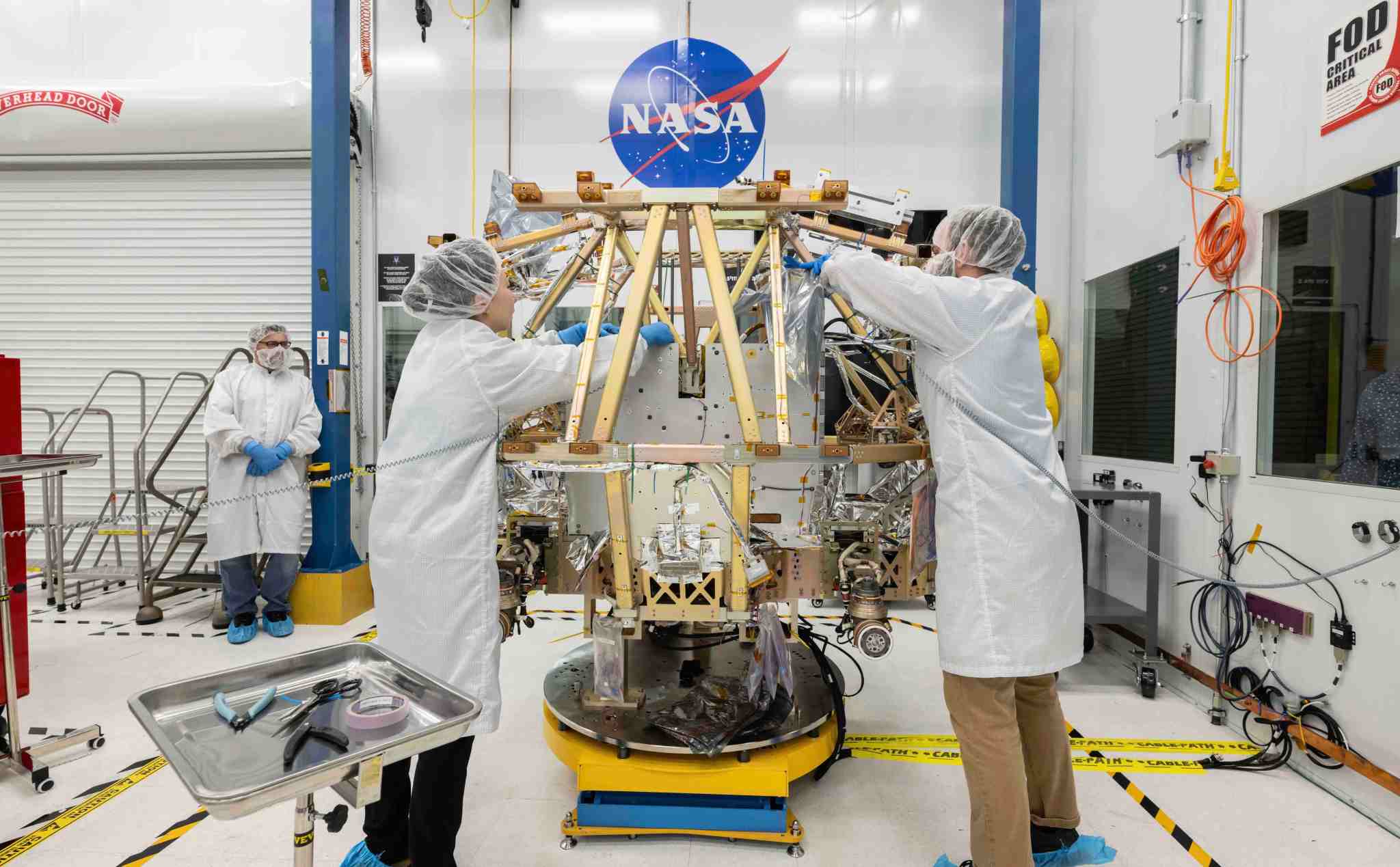
The VIPER team continues to push forward with the build of the flight rover that’ll go to the surface of the Moon. As of this writing, all of VIPER’s flight instruments are installed, and the rover is more than 80% built! This is a major accomplishment and shows the great progress being made by the dedicated VIPER team, who are excited to see the rover coming together.
What comes next – the confirmational tests of the rover – will strengthen our confidence in the rover’s ability to survive launch, landing, and the challenging environment of the lunar South Pole.
For example, as we assemble and install various subsystems onto the rover, we also perform channelization tests. Channelization tests let us confirm that through our design and build of the rover system – from piece-parts to cable harnesses and connectors, and mechanical installation activities, and even through avionics software – the connections all work. Now, you might think, “Of course what we installed should work!” but it’s important to remember how complicated these space systems are (and planetary rover systems in particular).
An example of an upcoming channelization test for VIPER is to command the flight vehicle’s high gain antenna to move in a particular way: Does it actually move in the correct direction and to the correct position? Sometimes we will perform even more complex tests, like sending a command to the NIRVSS instrument to take an image: Is the image taken successful? Is the field of view of the image correct? Did the image make its way into the rover’s avionics for downlink? We make these determinations now because we don’t want to discover any issues later in the assembly flow that could result in us needing to perform some disassembly to correct matters.
So we test as we go, to decrease risk later when we’re performing whole-rover environmental tests. This way if the rover doesn’t work as expected after one of VIPER’s environmental tests, we know it once worked fine, and that can help us more quickly problem solve what might have gone wrong.
The pace in which we’ve been working through the build and subsystem checkouts has been blistering lately, and we’ve had a good run of successes.
Go VIPER!
– Dan Andrews, VIPER Project Manager