This article is for students grades K-4.
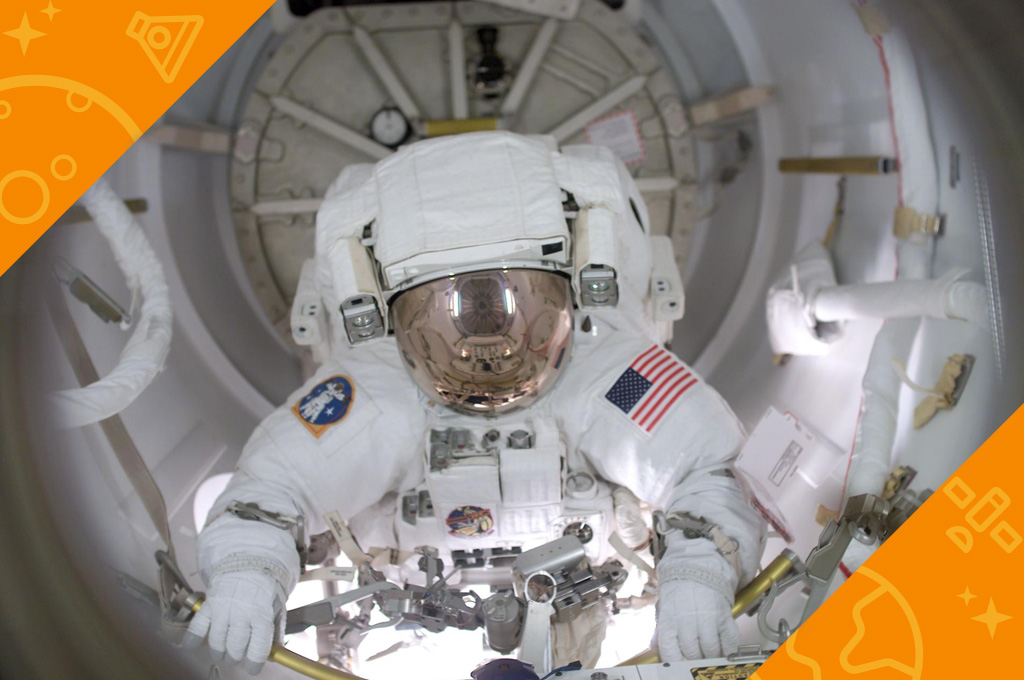
Any time an astronaut gets out of a vehicle while in space, it is called a spacewalk. A spacewalk is also called an EVA. EVA stands for extravehicular activity.
The first person to go on a spacewalk was Alexei Leonov. He was from Russia. The first spacewalk was on March 18, 1965. It was 10 minutes long.
The first American to go on a spacewalk was Ed White. His spacewalk was on June 3, 1965, during the Gemini 4 mission. White’s spacewalk lasted 23 minutes.
Today, astronauts go on spacewalks outside the International Space Station. Spacewalks usually last between five and eight hours, depending on the job.
The world record for the most spacewalks is held by Russian astronaut Anatoly Solovyev. He has been on 16 spacewalks. Those spacewalks equal more than 82 hours outside in space. That’s almost 3 ½ days total! The U.S. record for most spacewalks is a four-way tie. Four NASA astronauts have made 10 spacewalks each. They are Michael Lopez-Alegria, Peggy Whitson, Bob Behnken and Chris Cassidy. Of the four, Michael spent the most time outside the space station. His total is more than 67 hours.
Why Do Astronauts Go on Spacewalks?
Astronauts go on spacewalks for many reasons. Spacewalks let astronauts work outside their spacecraft while still in space. Astronauts can do science experiments on a spacewalk. Experiments can be placed on the outside of a spacecraft. This lets scientists learn how being in space affects different things.
Spacewalks also let astronauts test new equipment. They can repair satellites or spacecraft that are in space. By going on spacewalks, astronauts can fix things instead of bringing them back to Earth to fix.
How Do Astronauts Go on Spacewalks?
When astronauts go on spacewalks, they wear spacesuits to keep themselves safe. Inside spacesuits, astronauts have the oxygen they need to breathe. They have the water they need to drink.
Astronauts put on their spacesuits several hours before a spacewalk. The suits are pressurized. This means that the suits are filled with oxygen.
Once in their suits, astronauts breathe pure oxygen for a few hours. Breathing only oxygen gets rid of all the nitrogen in an astronaut’s body. If they didn’t get rid of the nitrogen, the astronauts might get gas bubbles in their body when they walked in space. These gas bubbles can cause astronauts to feel pain in their shoulders, elbows, wrists and knees. This pain is called getting “the bends” because it affects the places where the body bends. Scuba divers can also get “the bends.”
