Sonic Inlet for the Quiet Engine Program
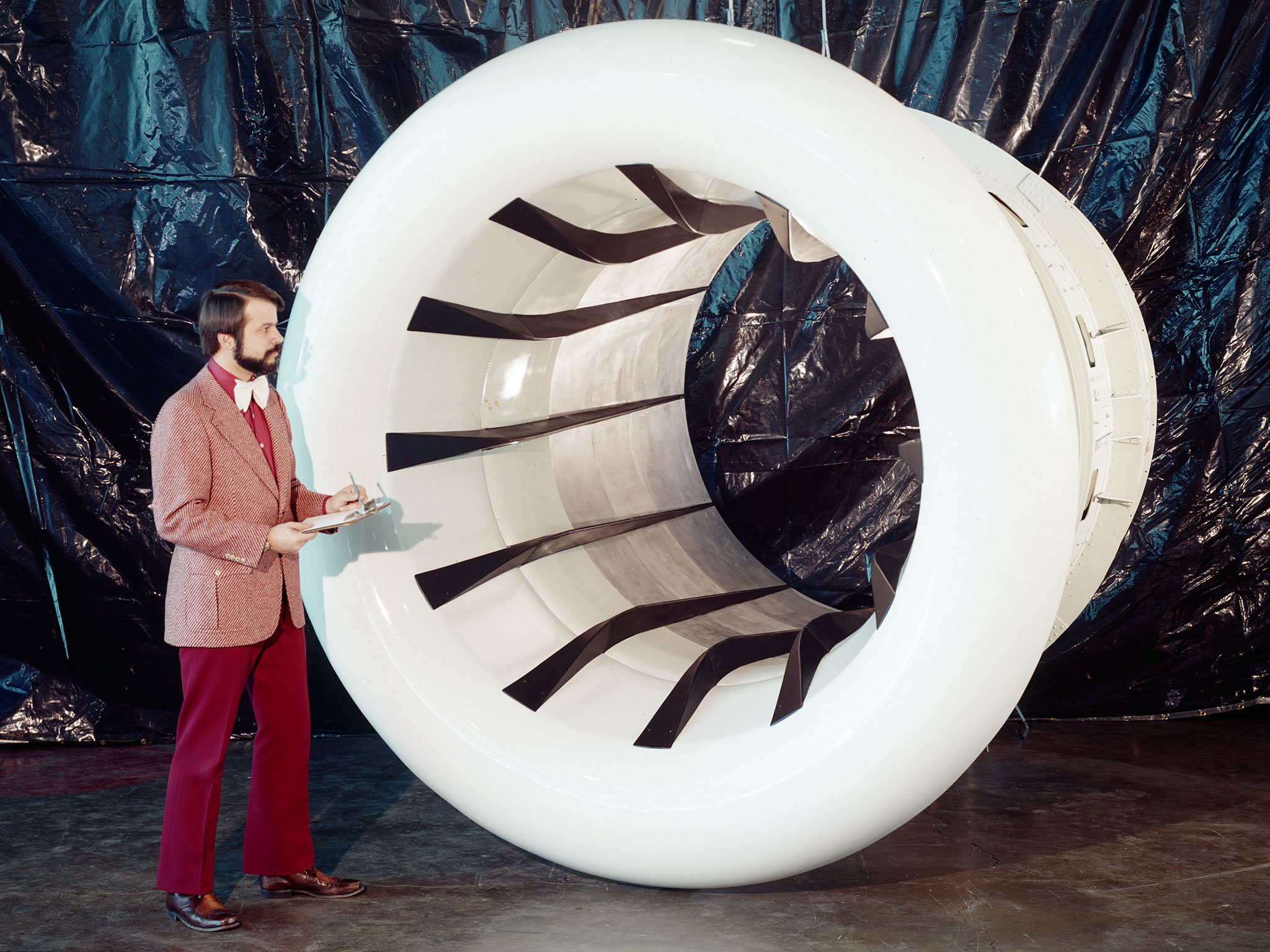
Brent Miller, of the V/STOL and Noise Division at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center, poses with a sonic inlet for the NASA Quiet Engine Program. NASA Lewis had first investigated methods for reducing aircraft engine noise in the mid-1950s. Those efforts were resurrected and expanded in the late 1960s. The researchers found that the use of a sonic, or high-throat-Mach-number, inlet was effective at reducing the noise from the engine inlet. The device accelerated the inlet air to near-sonic speeds which kept the forward moving sound waves away from the inlet. The device also deflected the sound waves into the wall to further reduce the noise. NASA Lewis researchers tested models of the sonic inlet in their 9- by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel. They found that the general level of aerodynamic performance was good. The tests during simulated takeoff and landing conditions demonstrated the sonic inlet’s ability to provide good aerodynamic and acoustic performance The researchers then successfully tested two full-scale sonic inlet designs, one from Pratt and Whitney and one from General Electric, with fans. A full-scale engine was installed on a thrust stand to determine the sonic inlet’s effect on the engine’s performance. The amount of noise reduction increased as the inlet flow velocity increased, but the full-scale tests did not produce as great a decrease in noise as the earlier small-scale tests.
- X