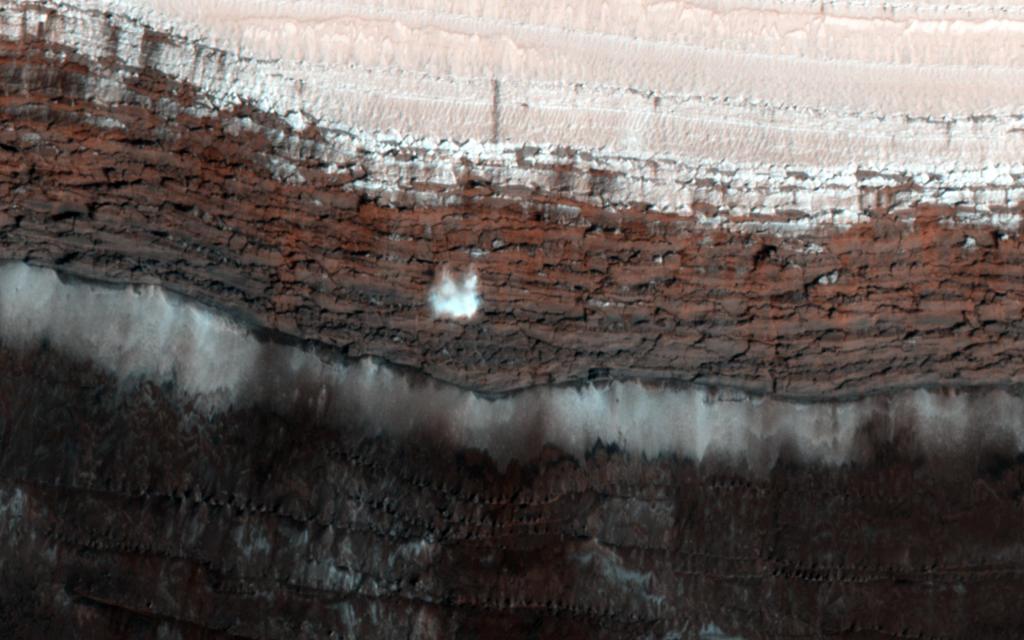
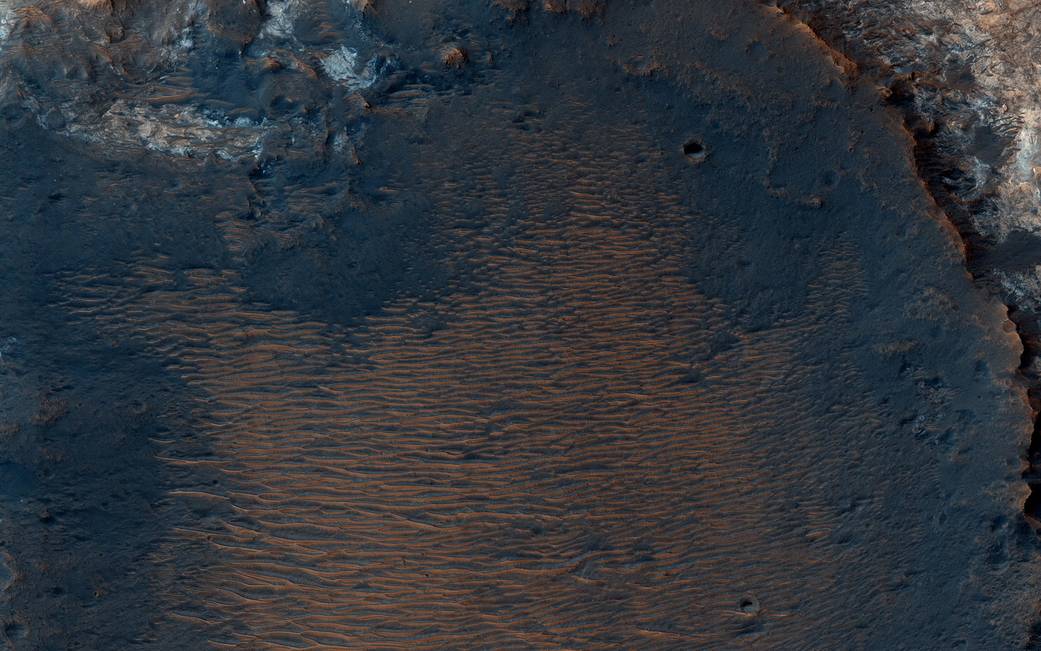
This image from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures details of an approximately 1-kilometer inverted crater west of Mawrth Vallis. A Context Camera image provides context for the erosional features observed at this site. The location of this HiRISE image is north of the proposed landing ellipse for the ExoMars 2020 rover mission that will investigate diverse rocks and minerals related to ancient water-related activity in this region.
Prolonged erosion removed less resistant rocks leaving behind other rocks that stand up locally such as the crater seen here and other nearby remnants. These resistant layers may belong to a phase of volcanism and/or water-related activity that carved Mawrth Vallis and filled in existing craters, and other lower-lying depressions, with darker materials.
Erosion has also exposed these layers down to older, more resistant lighter rocks that are clay-bearing. The diversity of exposed bedrock made this location an ideal candidate for exploring a potentially water-rich ancient environment that might have once harbored life.
The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.7 centimeters (11.3 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 86 centimeters (33.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington.