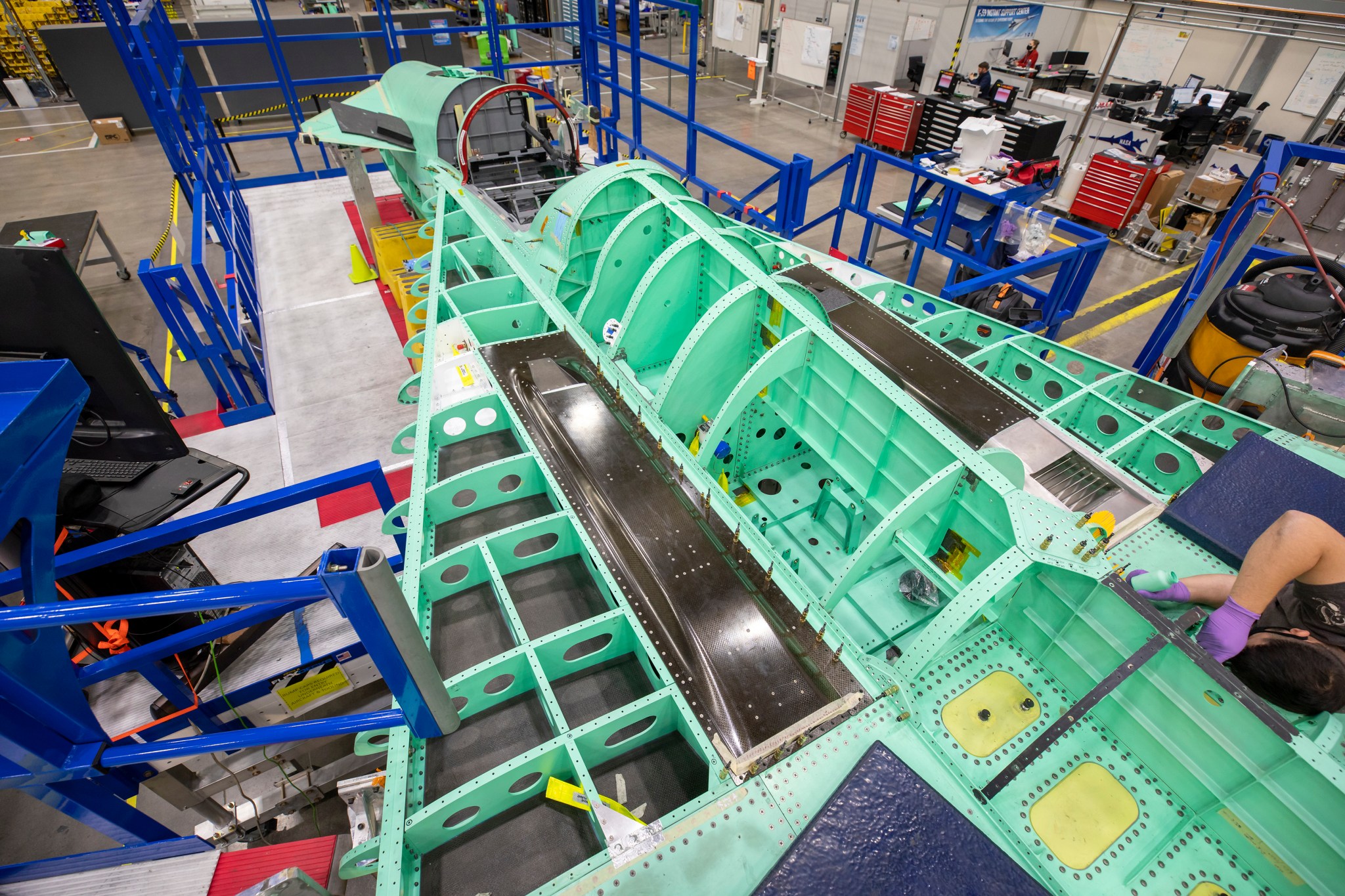
NASA is targeting 2022 for the first flight of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) research aircraft. Its mission – fly over communities to collect data that could cut passenger travel time in half without disturbing people on the ground.
NASA’s X-59 is equipped with supersonic technologies that aid in lowering the sound of the sonic boom. In this picture, the black rectangle panels are the air intakes for the environmental control system (ECS) that regulates the temperature, cabin pressure, and air distribution. The silver grate located at the rear of one of the ECS panels is the exhaust — both of these sections are traditionally housed on the underside of the plane. By placing these features on top of the X-59 wing, the wing blocks and prevents the ECS exhaust from interacting with the shock waves on the bottom of the aircraft. This unique design approach to re-shaping the shock wave pattern substantially reduces the sonic boom to more of a sonic “thump” when it reaches the ground.