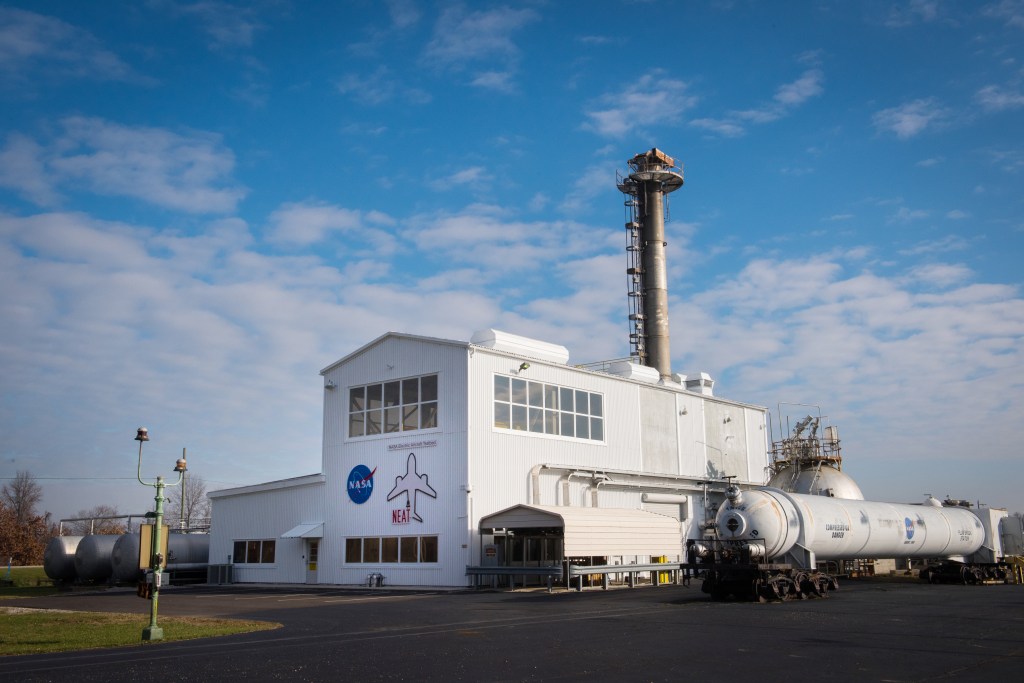
New Exhauster Equipment at the Propulsion Systems Laboratory
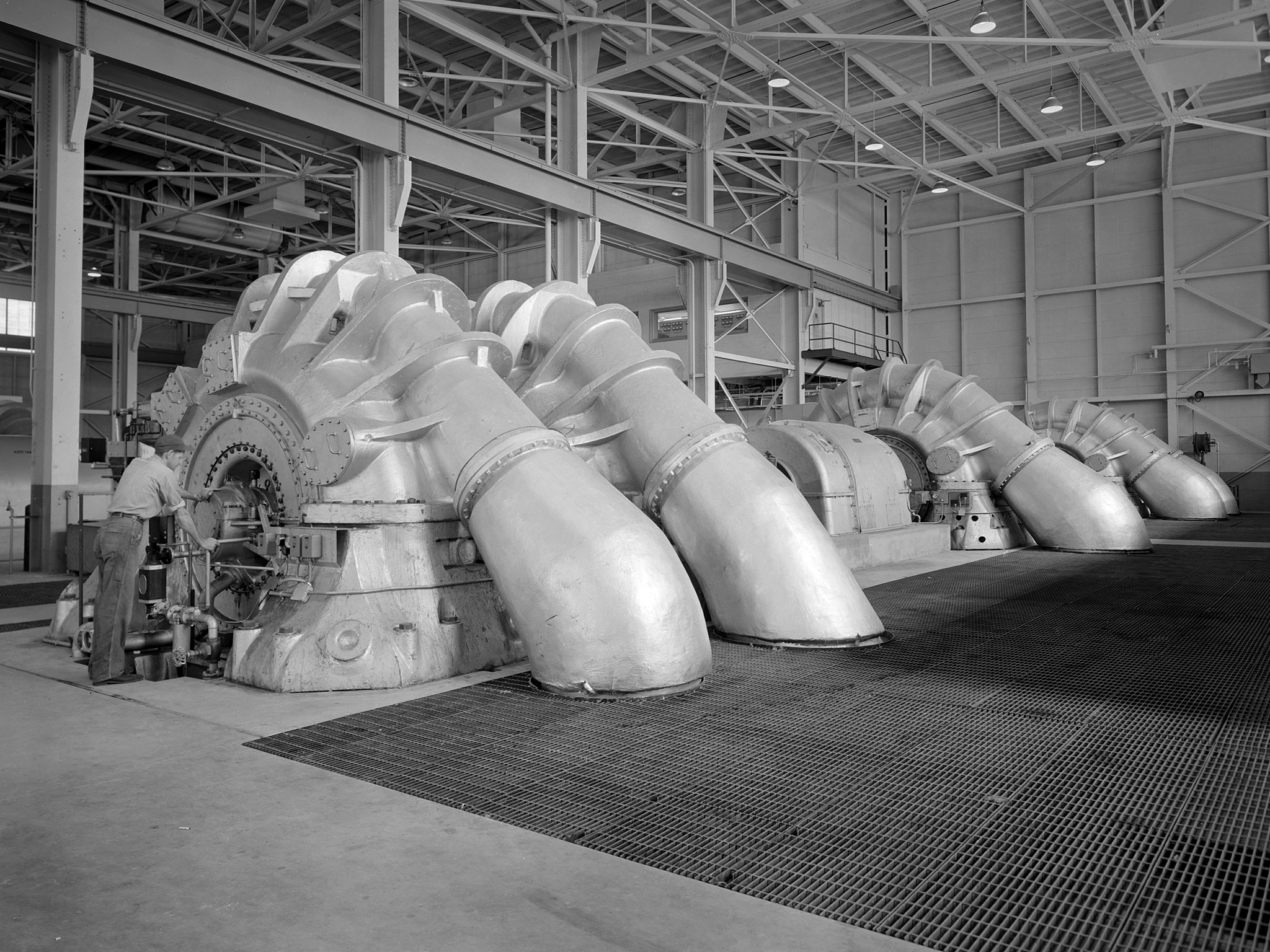
The Propulsion Systems Laboratory’s exhaust system was expanded in 1955 at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The facility contained two altitude chambers that were first used to study the increasingly-powerful jet engines of the early 1950s and the ramjets for missile programs such as Navaho and Bomarc. Later, the facility tested large rocket engines and a variety of turbofan engines. The exhaust system served two roles: reducing the density of the air in the test chambers to simulate high altitudes and removing the hot gases exhausted by the engines being tested. These tasks were accomplished by large Roots-Connersville exhauster equipment in the Equipment Building. The original configuration could exhaust the 3500° F gases at a rate of 100 pounds per second when the simulated altitude was 50,000 feet. In 1955, three years after operation started, a fourth line of exhausters was added. There were three centrifugal exhausters capable of supplying 166 pounds of air per second at the test chamber altitude of 50,000 feet or 384 pounds per second at 32,000 feet. These exhausters had two first-stage castings driven by a 10,000-horsepower motor; one second; one third; and one fourth-stage casting driven by a 16,500-horsepower motor. The total inlet volume of the exhausters is 1,650,000 cubic feet of gas per minute. The exhausters were continually improved and upgraded over the years.
- X