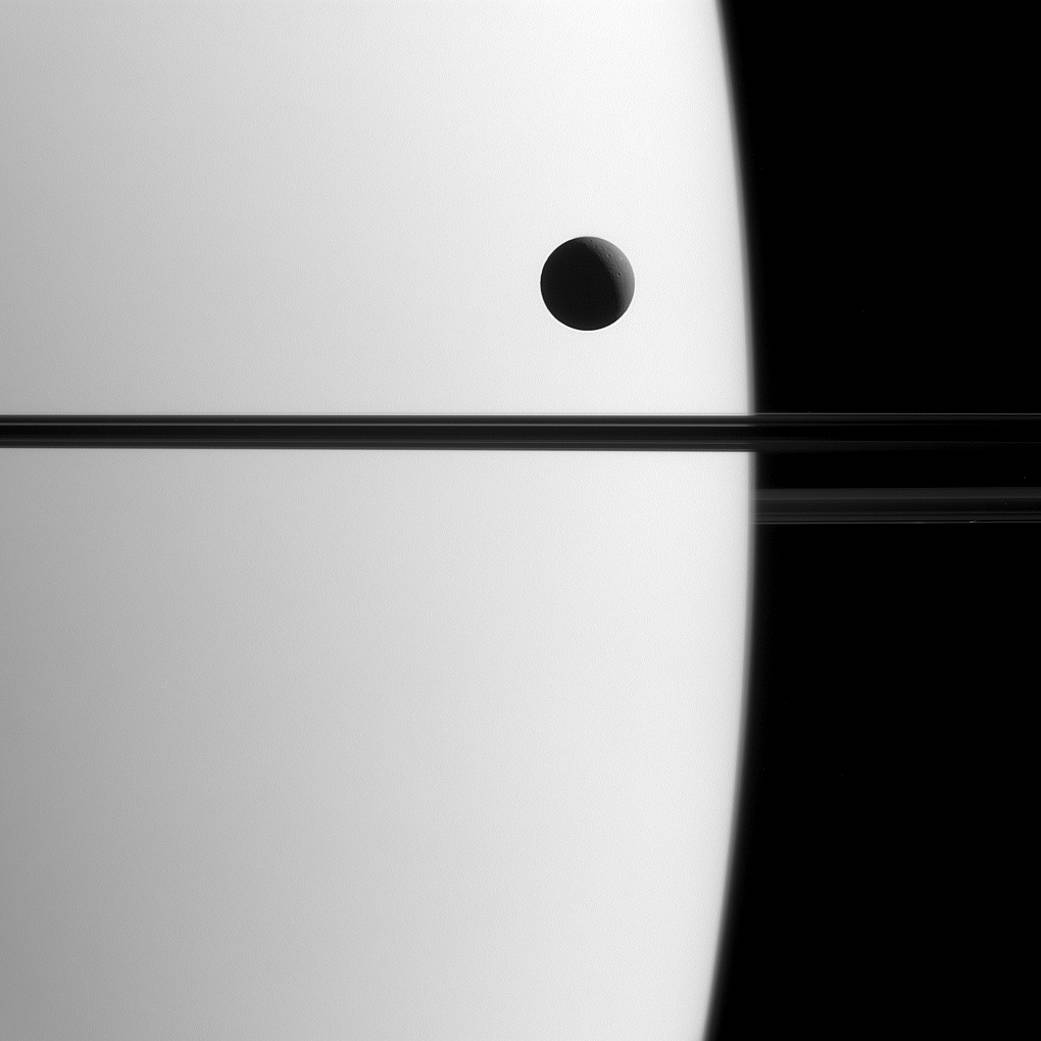
Saturn’s moon Dione crosses the face of the giant planet in this view, a phenomenon astronomers call a transit. Transits play an important role in astronomy and can be used to study the orbits of planets and their atmospheres, both in our solar system and in others.
By carefully timing and observing transits in the Saturn system, like that of Dione (698 miles or 1123 kilometers across), scientists can more precisely determine the orbital parameters of Saturn’s moons.
This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 0.3 degrees below the ring plane. The image was taken in visible green light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 21, 2015.
The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.4 million miles (2.3 million kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 119 degrees. Image scale is 9 miles (14 kilometers) per pixel.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov or https://www.nasa.gov/cassini . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute