Japanese Experiment Module Kibo
Quick Facts
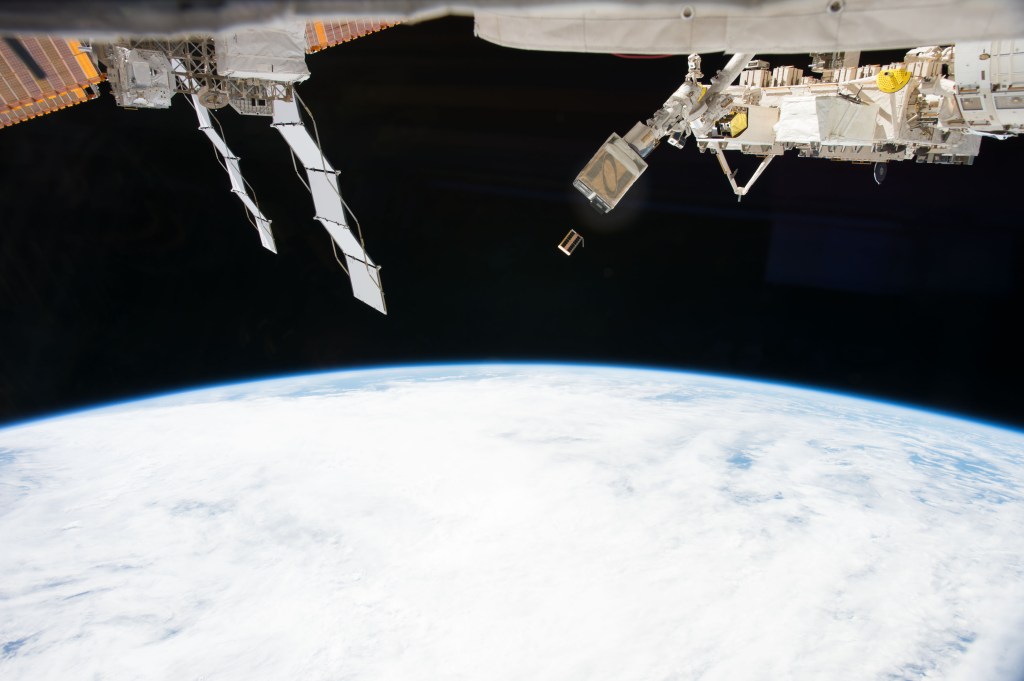
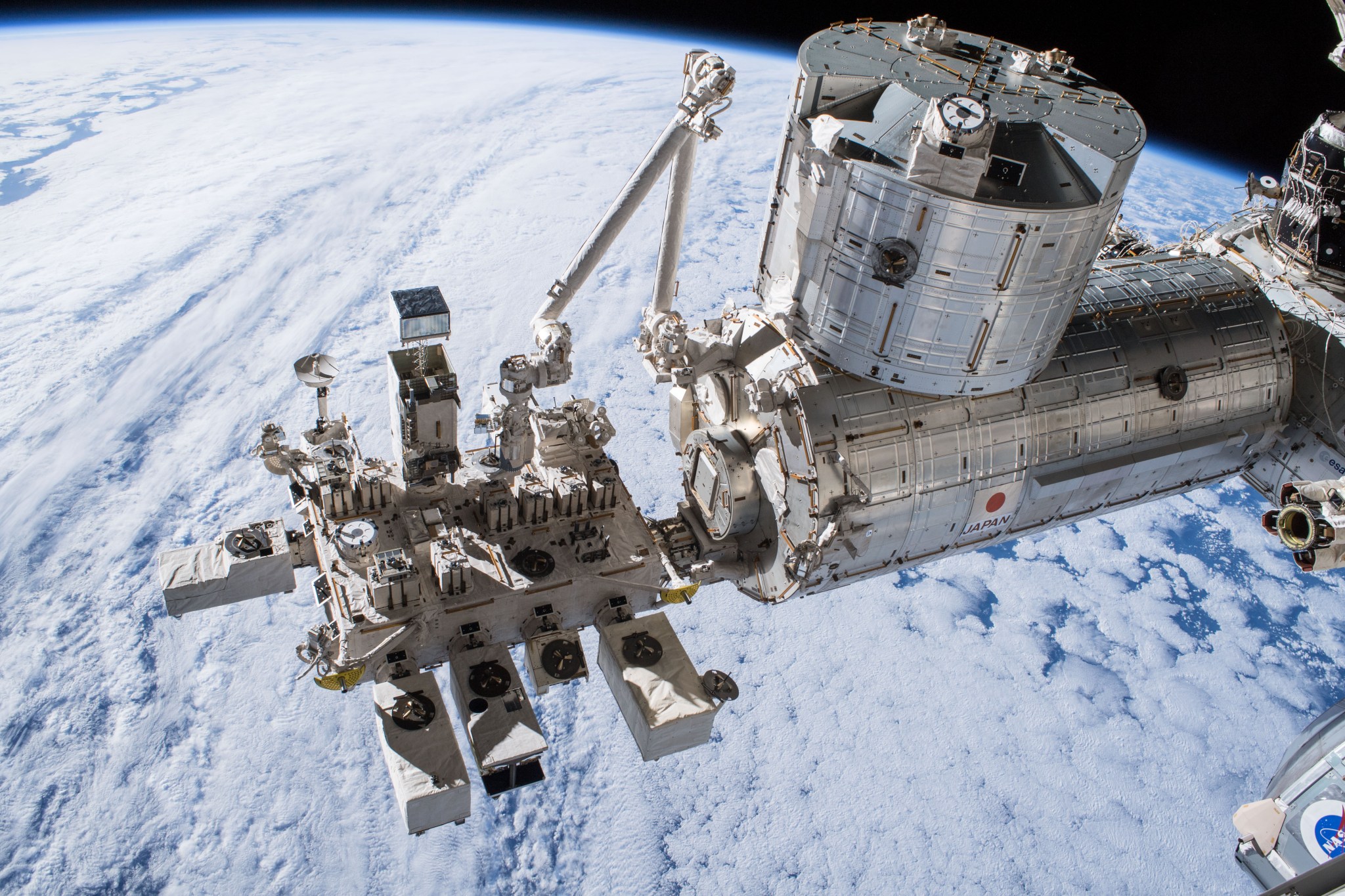
The Exposed Facility, or EF, is a unique platform on the ISS that is located outside of the Pressurized Module and is continuously exposed to the space environment. Astronauts exchange experiment payloads or hardware from the Pressurized Module through the scientific airlock using the Kibo Remote Manipulator System. Items positioned on the exterior platform focus on Earth observation as well as communication, scientific, engineering and materials science experiments.
The EF is a platform that can hold up to 10 experiment payloads at a time and measures 5.6 meters (18.4 feet) wide, 5 meters (16.4 feet) high and 4 meters (13.1 feet) long.
