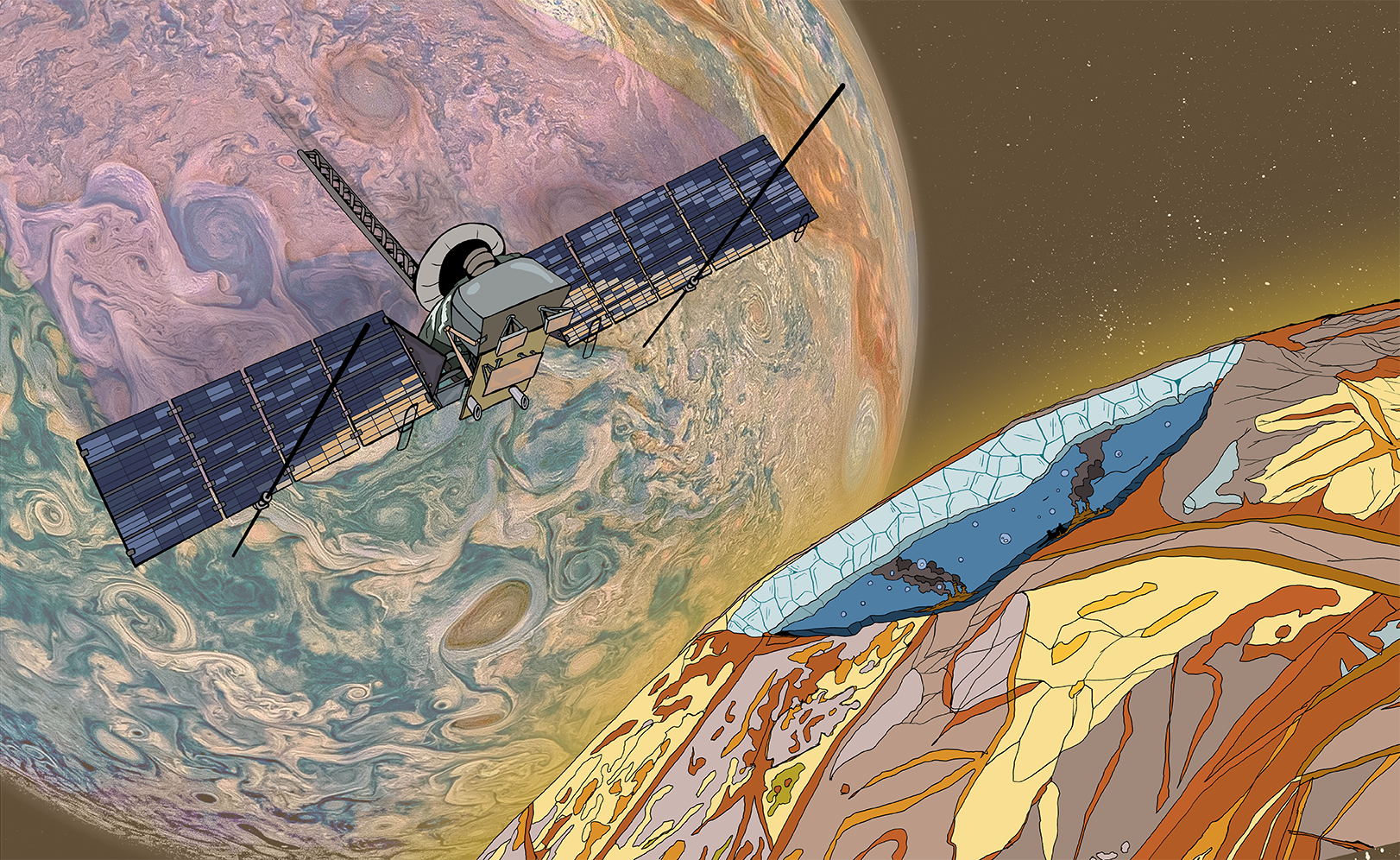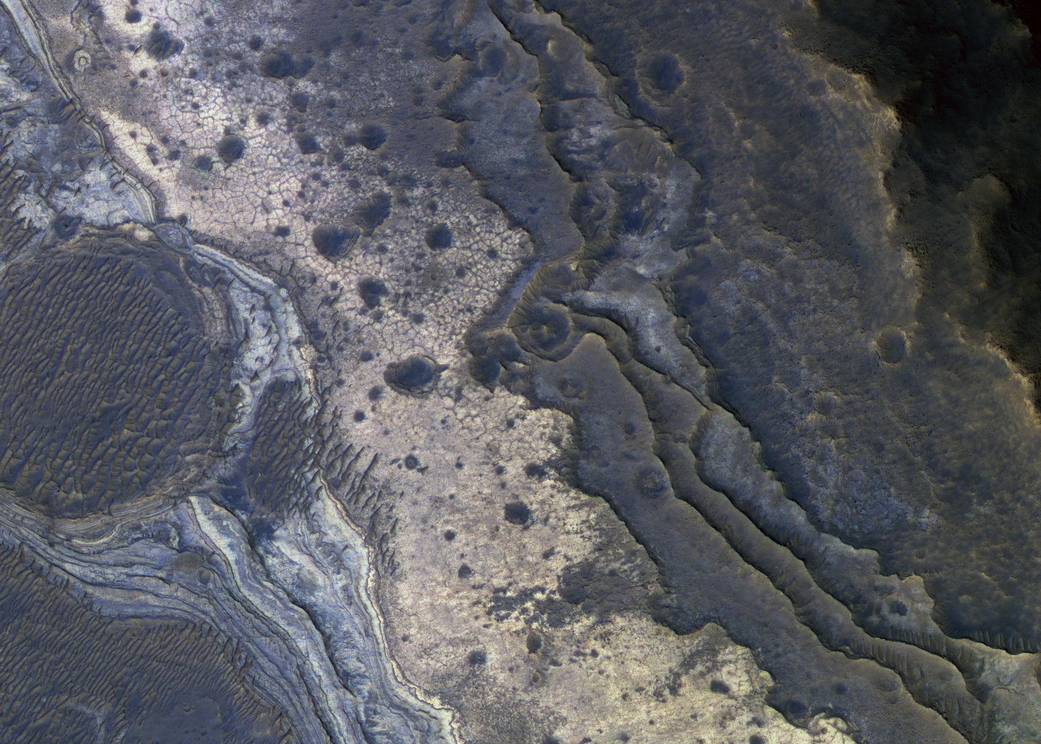
These Martian rocks, containing a hydrated mineral similar to opal, are light-toned and appear cream-colored in this false-color image taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, or MRO.
Images reveal that different layers of rock have different properties and chemistry. The opal-like minerals are located in distinct beds of rock outside of the large Valles Marineris canyon system and are also found in rocks within the canyon. The presence of opal in these relatively young rocks tells scientists that water, possibly as rivers and small ponds, interacted with the surface as recently as two billion years ago, one billion years later than scientists had expected. The discovery of this new category of minerals spread across large regions of Mars suggests that liquid water played an important role in shaping the planet’s surface and possibly hosting life.Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Ariz