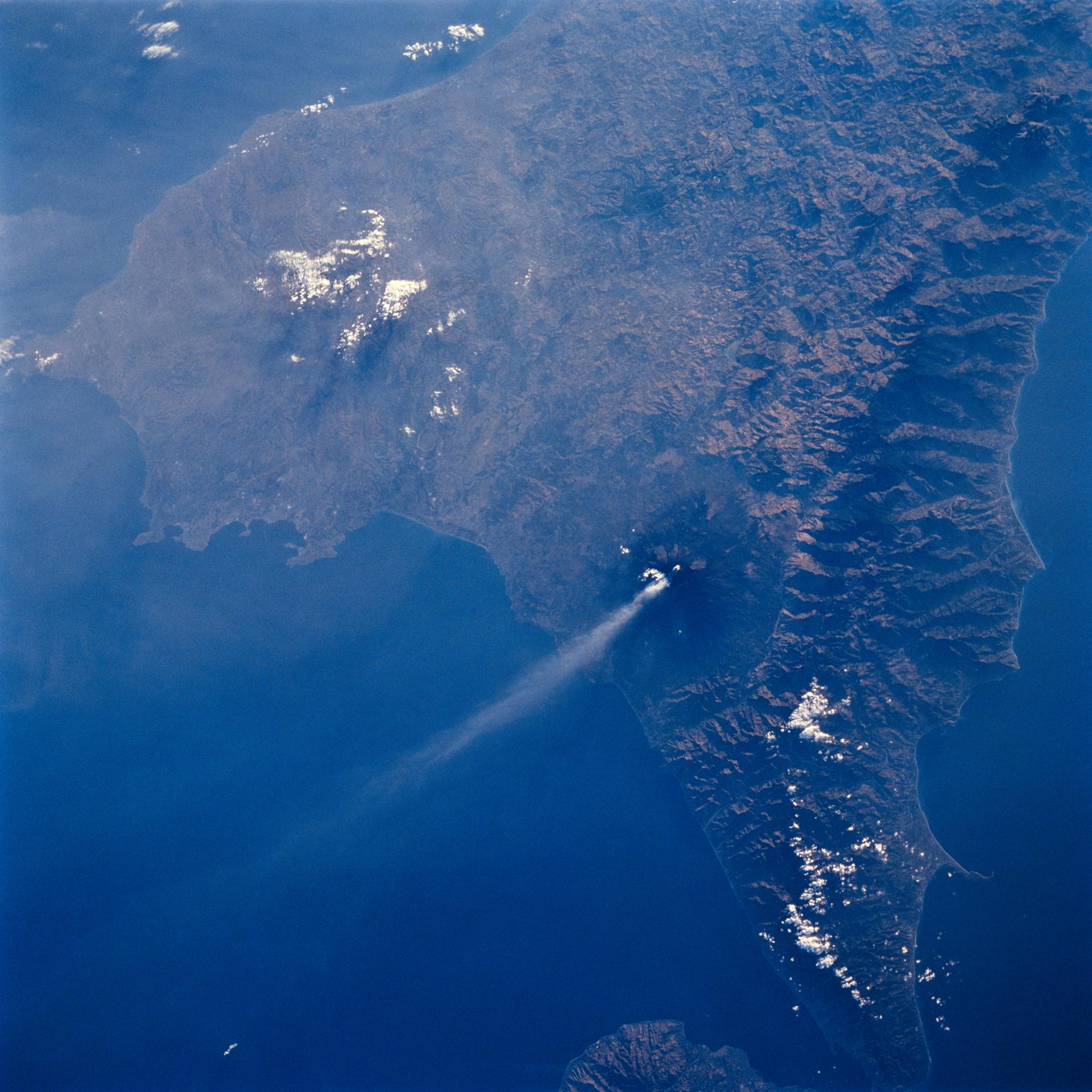
Mt. Etna, Sicily as seen from STS-64
STS064-71-037 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Mt. Etna on Sicily displays a steam plume from its summit. Geologists attribute the volcano's existence to the collision of tectonic plates. Unlike the sudden, explosive eruption at Rabaul, Mt. Etna's activity is ongoing and is generally not explosive - Etna's slopes have been settled with villages and cultivated land for centuries. Other Mediterranean volcanoes (like Santorini) have experienced large catastrophic eruptions. Etna recently finished a two-year eruption (ending in 1993), marked by relatively gentle lava flows down the eastern flank. It has been continually degassing since then, according to the geologists, producing an omnipresent steam plume, as seen here. The 1993 flow is difficult to identify in this image because it lies within shadows on the eastern flank, but small cinder cones on the western flank mark earlier episodes of volcanic activity. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- X