Astronauts are now ready to get out of their spacecraft. They leave the spacecraft through a special door called an airlock. The airlock has two doors. When astronauts are inside the spacecraft, the airlock is airtight so no air can get out. When astronauts get ready to go on a spacewalk, they go through the first door and lock it tight behind them. They can then open the second door without any air getting out of the spacecraft. After a spacewalk, astronauts go back inside through the airlock.
How Do Astronauts Stay Safe During Spacewalks?
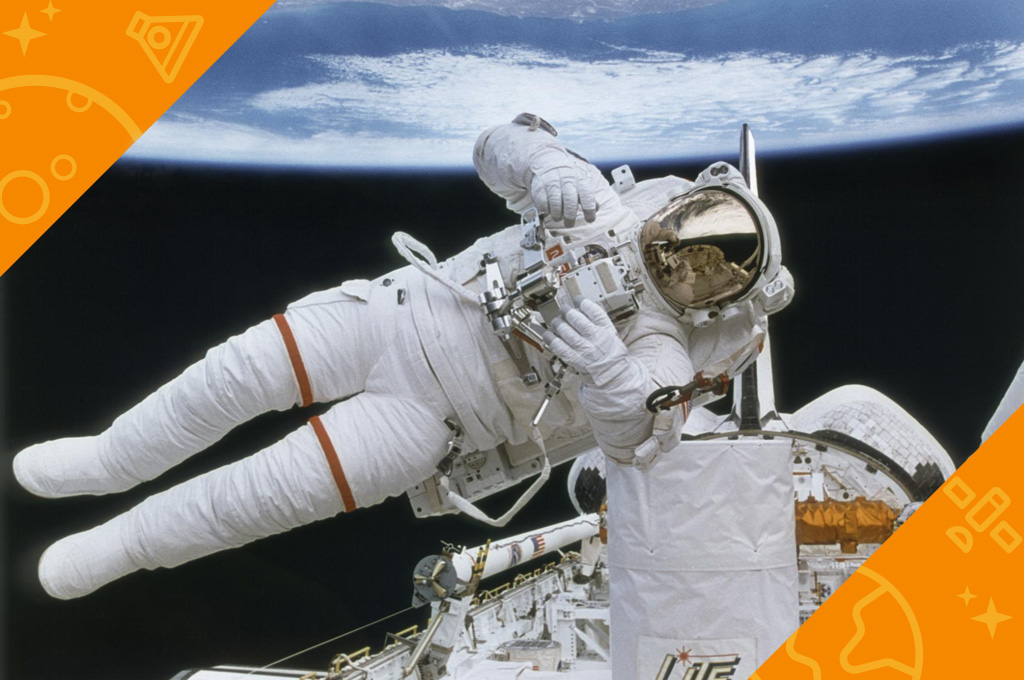
When on a spacewalk, astronauts use safety tethers to stay close to their spacecraft. Tethers are like ropes. One end is hooked to the spacewalker. The other end is connected to the vehicle. The safety tethers keep astronauts from floating away into space. Astronauts also use tethers to keep tools from floating away. They tether their tools to their spacesuits.
Another way astronauts stay safe during spacewalks is by wearing a SAFER. SAFER stands for Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue. SAFER is worn like a backpack. It uses small jet thrusters to let an astronaut move around in space. If an astronaut were to become untethered and float away, SAFER would help him or her fly back to the spacecraft. Astronauts control SAFER with a small joystick, like on a video game.
How Do Astronauts Train for Spacewalks?
