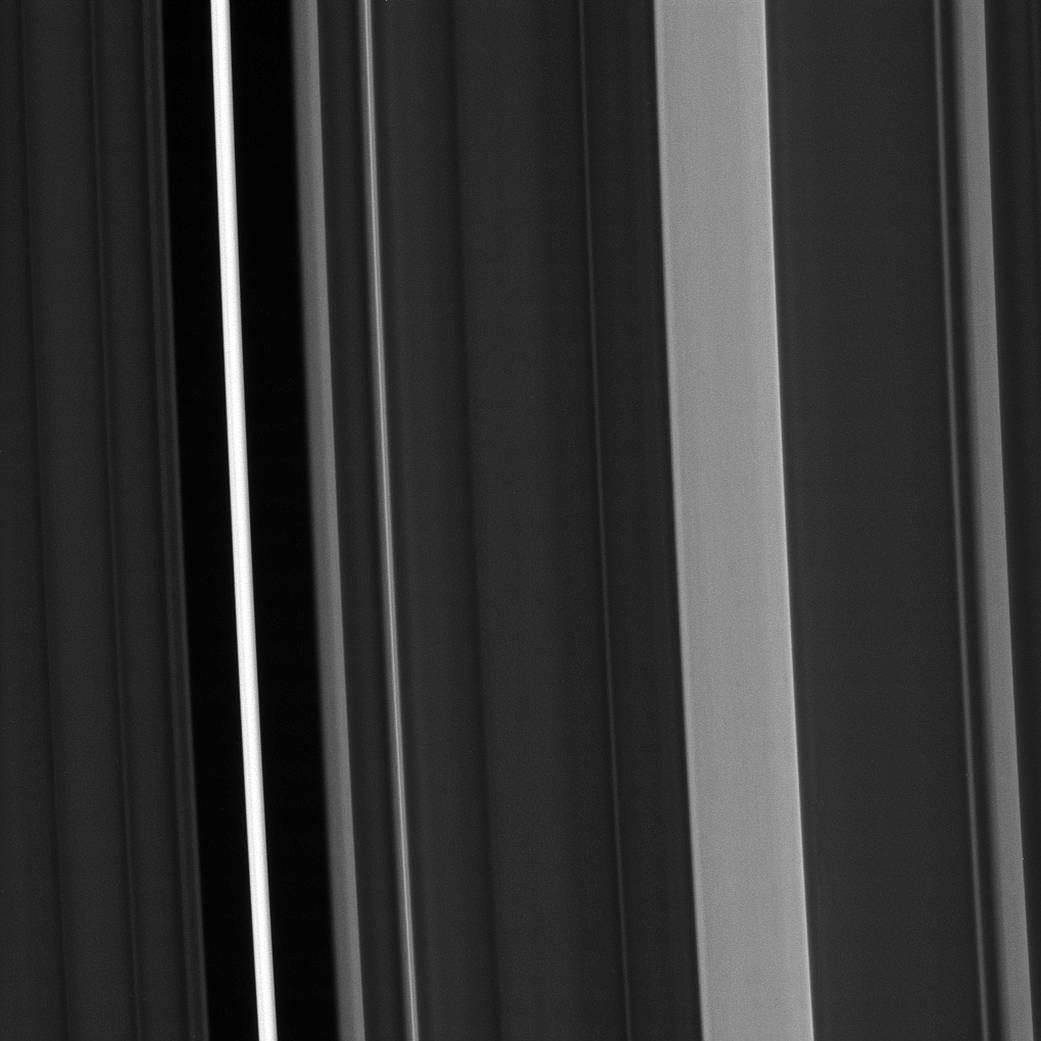
Saturn’s C ring isn’t uniformly bright. Instead, about a dozen regions of the ring stand out as noticeably brighter than the rest of the ring, while about half a dozen regions are devoid of ring material. Scientists call the bright regions “plateaus” and the devoid regions “gaps.”
Scientists have determined that the plateaus are relatively bright because they have higher particle density and reflect more light, but researchers haven’t solved the trickier puzzle of how the plateaus are created and maintained.
This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 62 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken Jan. 9, 2017 in green light with the Cassini spacecraft’s narrow-angle camera.
Cassini obtained the image while approximately 194,000 miles (312,000 kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 67 degrees. Image scale is 1.2 miles (2 kilometers) per pixel.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit https://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and https://www.nasa.gov/cassini . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute