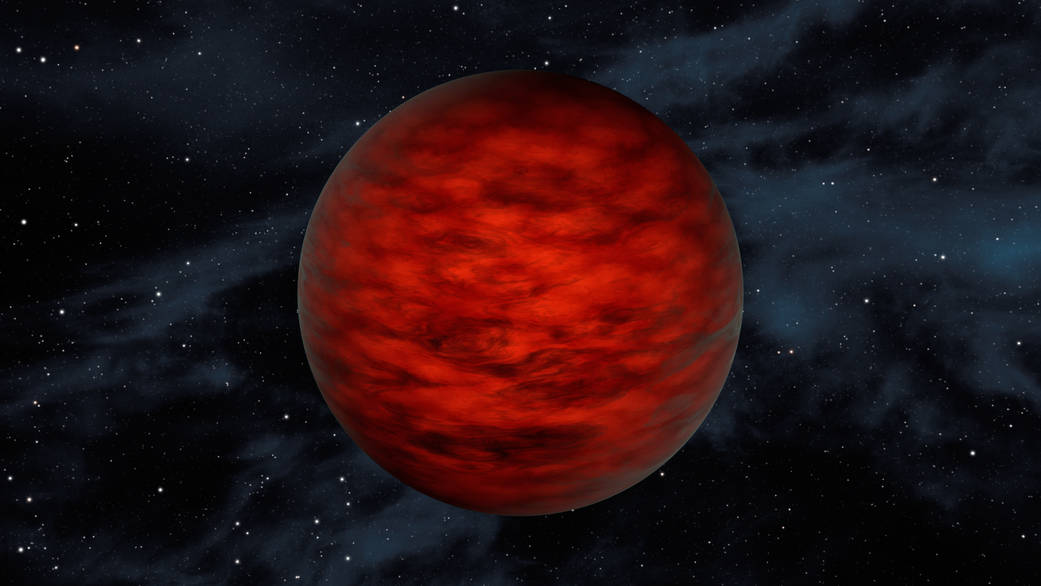
A young, free-floating world sits alone in space in this illustration. The object, called WISEA J114724.10−204021.3, is thought to be an exceptionally low-mass “brown dwarf,” which is a star that lacked enough mass to burn nuclear fuel and glow like a star. Astronomers using data from NASA’s WISE and 2MASS sky surveys found the object in TW Hydrae – a young, 10-million-year-old association of stars.
Specifically, scientists think the youthful brown dwarf belongs to a class called “L dwarfs” and has a temperature of about 2,250 degrees Fahrenheit. The object would appear reddish in hue. It has a mass between about 5 and 10 times that of Jupiter.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, managed and operated WISE for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The spacecraft was put into hibernation mode in 2011, after it scanned the entire sky twice, completing its main objectives. In September 2013, WISE was reactivated, renamed NEOWISE and assigned a new mission to assist NASA’s efforts to identify potentially hazardous near-Earth objects. The 2MASS mission was a joint effort between the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena; the University of Massachusetts, Amherst; and JPL. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. WISE, NEOWISE and 2MASS data are archived at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center, or IPAC, at Caltech.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech