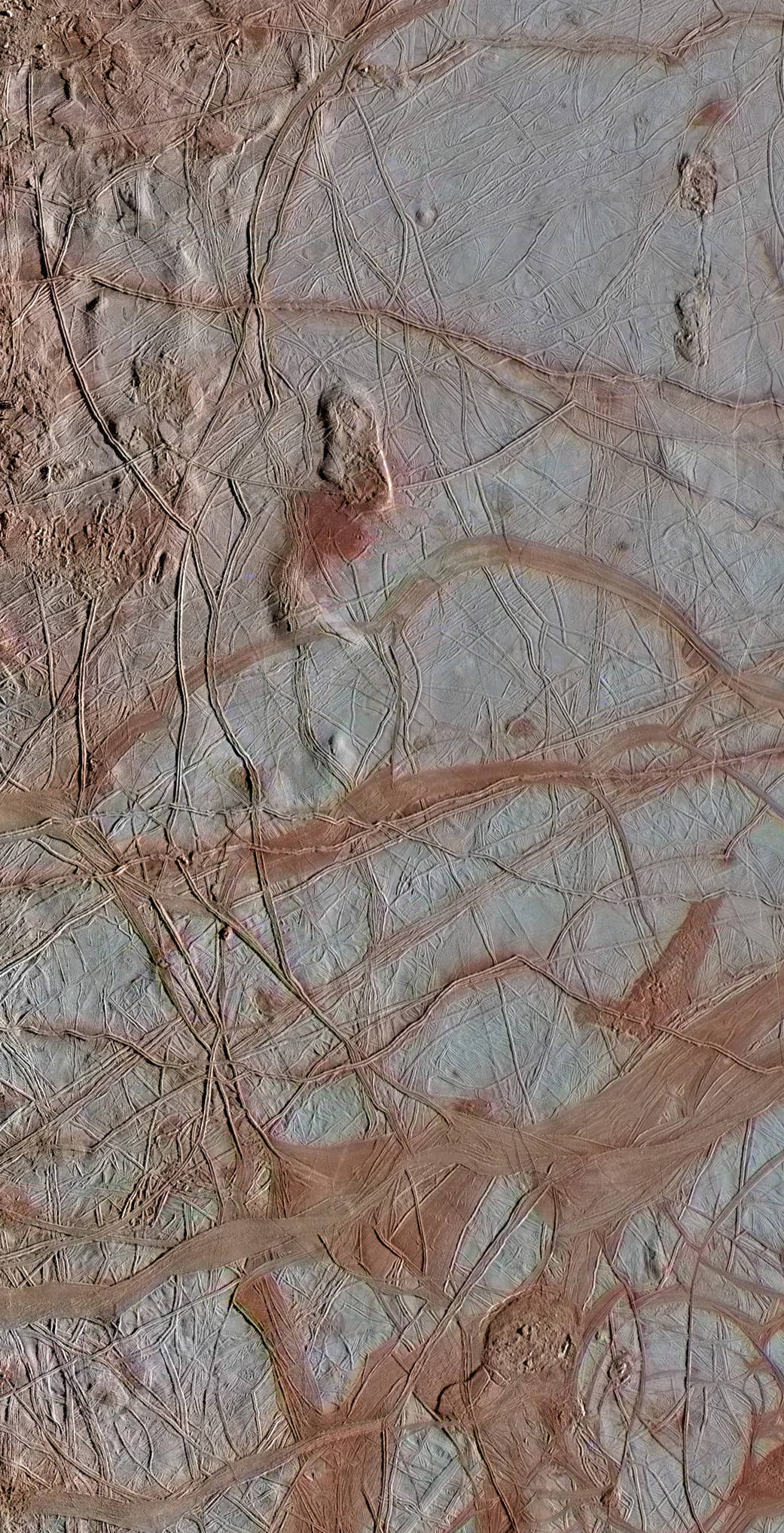
This enhanced-color view from NASA’s Galileo spacecraft shows an intricate pattern of linear fractures on the icy surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa. Newer fractures crosscut older ones, and several wide, dark bands are visible where the surface has spread apart in the past. The scene also contains several regions of “chaos terrain,” where the smooth surface has been disrupted into jumbled blocks of material.
Scientists are interested in studying Europa’s surface materials from orbit and from the surface in order to understand their composition. If the surface ice is geologically active and convecting, as researchers have inferred, it is likely carrying chemical products produced by bombardment from Jupiter’s radiation into the ocean thought to lie below. Those ingredients, called oxidants, may then be available to react with other chemicals, called reductants, coming from the seafloor, making useful chemical energy available for biology.
The high-resolution images for this view were obtained by the Galileo Solid-State Imaging (SSI) experiment on September 25, 1998. They were then combined with lower-resolution color data from an observation taken on March 29, 1998. The high-resolution images have a pixel scale of 735 feet (224 meters) per pixel, and the image is approximately 220 miles (350 kilometers) wide.
The Galileo mission was managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
Additional information about Galileo and its discoveries is available on the Galileo mission home page athttp://solarsystem.nasa.gov/galileo/. More information about Europa is available at http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/europa.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ SETI Institute