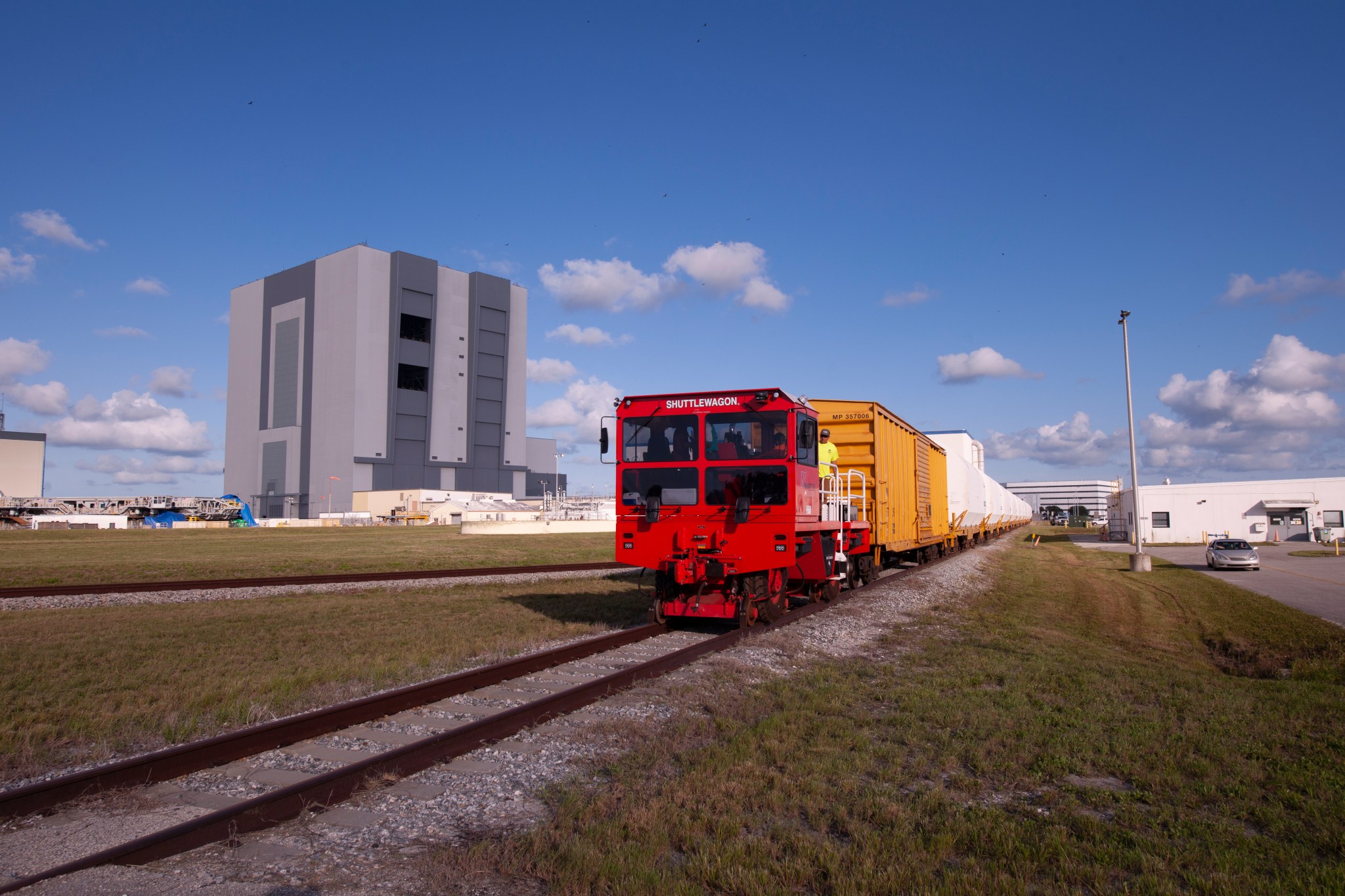
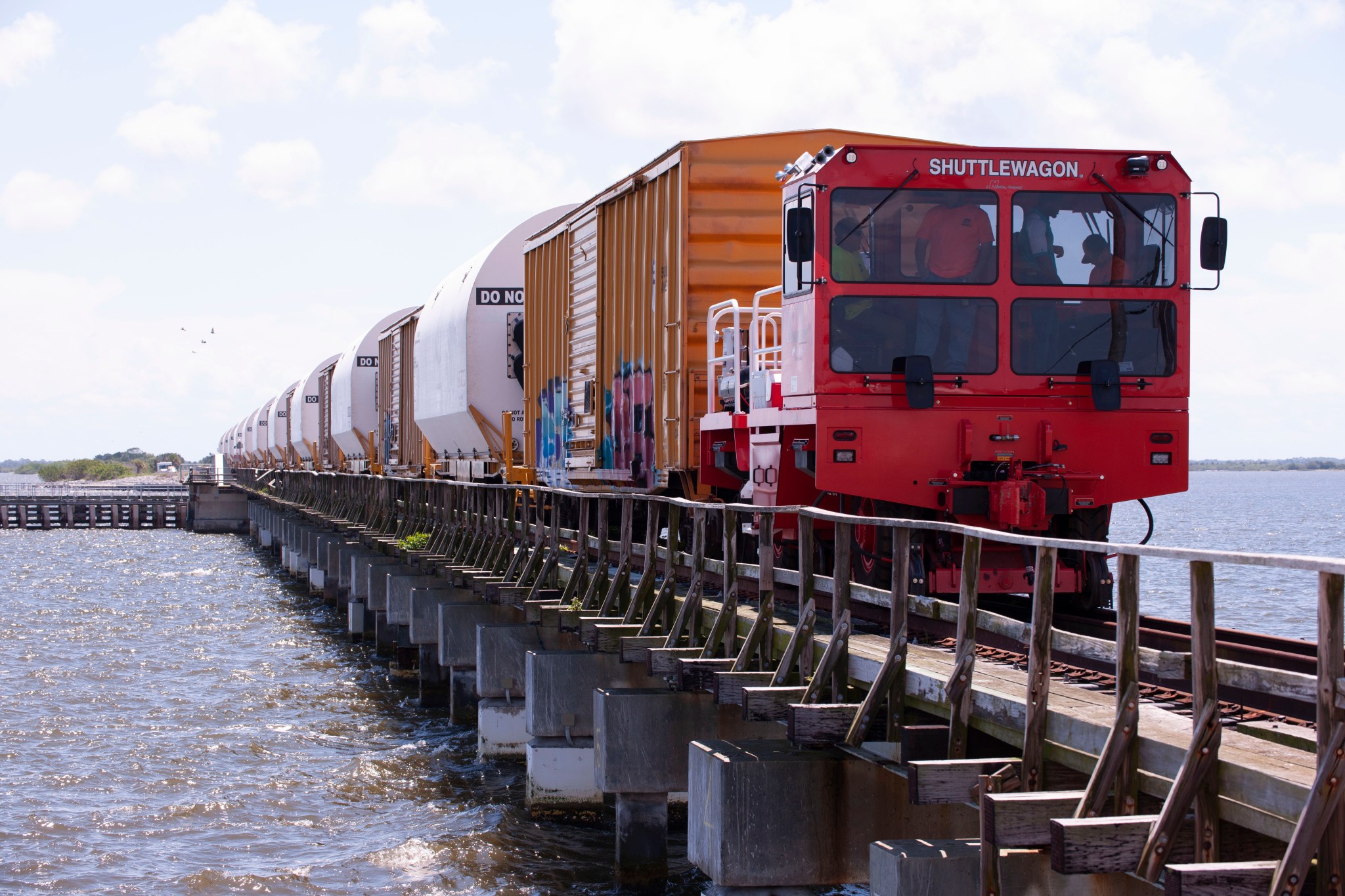
The rocket booster segments that will help power NASA’s first Artemis flight test mission around the Moon arrived at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday for launch preparations.
All 10 segments for the inaugural flight of NASA’s first Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft were shipped by train from Promontory, Utah. The 10-day, cross-country journey is an important milestone toward the first launch for NASA’s Artemis program.
“The arrival of the booster segments at Kennedy is just the beginning of the SLS rocket’s journey to the pad and onward to send the Orion spacecraft to the Moon,“ said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. “Artemis I will pave the way toward landing the first woman and the next man on the surface of the Moon in 2024 and expanding human exploration to Mars.”

Each rocket booster has individual motor segments, located between the forward assemblies and aft skirts, making up the largest single component of the entire booster. The two SLS rocket boosters, four RS-25 engines, and core stage, produce a combined total of more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust power during launch.
“It’s an exciting time at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center as we welcome Artemis flight hardware and continue working toward the Artemis I launch,” said Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana.
Each booster segment, weighing 180 tons, is filled with propellant and outfitted with key flight instrumentation. Due to their weight, Northrop Grumman, which is the booster lead contractor, transported the segments in specially outfitted railcars to make the 2,800-mile trip across eight states to Florida’s Space Coast.
