Using data from NASA’s three Great Observatories, scientists have found the best evidence to date of a mechanism that produced supermassive black holes in the early universe. If confirmed, this result, described in our latest press release, could lead to new insight into how black holes were formed and grew billions of years ago.
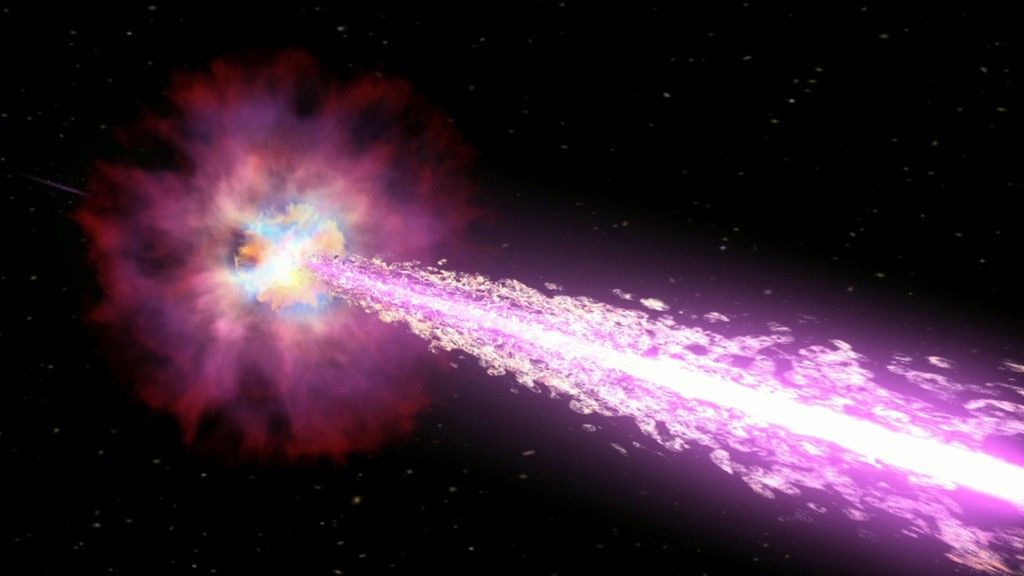
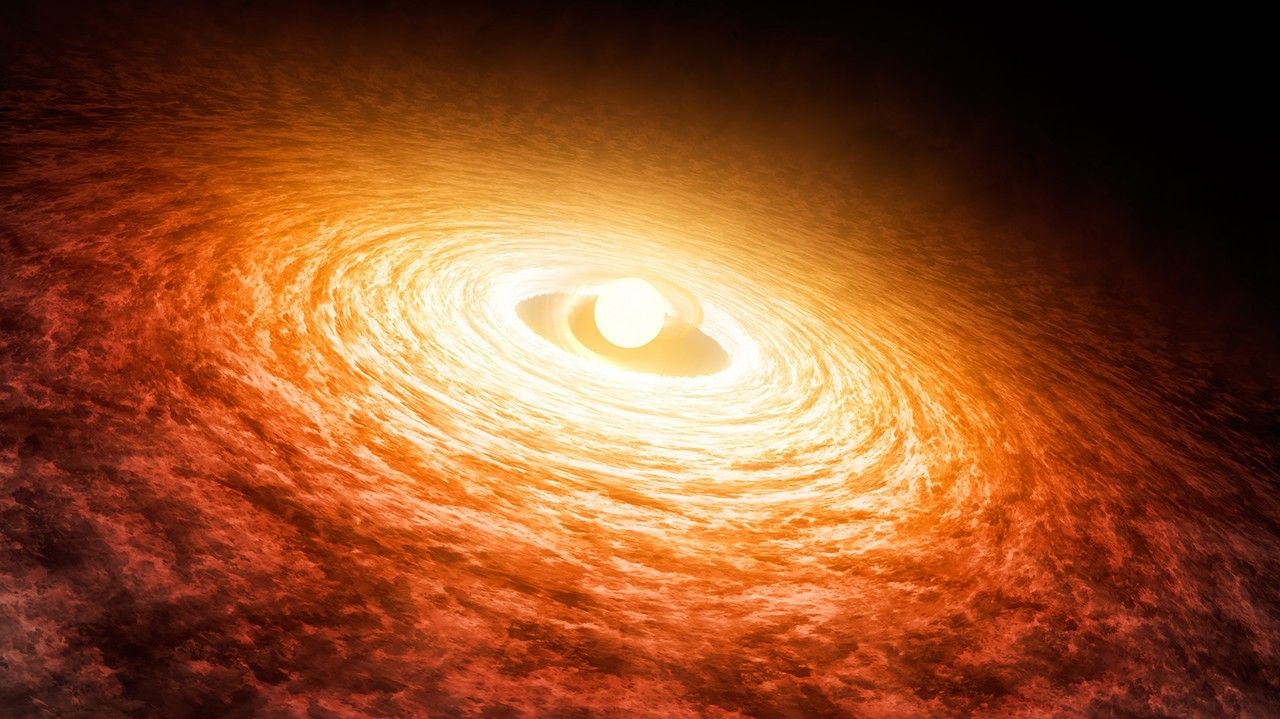
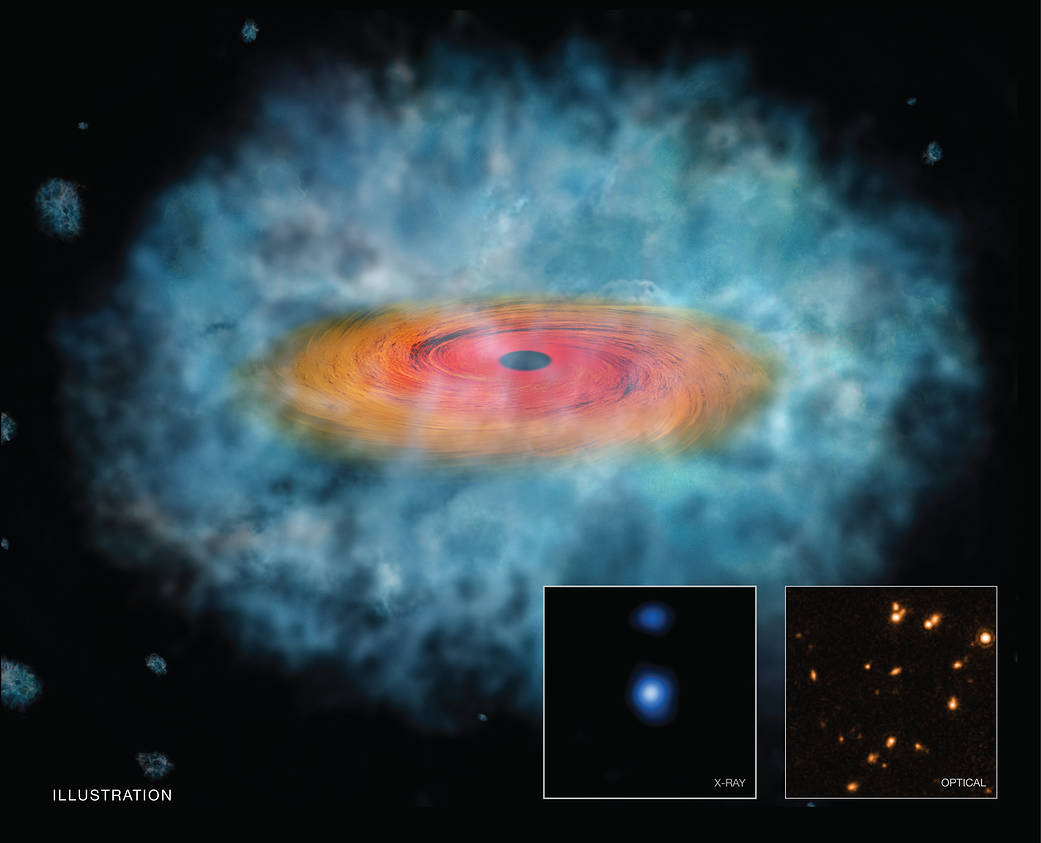
This artist’s illustration depicts a possible “seed” for the formation of a supermassive black hole, an object that contains millions or even billions of times the mass of the Sun. In the artist’s illustration, the gas cloud is shown as the wispy blue material, while the orange and red disk is showing material being funneled toward the growing black hole through its gravitational pull. Researchers found evidence that two objects could have formed in this way, by directly collapsing into a black hole from a large cloud of gas. These two candidates for being “direct collapse black holes” are so distant that they may have formed less than one billion years after the Big Bang.
