Flight Computing & Avionics Subsystems

Contents
Introduction
NASA’s Johnson Space Center has facilities and expertise that specialize in the unique aspects of the design, development, testing and evaluation of avionics systems and architectures for human space flight. From critical commanding and data handling architectures to comprehensive component level testing and analysis, the Johnson Space Center stands as a beacon of expertise in the realm of aerospace technology. Explore the capabilities below, as we invite you to join us in shaping the future of flight computing and avionics at the forefront of human spaceflight advancement.
Capabilities
Network Validation & Integration
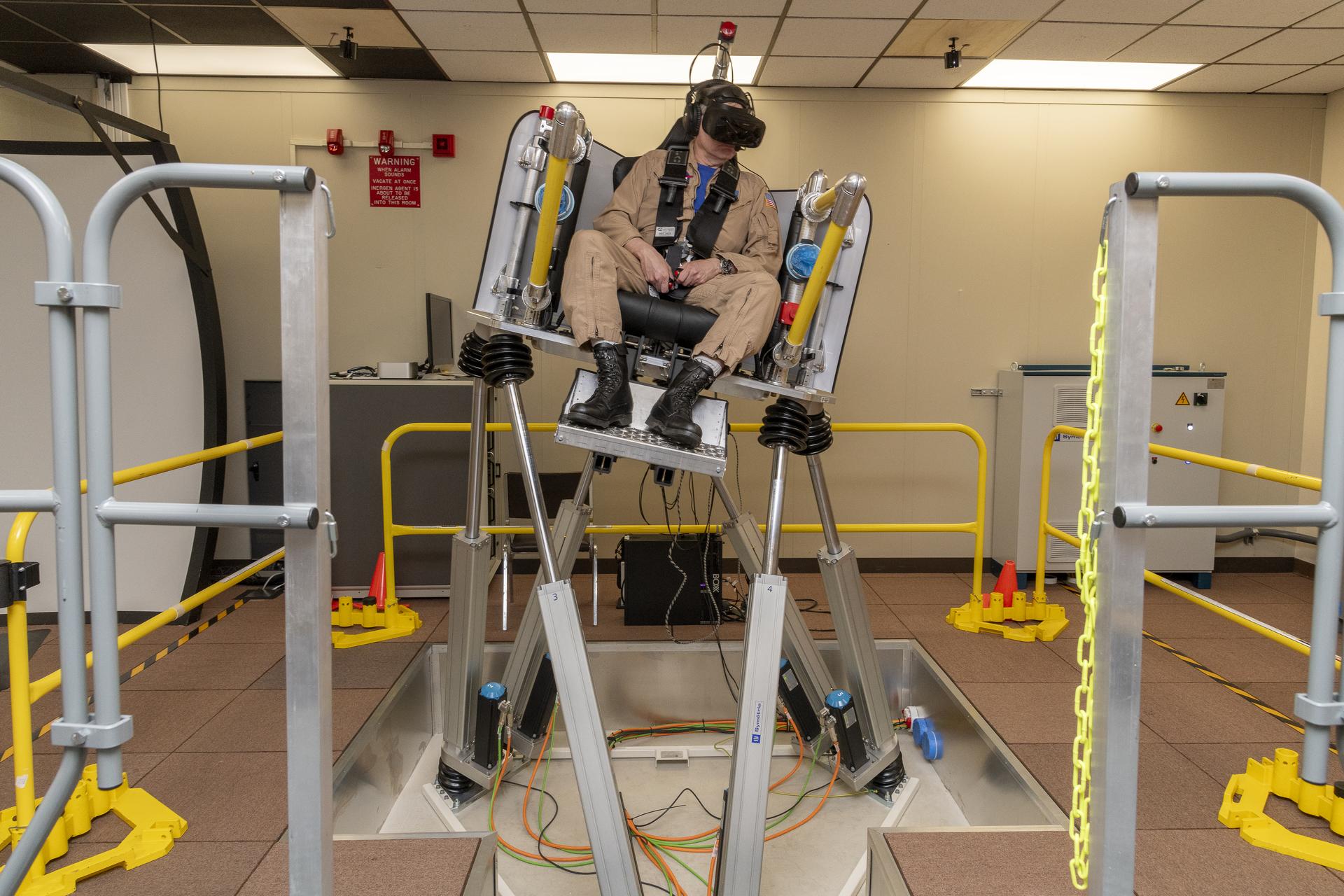
Overview | The Artemis Network Validation and Integration Lab (ANVIL) provides a medium fidelity dynamic lab environment to support the development and testing of both standard and Time-Triggered Ethernet real-time spacecraft networks for the Artemis and Gateway Programs.