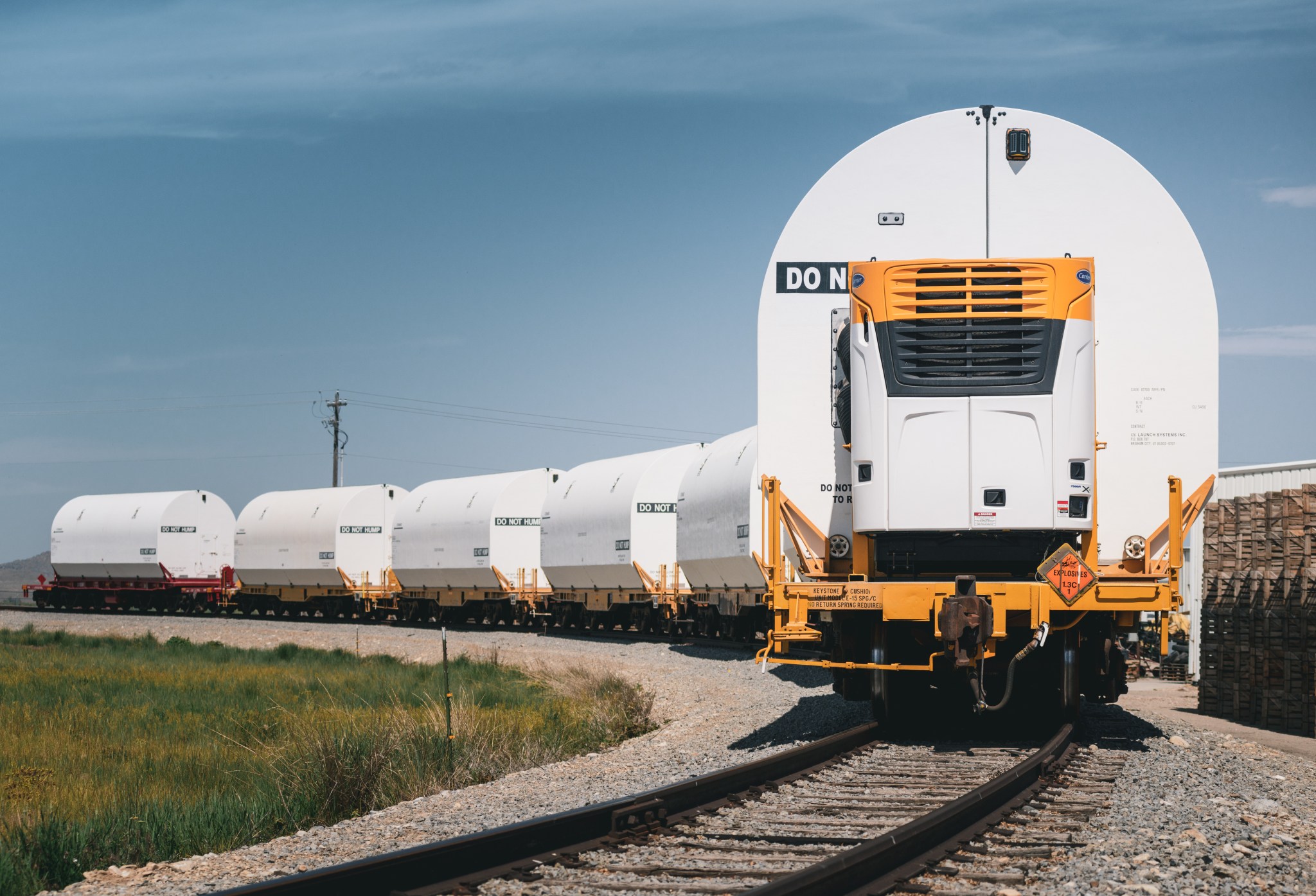

“The fully assembled boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket are the largest, most powerful solid propellant boosters ever built for flight,” said Bruce Tiller, manager of the SLS Boosters Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. “These enormous rocket motors help provide the necessary launch power for the SLS deep space rocket.”
Now that the booster segments are at Kennedy, NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems team will prepare them for assembly and integration activities that start with offloading the segments. Teams will attach the aft segments to the aft skirts and offload and store the remaining segments from the railcars in preparation for stacking.
“It is good to see booster segments rolling into the Kennedy Space Center,” said Mike Bolger, program manager of Exploration Ground Systems. “The team can’t wait to get started working on the boosters that will send the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the first Artemis mission to the Moon.”
The solid rocket boosters are the first elements of the SLS rocket to be installed on the mobile launcher in preparation for launch. The aft booster assemblies will be lifted on to the mobile launcher, followed by the remaining booster segments, and then topped with the forward assembly.
Teams at Kennedy have been preparing for the arrival of the booster segments by assembling and testing the aft skirts and forward assemblies of the boosters, and practicing stacking procedures with booster pathfinders, or hardware replicas, earlier this year. NASA and Northrop Grumman completed casting in 2019 of all 10 of the motor segments for both the first and second Artemis lunar missions, and are now working on the boosters for the Artemis III mission, which will land the first woman and next man on the Moon in 2024.
With the arrival of the boosters, the only remaining pieces of hardware for the Artemis I flight test to be delivered to Kennedy are the launch vehicle stage adapter, which connects the rocket to the Orion spacecraft and will arrive this summer, and the SLS core stage, which will be transported to Kennedy by barge after the Green Run hot fire test later this year at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi.
Through the Artemis program, NASA will return astronauts to the Moon’s surface in four years. SLS, along with NASA’s Orion spacecraft, the Human Landing System and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, will serve as NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon on a single mission. We’ll explore more of the lunar surface than ever before, and collaborate with our commercial and international partners to establish sustainable exploration by the end of the decade. Then, we will use what we learn on and around the Moon to take the next giant leap – sending astronauts to Mars.
For more on NASA’s SLS, visit:
For more on NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, visit:
For a digital press kit with booster video and imagery, visit:
-end-
Kathryn Hambleton
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1100
kathryn.hambleton@nasa.gov
Laura Aguiar
Kennedy Space Center, Fla.
321-867-2468
laura.aguiar@nasa.gov
Tracy McMahan
Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala.
256-682-5326
tracy.mcmahan@nasa.gov