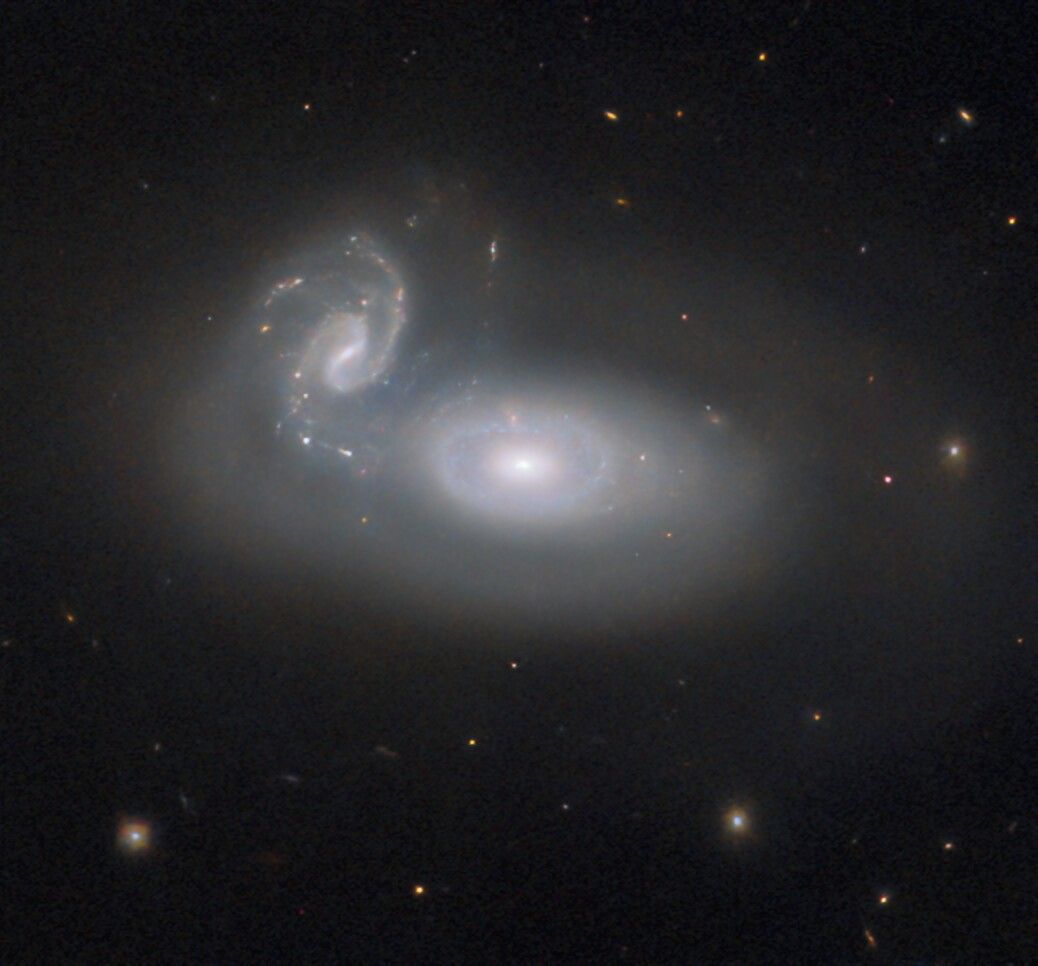
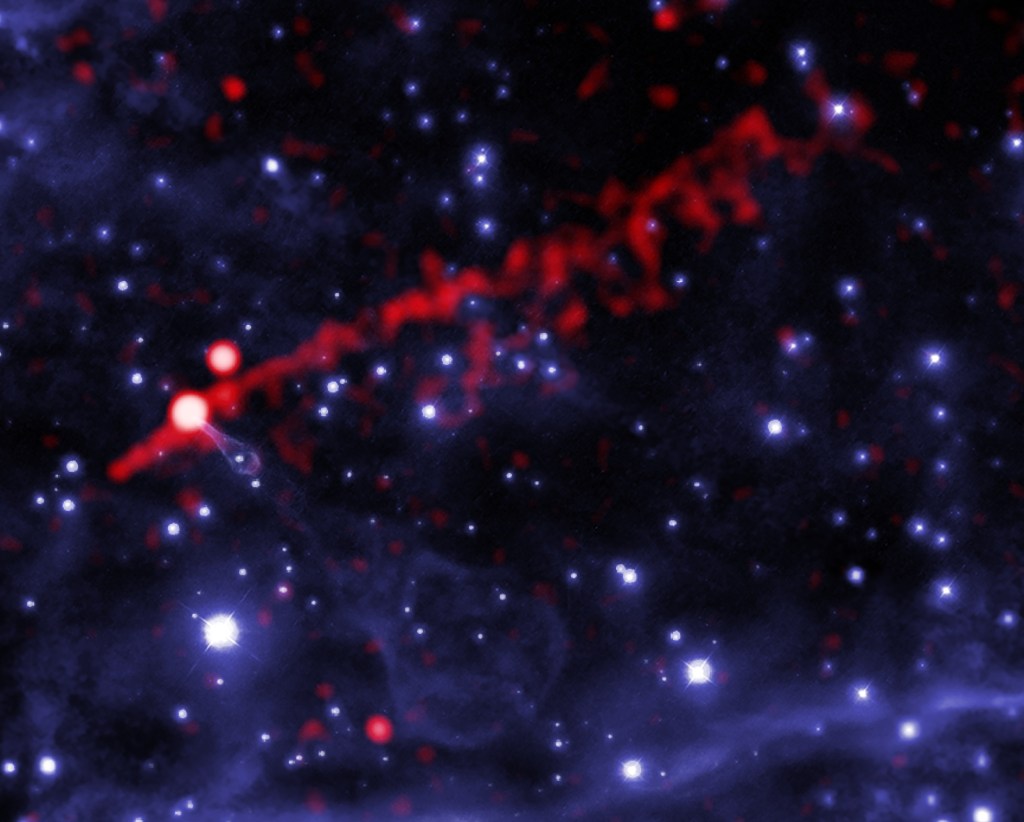
The inset boxes show data from the Hubble Space Telescope (top) and Chandra X-ray Observatory (bottom) of one of the objects described above. The Hubble image shows the faint, distant galaxy at the center of the image and the Chandra image shows X-ray emission from material falling onto the black hole in the same galaxy.
The researchers used computer models of black hole seeds combined with a new method to select candidates for these objects from long-exposure images from Chandra, Hubble, and Spitzer (not shown in this graphic). By analyzing the combined light from the three telescopes, the team was able to search through thousands of objects to look for any that had properties that matched those predicted by their models.
Two candidates emerged that had the expected red color, seen by Hubble and Spitzer, as well as the X-ray profile predicted from Chandra. These objects were found in the Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey and the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey-South surveys. The next steps will involve getting more data on these two intriguing objects as well as extending the analysis to other surveys to look for more direct collapse black hole candidates.
These results will appear in the June 21st issue of the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and is available online. The authors of the paper are Fabio Pacucci (SNS, Italy), Andrea Ferrara (SNS), Andrea Grazian (INAF), Fabrizio Fiore (INAF), Emaneule Giallongo (INAF), and Simonetta Puccetti (ASI Science Data Center). NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts, controls Chandra’s science and flight operations.
Image credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Scuola Normale Superiore/Pacucci, F. et al, Optical: NASA/STScI; Illustration: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss
Read More from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
For more Chandra images, multimedia and related materials, visit: