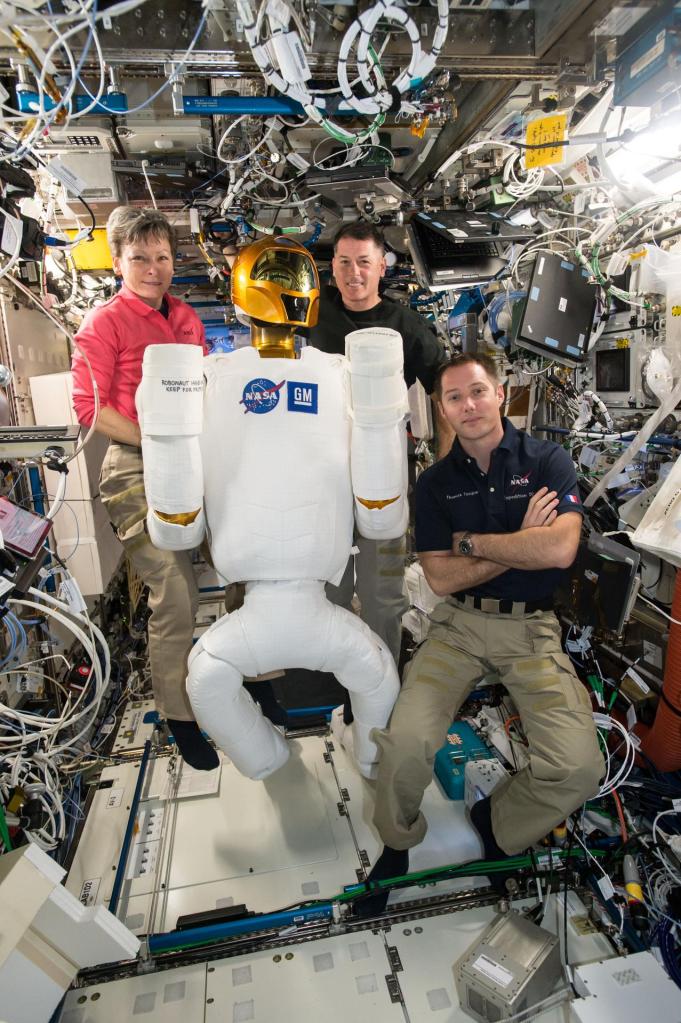
On February 24th 2011, NASA launched the first human-like robot to space on space shuttle Discovery as part of the STS-133 mission to become a resident of the International Space Station. Robonaut 2, or R2, was developed jointly by NASA and General Motors under a cooperative agreement to develop a robotic assistant that can work alongside humans, whether they are astronauts in space or workers at GM manufacturing plants on Earth.
Initially deployed as a torso-only humanoid restricted to a stanchion, the R2 mobility platform was added in 2014, augmenting R2 with two new legs for maneuvering inside the ISS.
“This project exemplifies the promise that a future generation of robots can have both in space and on Earth, not as replacements for humans but as companions that can carry out key supporting roles,” said John Olson, director of NASA’s Exploration Systems Integration Office at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “The combined potential of humans and robots is a perfect example of the sum equaling more than the parts. It will allow us to go farther and achieve more than we can probably even imagine today.”
The dexterous robot not only looks like a human but also is designed to work like one. With human-like hands and arms, R2 is able to use the same tools station crew members use. In the future, the greatest benefits of humanoid robots in space may be as assistants or stand-in for astronauts during spacewalks or for tasks too difficult or dangerous for humans. For now, R2 is still a prototype and does not have adequate protection needed to exist outside the space station in the extreme temperatures of space.
Testing the robot inside the station will provide an important intermediate environment. R2 will be tested in microgravity and subjected to the station’s radiation and electromagnetic interference environments. The interior operations will provide performance data about how a robot may work side-by-side with astronauts. As development activities progress on the ground, station crews may be provided hardware and software to update R2 to enable it to do new tasks.
R2 underwent extensive testing in preparation for its flight. Vibration, vacuum and radiation testing along with other procedures were conducted on R2 also benefited the team at GM. The automaker plans to use technologies from R2 in future advanced vehicle safety systems and manufacturing plant applications.
“The extreme levels of testing R2 has undergone as it prepares to venture to the International Space Station are on par with the validation our vehicles and components go through on the path to production,” said Alan Taub, vice president of GM’s global research and development. “The work done by GM and NASA engineers also will help us validate manufacturing technologies that will improve the health and safety of our GM team members at our manufacturing plants throughout the world. Partnerships between organizations such as GM and NASA help ensure space exploration, road travel and manufacturing can become even safer in the future.”
Learn more about NASA's Robonaut
Return to Robonaut Homepage