B-Complex
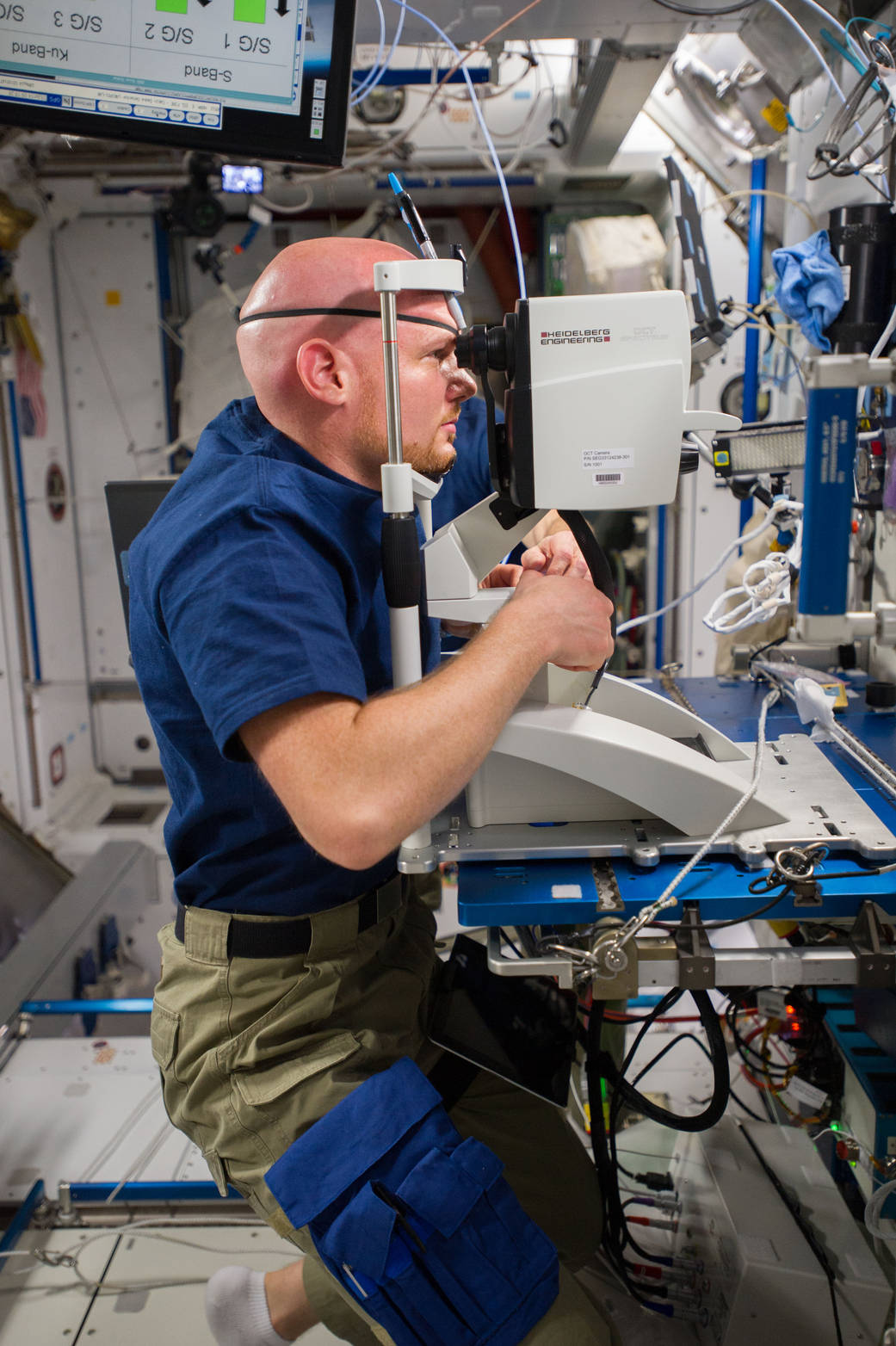

Description: This study aims to counteract the eye and brain changes called Spaceflight-Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome, or SANS, that develop in some astronauts during space missions. The work investigates if a daily B vitamin supplement – taken for six months prior to flying, during the mission, and for 30 days after – can prevent or mitigate swelling at the back of the eye. The research will also assess how an individual’s genetics may influence this approach. Blood draws, genetic analysis, and eye exams will help determine efficacy of the countermeasure.
Impact: Data from this work could help astronauts safeguard their vision during and after future long-duration missions. One potential future terrestrial benefit is that this work may also benefit women on Earth with a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which appears to have similar predisposing factors. PCOS patients may benefit from this countermeasure by targeting the same genetic pathway.
Type of study: Flight
Formal project title: B-Complex: A Nutraceutical SANS Countermeasure