Health and Medical Technical Authority (HMTA)
The goal of the HMTA for NASA spaceflight programs and projects is to: (a) provide provision for direct management of health and performance of flight crews in operations and (b) provide protection of human health.
HMTA Delegation
The delegation structure of HMTA highlights responsibilities of the Chief Health Medical Officers (CHMO), Chief Medical Officers (CMOs) and Crew Health and Performance Officers (CHPOs).
Learn More About the roles of CHMOs, CMOs and CHPOs.
HMTA Spaceflight Program Support
HMTA is given oversight throughout NASA Spaceflight Program lifecycles by Program Crew Health and Performance Officers (CHPOs) and their teams. This oversight includes spacecraft design and development; and spaceflight mission operations. The programs below have designated CHPOs to support during development and operations.

Gateway Program (GP)
The Gateway Program is building a small, human-tended space station orbiting the Moon that will provide extensive capabilities to support NASA’s Artemis campaign.

Orion
NASA’s Orion spacecraft was built to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before. Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.

Human Landing System (HLS)
The Human Landing System (HLS) is the mode of transportation that will take astronauts to the lunar surface as part of the Artemis program, including the first woman and the first person of color. The program is managed at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.

Exploration Ground System (EGS)
The Exploration Ground System is based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. EGS was established to develop and operate the systems and facilities necessary to process and launch rockets and spacecraft during assembly, transport and launch.

International Space Station (ISS)
The International Space Station is a large spacecraft in orbit around Earth. It serves as a home where crews of astronauts and cosmonauts live. The space station is also a unique science laboratory.
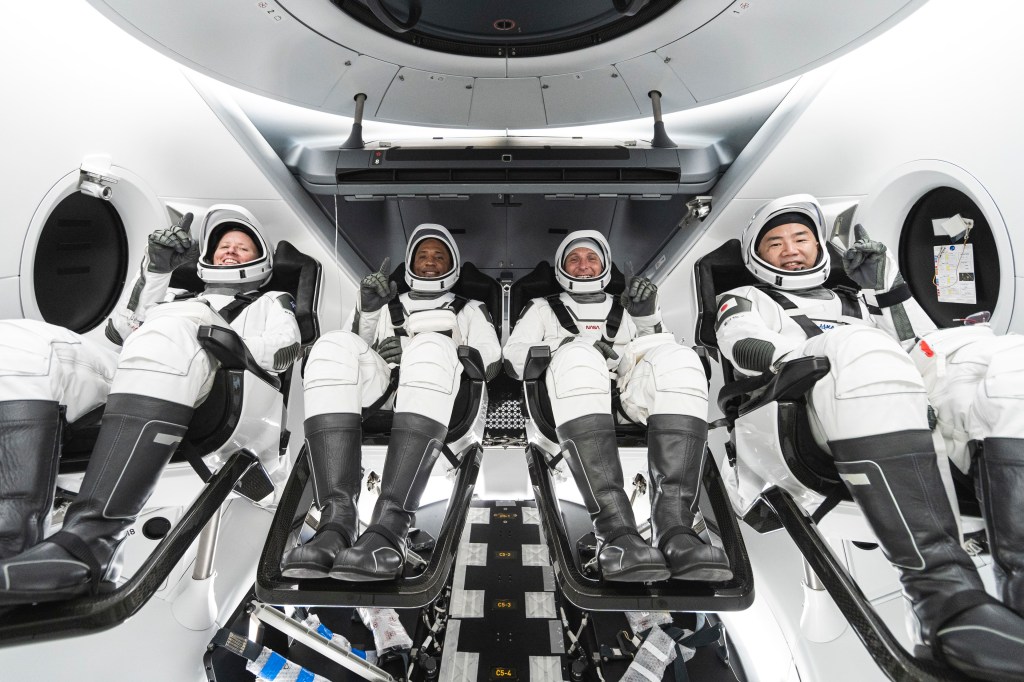