Details | The lab includes lab grade and flight-like hardware such as Layer 3 and Time-Triggered Ethernet switches, Network Interface Cards, and end system computers, and offers the capability to represent a network and multiple traffic classifications that will be required for future spacecraft network designs.
Cable Transfer Impedance and Equipment Shielding Effectiveness Assessment
Overview | The cable transfer impedance and equipment shielding effectiveness assessment is available.
Details |
- Testing and measurement of shielding effectiveness of materials
- Capability for quantifying cable coupling and transfer impedance
Conducted and Radiated Emissions and Susceptibility Testing
Overview | The JSC EMI Test Facility (JETF) is comprised of two independent shielded test facilities. The JSC EMI Test Facility (JETF) performs testing of systems and subsystems according to MIL-STD 461G requirements. Consultation services can also be arranged for developing a suitable test plan to meet imposed test requirements.
Details |
- The two independent shielded test facilities have dimensions: 23 feet x 18 feet x 10 feet and 10 feet x 16 feet x 8.5 feet
- Larger Equipment Under Test (EUT) assessments can be accommodated but require additional coordination
Electrostatic Discharge Assessment
Overview | The JSC EMI Test Facility (JETF) provides Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) testing per MIL-STD requirements.
Details | The JSC EMI Test Facility (JETF) staff has expertise and equipment for performing ESD testing in accordance with standard MIL-STD 461G requirements. Apparatus required to support any unique requirements can be arranged with the JETF ESD equipment vendor.
Engineering Support and Evaluation in Shielded Chambers for Conducted and Radiated Emissions and Susceptibility
Overview | The JSC EMI Test Facility (JETF) supports engineering development and provides EMI/EMC evaluation and qualification.
Details | Testing of crew, flight, and ground support equipment, including but not limited to communication, instrumentation, biomedical, guidance and navigation, computation and robotics systems is available. Complete EMC testing of systems and subsystems per MIL-STD 461G requirements is performed.
Wireless and Radio Frequency Identification (WRFID) Laboratory
Overview | The Wireless and Radio Frequency Identification (WRFID) laboratory provides capabilities for the design, development, testing, and analysis of RFID and other wireless technologies for space applications.
Details | The WRFID laboratory provides capabilities for the design, development, testing, and analysis of RFID and other wireless technologies for space applications.
Counterfeit Parts Detection – Electronics and Electrical Component Testing and Analysis
Overview | The Receiving, Inspection and Test Facility (RITF) team of engineers and technicians have years of experience and capabilities to support the full range of test article preparation and testing to both validate the integrity of parts before they enter NASA’s supply chain, and to determine the cause of failure, including counterfeit parts.
Details | Counterfeit parts are marketed with the intent to deceive the customer into purchasing substandard parts while believing they have purchased high-quality parts from reputable manufacturers. This intent to deceive defines a counterfeit part which likely has defects that are unknown to the manufacturer or the distributor. Counterfeiters continue to improve their techniques, making it more difficult to detect counterfeit parts. These parts can cause system failures when they fail to function in the environment in which they are to be used, etc. Methods used to detect these parts include X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Destructive Physical Analysis, Optical Emission Spectroscopy, Real-Time Radiography, and Scanning Electron Microscopy.