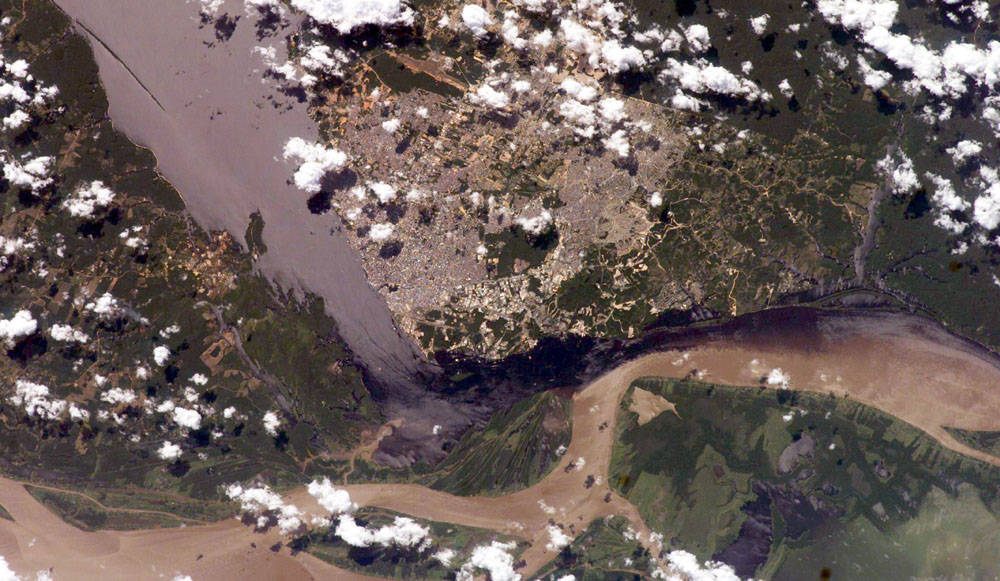
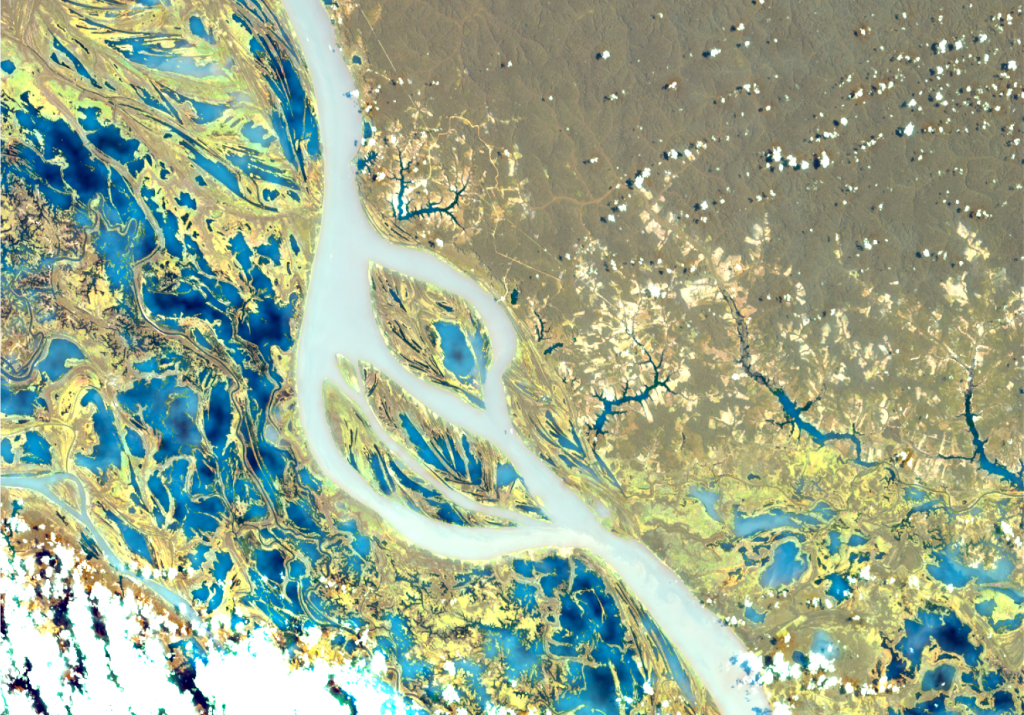
The largest river on the planet, the Amazon, forms from the confluence of the Solimões (the upper Amazon River) and the Negro at the Brazilian city of Manaus in central Amazonas. At the river conjunction, the muddy, tan-colored waters of the Solimões meet the “black” water of the Negro River. The unique mixing zone where the waters meet extends downstream through the rainforest for hundreds of miles, and attracts tourists from all over the world, which has contributed to substantial growth in the city of Manaus.
It is the vast quantity of sediment eroded from the Andes Mountains that gives the Solimões its tan color. By comparison, water in the Negro derives from the low jungles where reduced physical erosion of rock precludes mud entering the river. In place of sediment, organic matter from the forest floor stains the river the color of black tea.
The Solimões provides nutrient-rich mud to lakes on the floodplain (lower right). The ecology of muddy lakes differs correspondingly from that of nutrient-poor, blackwater rivers and lakes. Solimões water can be seen leaking into the Negro west of the main meeting zone (lower left). The Solimões is much shallower than the Negro because it has filled its valley and bed with great quantities of sediment since the valleys were excavated. Widths of the rivers differ for this reason.Image credit: NASA
2 min read