Commercial Crew Program (CCP)
NASA's Commercial Crew Program is a partnership to develop and fly human space transportation systems.
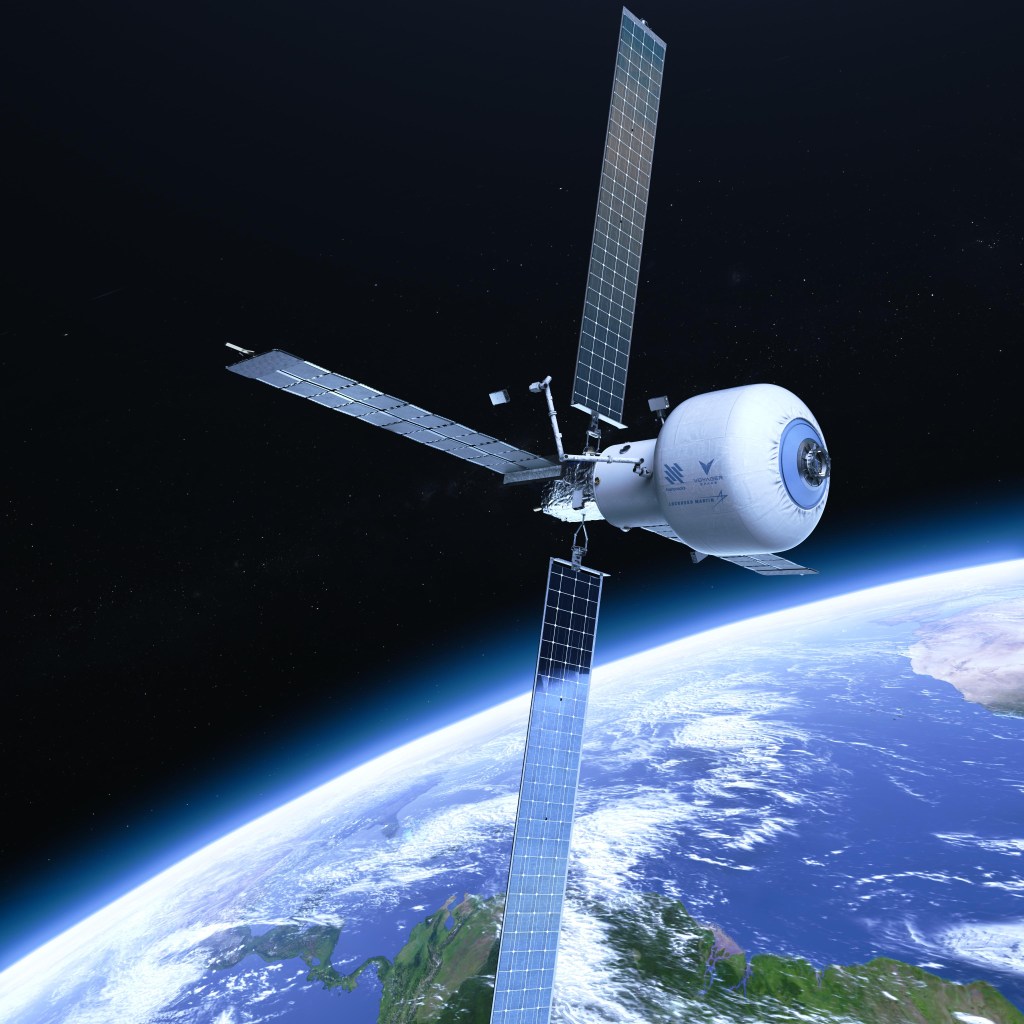

Commercial Destination-Free Fliers (CDFF)
Learn about NASA partnerships with Commercial Destinations-Free Fliers (CDFF). CDFFs are independent, free-flying facilities operating in orbit.

Extravehicular Activity (EVA) and Habitat Mobility Program (EHP)
Learn about NASA's EVA and Space Suit Community.
Human Spaceflight Hazards
There are 5 Hazards of Human Spaceflight that drive risks to the human system encountered during spaceflight pertaining to pre, post, and in-flight challenges affecting the crew’s health and their ability to perform the mission.