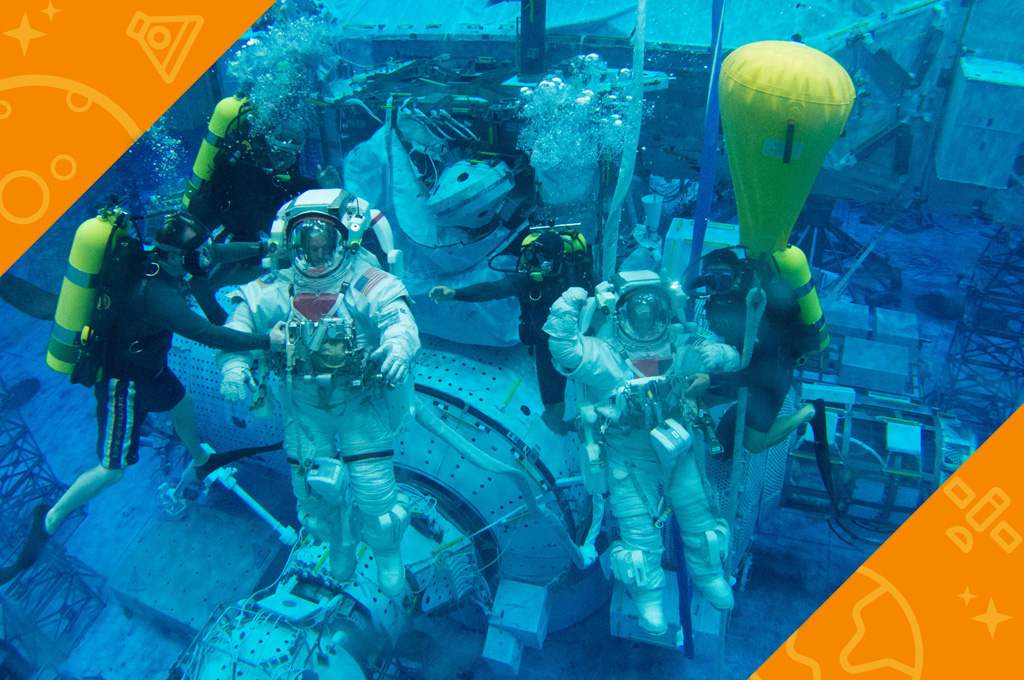
One way astronauts train for spacewalks is by going for a swim. Floating in space is a lot like floating in water. Astronauts practice spacewalks underwater in a large swimming pool. The pool is called the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory, or NBL. It is near NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. The pool holds 6.2 million gallons of water. Astronauts train seven hours in the pool for every one hour they will spend on a spacewalk.
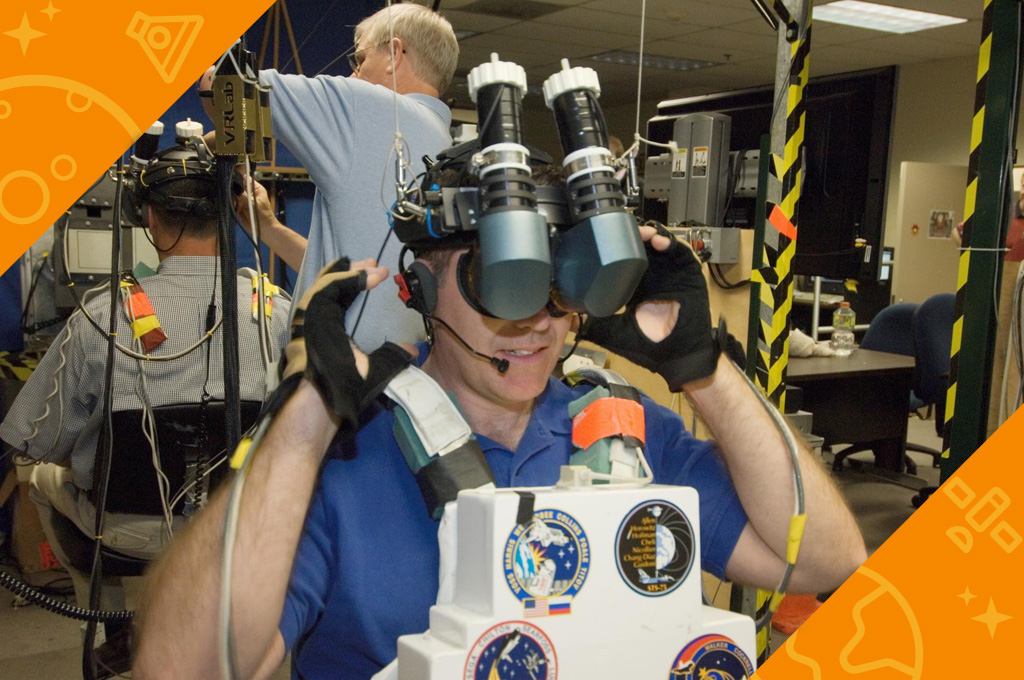
Another way astronauts practice for a spacewalk is by using virtual reality. This is sort of like playing a video game. Astronauts wear a helmet with a video screen inside. They also wear special gloves. A video of what they will see during a spacewalk is shown on the screen inside the helmet. When the astronaut moves, the special gloves allow the movements to be shown with the video. The virtual reality simulation looks and feels just like a spacewalk.
More About Spacewalks
Walking in Space Photo Gallery
What Is a Spacesuit?
Challenges of Spacewalking Videos