RadLab Portal Expands Horizons
On August 12, 2024, the Open Science Data Repository Visualization team unveiled the latest updates to the RadLab Portal. The RadLab Portal serves as a comprehensive platform providing access to radiation telemetry data from multiple databases maintained by various space agencies. Through its web interface, users can query, visualize, inspect, and download data, enabling analyses such as time series plots of radiation readings, pairwise comparisons of detector outputs, and geospatial visualizations of radiation dose and flux as recorded by different detectors, while its API enables sophisticated programmatic analyses of various combinations of these data. Originally focused on radiation data from detectors aboard the International Space Station, RadLab has now expanded its scope to include detectors on spacecraft operating Beyond Low Earth Orbit (BLEO).
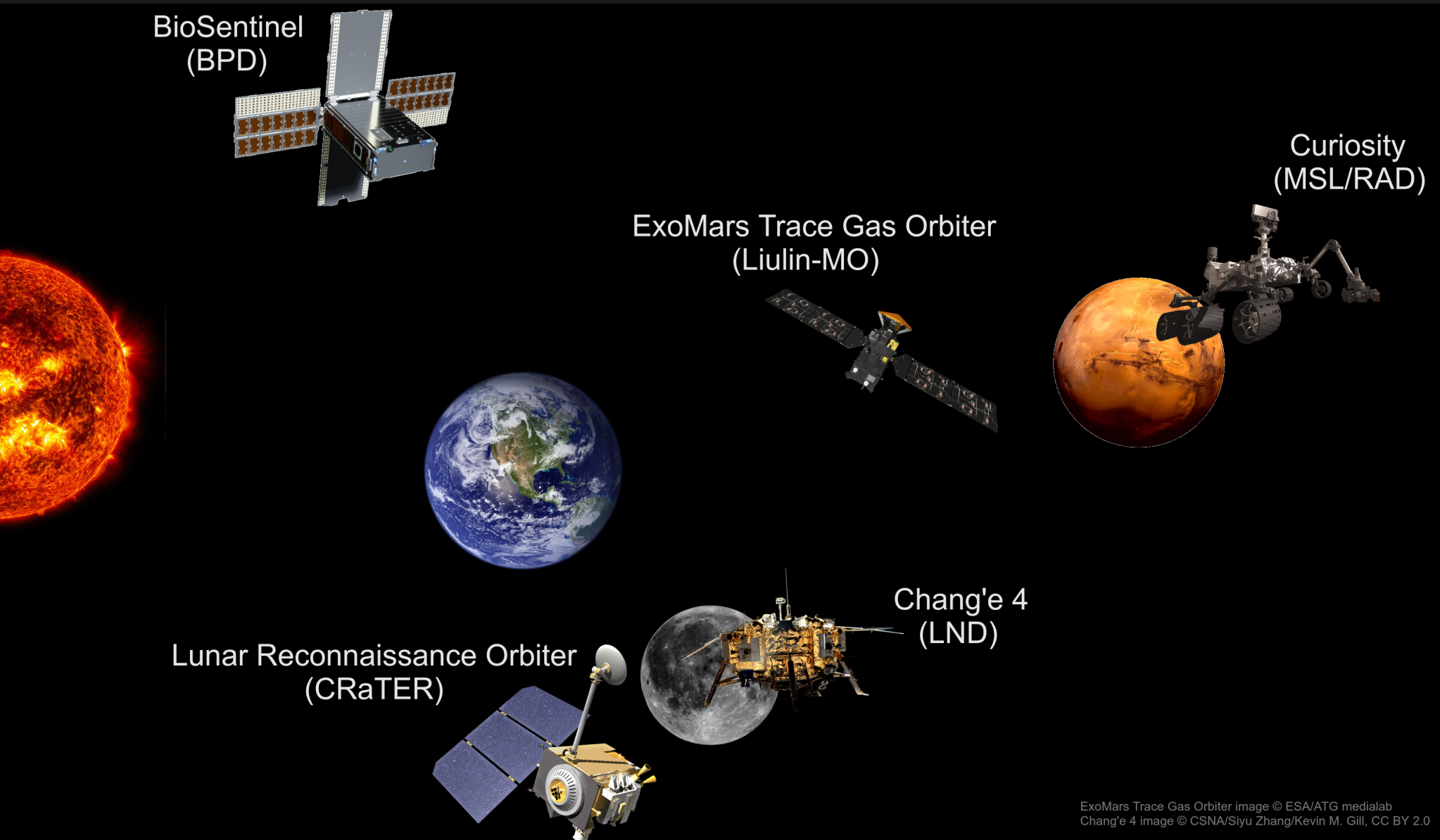
This latest update introduces new instruments, data, and significant performance improvements. Notably, it now incorporates a range of instruments from various space missions, including the BioSentinel CubeSat in heliocentric orbit at 1 AU around the Sun; the CRaTER instrument on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) in Moon orbit; the Liulin-MO instrument aboard the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), operational during Mars cruise and in Mars orbit; and the MSL/RAD instrument aboard the Curiosity rover on the surface of Mars. The update also includes enhancements to the API and GUI, with improved performance and quality-of-life improvements to visualizations. The updates are now live—explore the new features today!