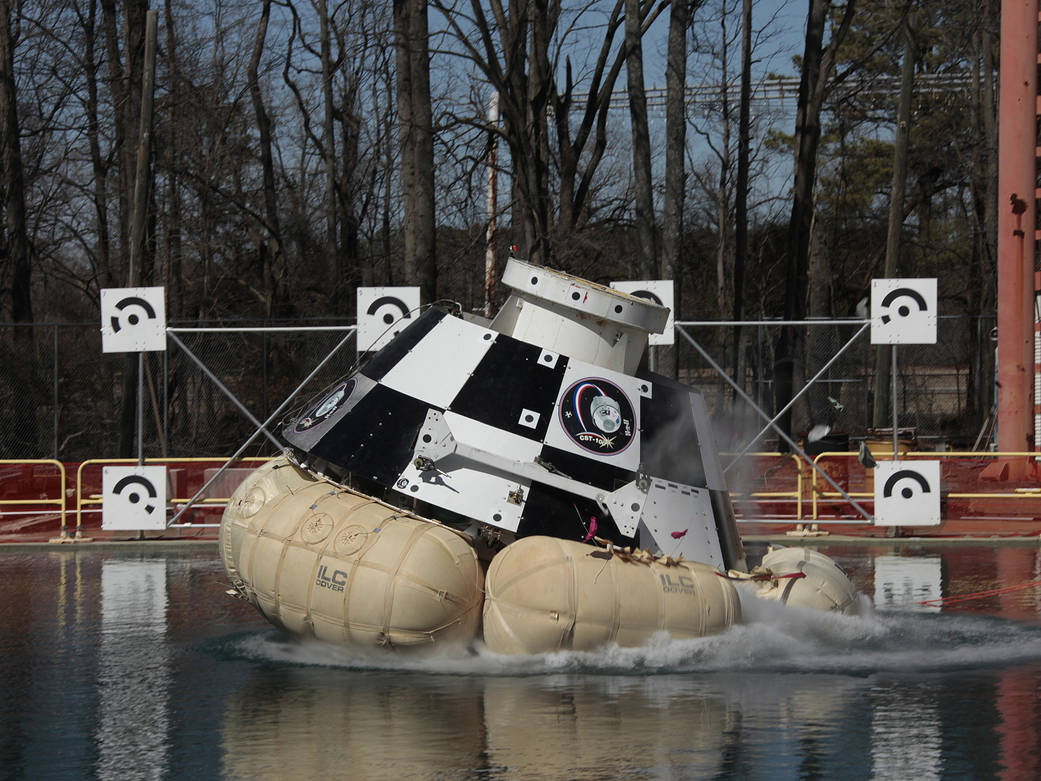
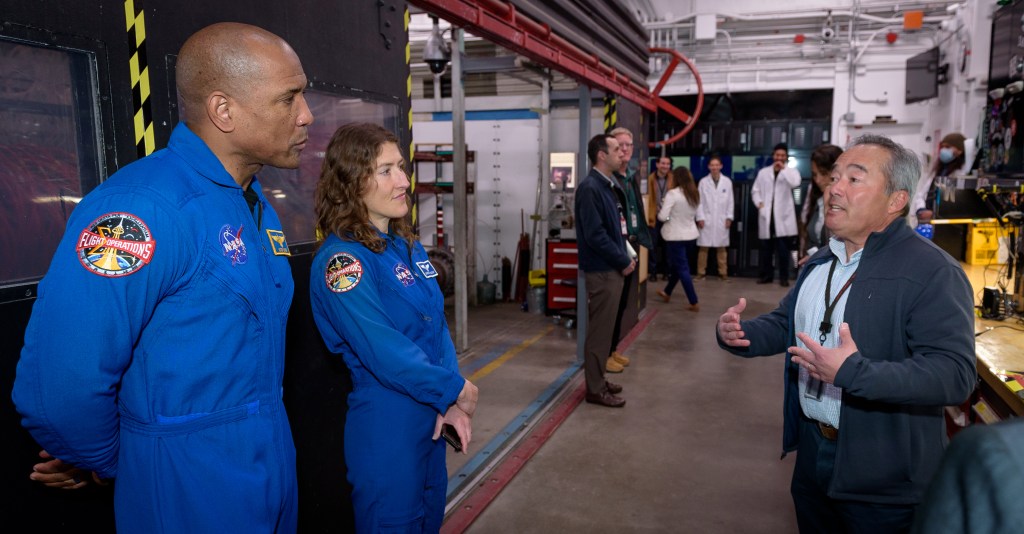
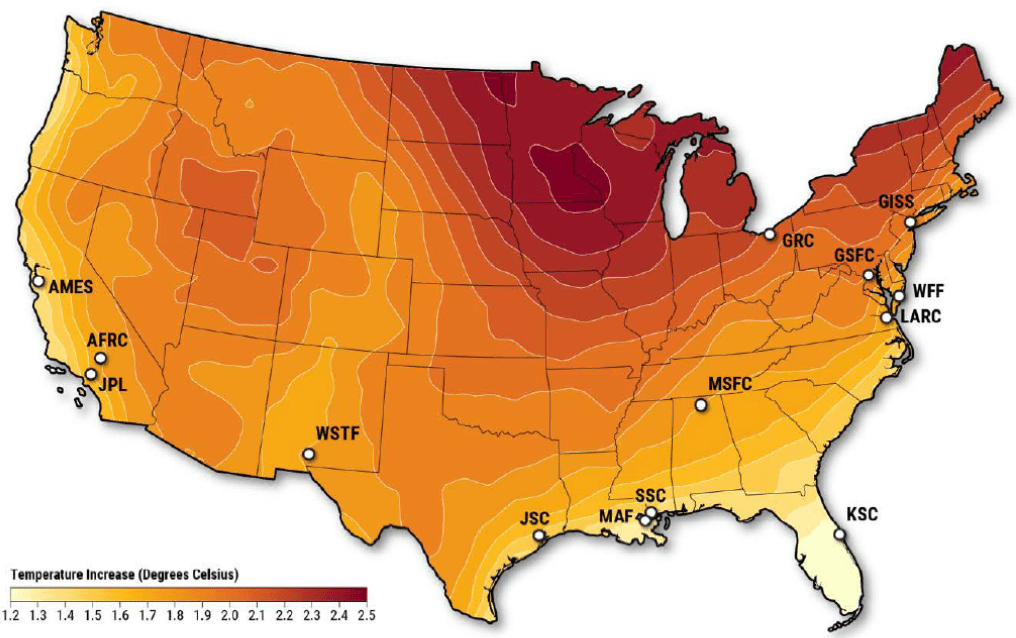
Boeing’s CST-100 system is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program for safe and reliable crew transportation to and from the International Space Station on American spacecraft launched from the United States.
The capsule – designed to land on land, making it reusable up to ten times with a six-month turnaround time between launches – can accommodate up to seven passengers or a mix of crew and cargo. The integrated CST-100 system features a pusher abort system that, in the case of an emergency on the pad or during ascent, would push the capsule off of its Atlas V rocket for a parachute landing the water.
Because crew safety is a top priority for America’s crew transportation systems, Boeing tested the CST-100 in water landing scenarios at Langley’s Landing and Impact Research Facility. These water drops test a variety of heights and angles from which the capsule could land in an abort scenario.
Credit: NASA/David C. Bowman