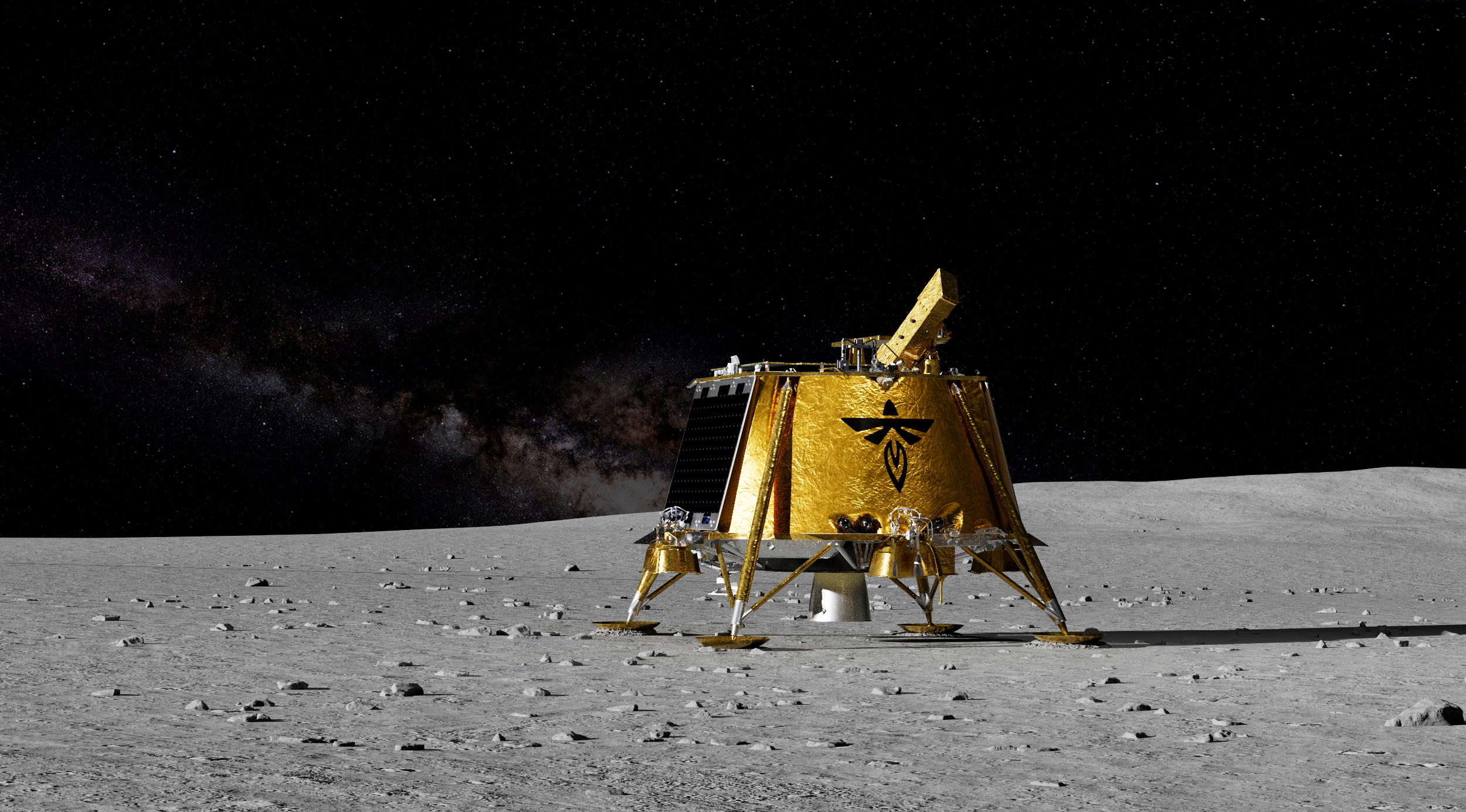
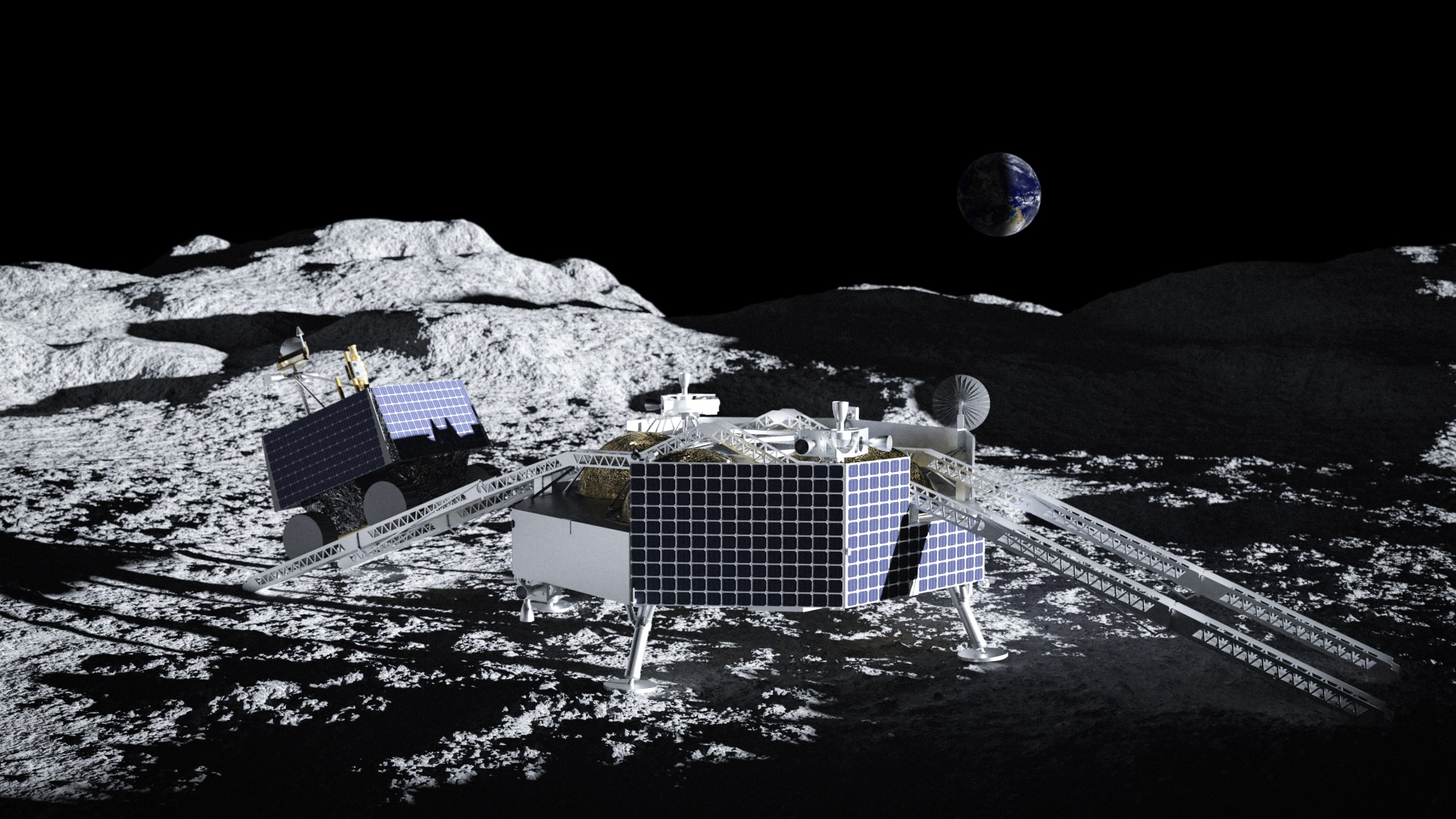
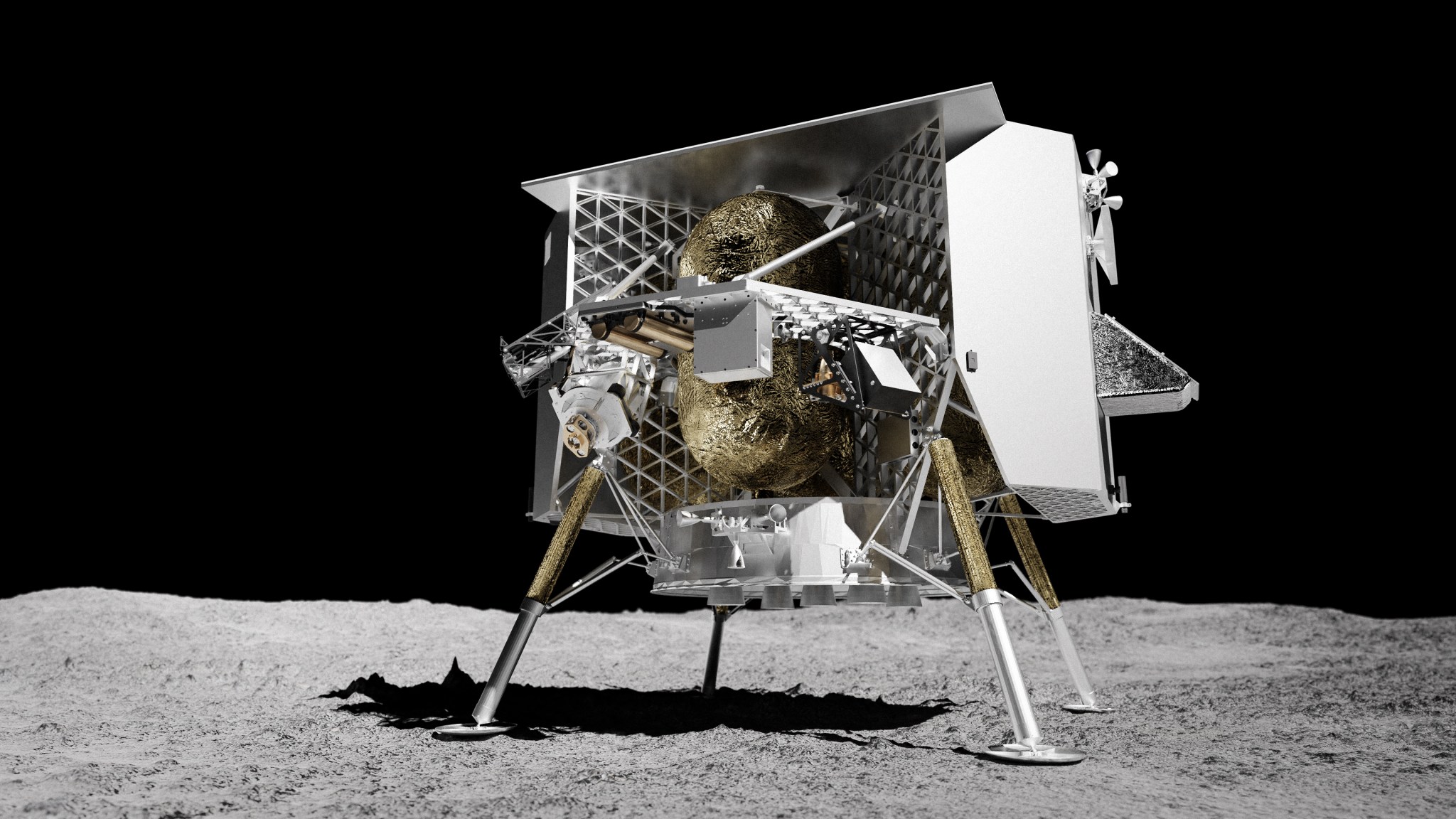
Astrobotic was selected to be part of the CLPS vendor pool in 2018, and has been awarded two task orders for scientific payload delivery. Astrobotic’s first flight will use the company’s Peregrine lunar lander and is scheduled to land in 2023 at a mare unit recently named Sinus Viscositatis. The site is adjacent to the Gruithuisen Domes, a geologic enigma along the mare/highlands boundary on the northeast border of Oceanus Procellarum, or Ocean of Storms, the largest dark spot on the Moon. The Peregrine flight will carry NASA payloads that will investigate specific aspects in and around the landing site.
Astrobotic’s second flight is scheduled to land at the lunar South Pole in 2024 using the company’s Griffin lunar lander. The Griffin flight will deliver NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, (VIPER). VIPER is a solar and battery powered rover that will characterize the distribution and physical state of lunar polar water and other volatiles in cold traps to evaluate the potential for future on-site, or in-situ, resource utilization at the South Pole. VIPER will operate over multiple lunar days and will be capable of traversing into permanently shadowed terrain. Subsurface volatile sampling will be accomplished by a one-meter drill paired with a quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Astrobotic Peregrine Mission-1
Expected Launch Date: 2023
Landing Site: Sinus Viscositatis
Payloads: CLPS Astrobotic Peregrine Mission-1 NASA-Provided Lunar Payloads
Lander Name: Peregrine
Task Order Information: TO2 AB
Astrobotic Griffin Mission-1
Expected Launch Date: 2024
Landing Site: Lunar South Pole
Payloads: CLPS Astrobotic Griffin Mission-1 NASA-Provided Lunar Payloads
Lander Name: Griffin
Task Order Information: TO 20A (VIPER)