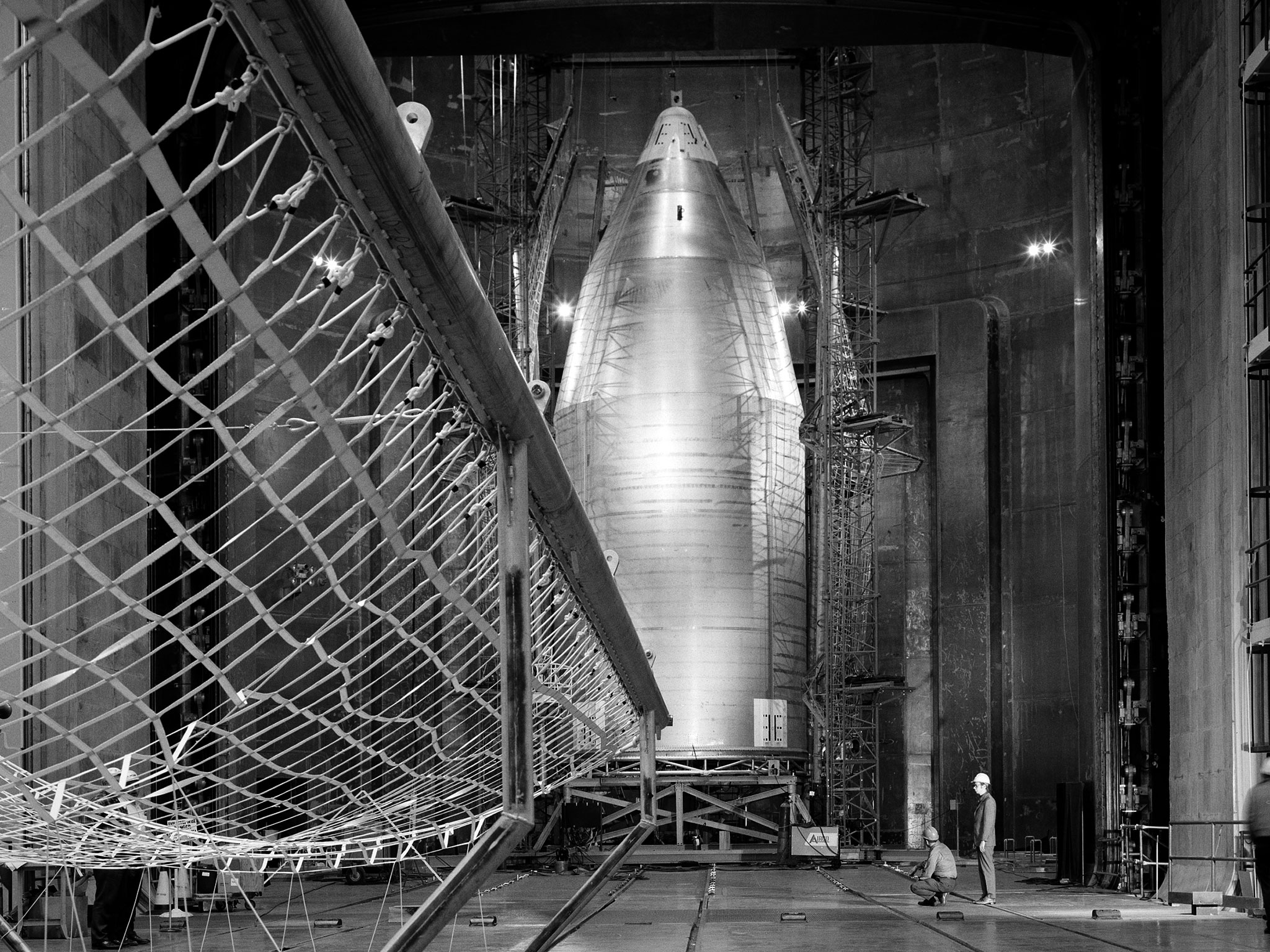
Skylab Shroud in the Space Power Facility
The 56-foot tall, 24,400-pound Skylab shroud installed in the Space Power Facility’s vacuum chamber at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The Space Power Facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It can produce a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear-power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. Payload shrouds are aerodynamic fairings to protect the payload during launch and ascent to orbit. The Skylab mission utilized the largest shroud ever attempted. Unlike previous launches, the shroud would not be jettisoned until the spacecraft reached orbit. NASA engineers designed these tests to verify the dynamics of the jettison motion in a simulated space environment. Fifty-four runs and three full-scale jettison tests were conducted from mid-September 1970 to June 1971. The shroud behaved as its designers intended, the detonators all fired, and early design issues were remedied by the final test. The Space Power Facility continues to operate today. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
- X