Exposed Facility Mass: 9,038 pounds
Length: 18.4 feet
Width: 13.1 feet
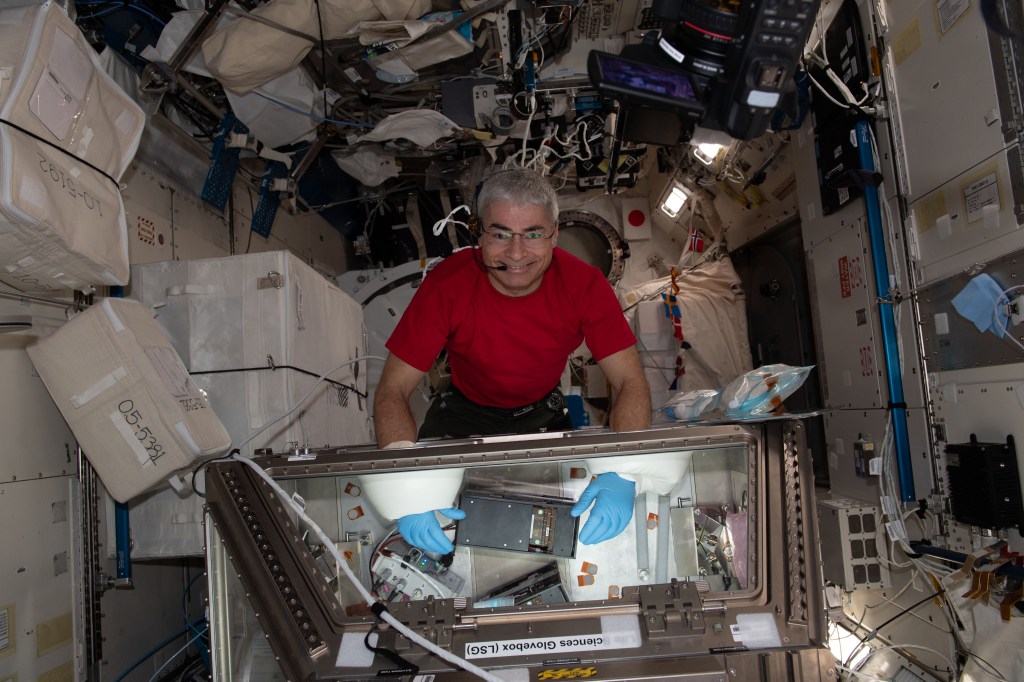
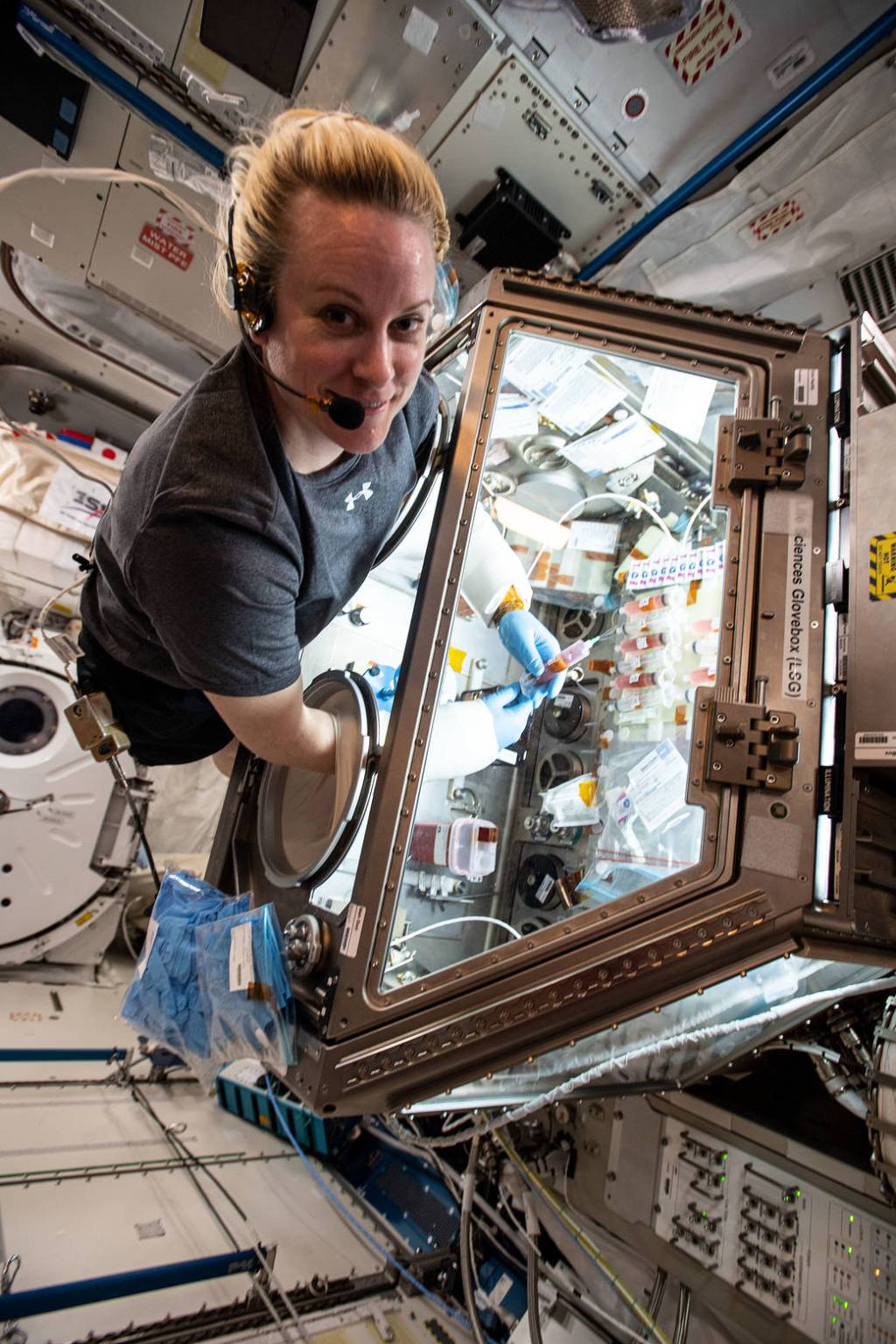
The Japanese Experiment Module – Kibo is Japan’s contribution to the station and was launched and assembled over three space shuttle missions. Kibo, Japanese for “hope,” is a space research facility enabling astronauts to investigate a variety of space phenomena. Experiments range from biology, physics, technology. and more and take place in Kibo’s numerous research racks. Kibo also provides an airlock allowing experiments to be exposed to the vacuum of space. was designed for scientific research activities on orbit and also enables educational, cultural, and commercial opportunities. The U.S. segment of the station provides Kibo with air, power, data, and cooling fluid.
Kibo Laboratory Module Mass: 35,050 pounds
Length: 36.7 feet
Diameter: 14.4 feet
The Logistics Module serves as an on-orbit storage area that houses materials for experiments, maintenance tools and supplies. It is attached to the top of the main pressurized section of Kibo.
Logistics Module Mass: 4,200 pounds
Length: 13.9 feet
Diameter: 14.4 feet
Mission Overview
Exposed Facility Launch: 7/15/09
Installation: 7/18/09
Kibo Laboratory Module Launch: 5/31/08
Installation: 6/3/08
Logistics Module Launch: 3/11/08
Installation: 3/14/08