Future lunar landers might come equipped with 3D printed rocket engine parts that help bring down overall manufacturing costs and reduce production time. NASA is investing in advanced manufacturing – one of five industries of the future – to make it possible.
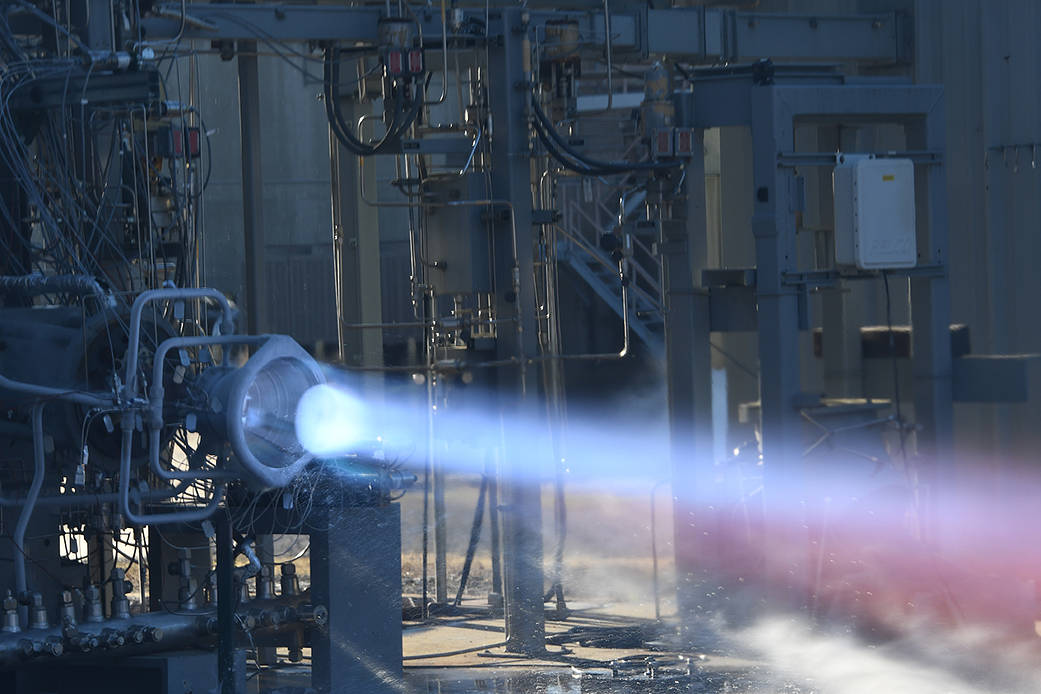
Through a series of hot-fire tests in November, NASA demonstrated that two additively manufactured engine components – a copper alloy combustion chamber and nozzle made of a high-strength hydrogen resistant alloy – could withstand the same extreme combustion environments that traditionally manufactured metal structures experience in flight.
This image shows the hot-fire testing of an additively manufactured copper alloy combustion chamber and a nozzle made of a high-strength hydrogen resistant alloy.
Learn more about the 3D printing process.
Image Credit: NASA