This article is for student grades 5-8.
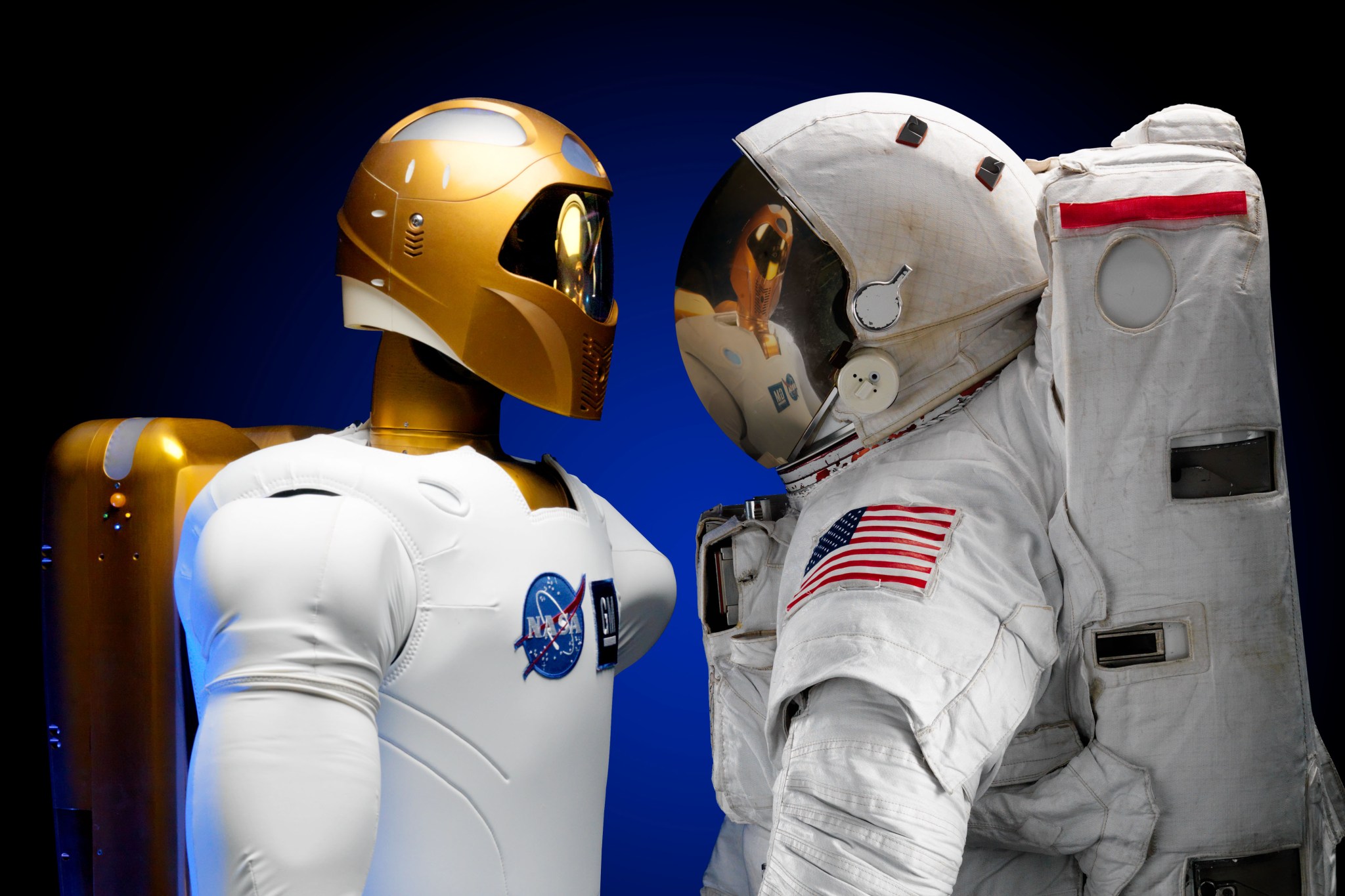
Robonaut is a NASA robot. Engineers designed Robonaut to be humanoid, which means it is built to look like a person. This makes it easier for Robonaut to do the same jobs as a person. Robonaut could help with anything from working on the International Space Station to exploring other worlds. A Robonaut has been to the station. It is back on Earth for upgrades, but will return to the station.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Words to Know
torso: the human body except for the head, arms, and legs
dexterous: skillful with the hands
_____________________________________________________________________________
What Does Robonaut Do?
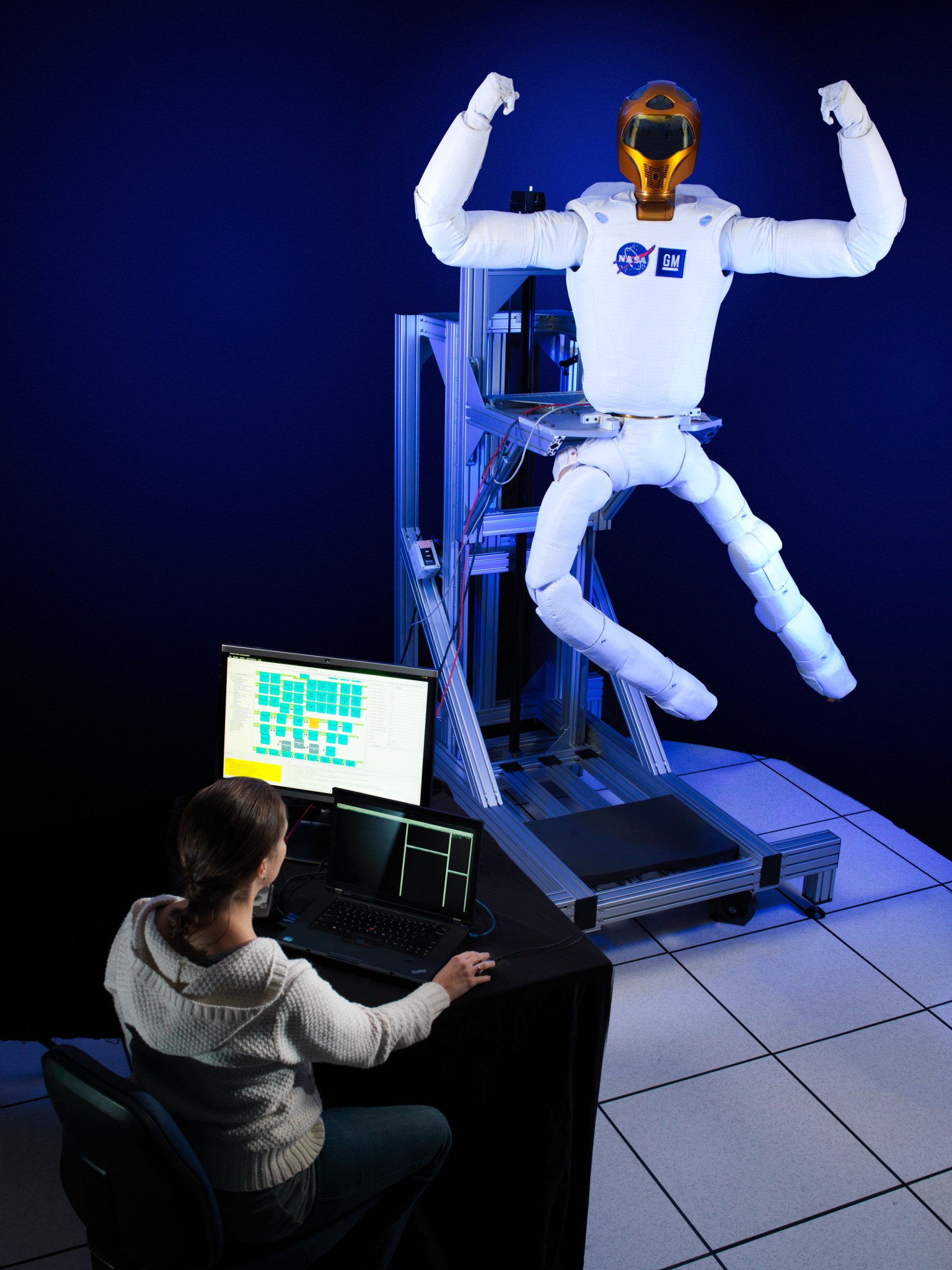
NASA began working on the Robonaut project in 1996 and produced the first version of the robot in 2000. Since that time, engineers have continued to improve Robonaut. The newest model is called Robonaut 2, or R2. NASA and car manufacturer General Motors worked together to create R2. Robonaut has a head, torso, arms and hands like a person. Cameras in the head provide vision. Robonaut is called a dexterous robot because its hands and fingers move like a person’s. So Robonaut can perform tasks designed to be done by human hands. For example, Robonaut can use many of the same tools as an astronaut. In addition, the robot’s torso can be attached to a “bottom” so Robonaut can move around. For example, Robonaut has been tested with a set of wheels. The robonaut even had a legs for work on the space station.
How Does Robonaut Work?
Robonaut can function in two ways. Software allows Robonaut to “think” for itself. The people who control R2 can give it a simple task to do, and R2 can figure out how to do it. R2’s software can be updated to allow it to do new tasks. R2 can also be operated by remote control. An operator can use a headset to see what Robonaut sees through its cameras. The operator can then use controls to make Robonaut move.
What Will Robonaut Do on the Space Station?
R2 flew to the space station on the space shuttle Discovery in 2011. On the station, Robonaut was like an extra pair of hands. Because R2 is a robot, it does not get tired or bored. So, it was perfect for measuring how the air moves on the station. The robot can stand very still. It also does not breathe. It can hold a tool to measure the air without breathing on the tool. R2 was also good at cleaning the many handrails inside the station, allowing astronauts to focus on the more important science and repair work. R2 also had a task board on which to practice flipping switches and pushing buttons. While on orbit, R2 sometimes acted as astronauts’ eyes and hands. The crew controlled the robot through the use of special virtual reality gear aboard the station.
NASA can now improve the humanoid robot by using what was learned about R2 while it was on the space station.
What Does the Future Hold for Robonaut?
NASA is still deciding what the future holds for Robonaut. Robonaut will conduct more tests aboard the space station, and may even take its first steps. This testing would determine how well Robonaut could move around spacecraft environments to help astronauts. Robonaut’s designers even have ideas for sending a robot like Robonaut to future destinations like the Moon and Mars. If testing goes well, who knows where Robonaut—or a better robot based on Robonaut—could end up?
More About Robonaut
Robonaut
NASA Edge @ Robonaut 2 (2010)
Download video
Transcript
Robonaut YouTube Playlist
Robonaut Image Gallery
What Is Robotics? (Grades 5-8)