Apprentices at the NACA’s Flight Propulsion Laboratory
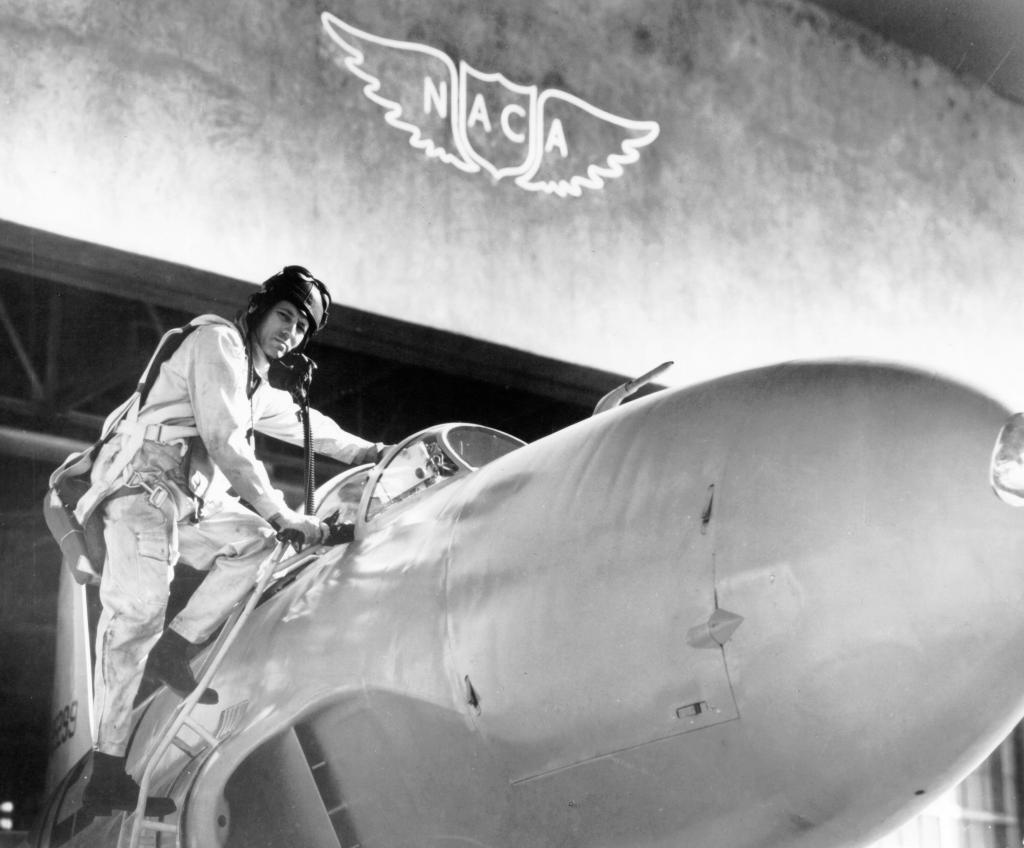
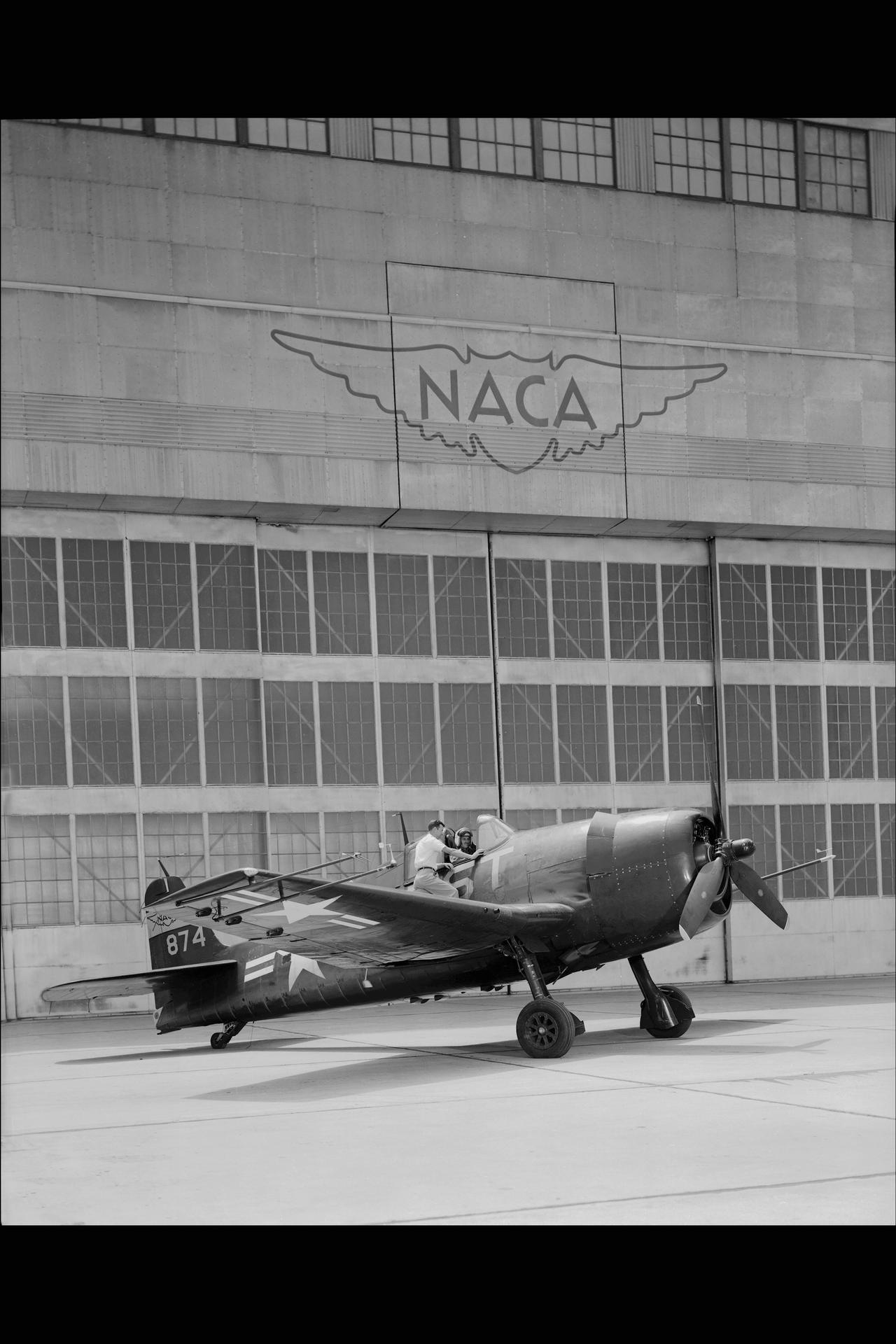
A group of apprentices takes a break from their studies to pose for a photograph at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. To facilitate the close interaction of the lab’s engineers, mechanics, technicians, and scientists, Lewis Director Ray Sharp established a four-year apprentice program to train craftsmen on a particular trade and basic scientific principles. The apprentice school covered a variety of trades, from aircraft mechanic to electronic instrumentation, machinist, and altitude systems mechanic. The school was established in 1942, but faltered when over 90 percent of its students entered the military. After World War II, 40 of the original members returned to the NACA lab. In some cases they were bumped to journeymen positions because of training received in the military. The honorary first class in 1949 had only 15 graduates, but the number steadily increased to 45 with the next class in 1952 and to 110 in 1957. There were over 600 graduates by 1969, and the program remained strong for decades. Many of the laboratory’s future managers began their careers as apprentices. The program, which was certified by both the Department of Labor and the State of Ohio, included classroom lectures, the study of models, and hands-on work. The apprentices rotated through the various shops and facilities to provide them with a well-rounded understanding of the work at the lab. One hundred fifty of the 2,000 hours of annual training were spent in the classroom. A series of examinations was coupled with evaluation by supervisors in the shops. The apprentices were promoted through a series of grades until they reached journeyman status. Those who excelled in the Apprentice Program would be considered for a separate five-year engineering draftsman program.
- X