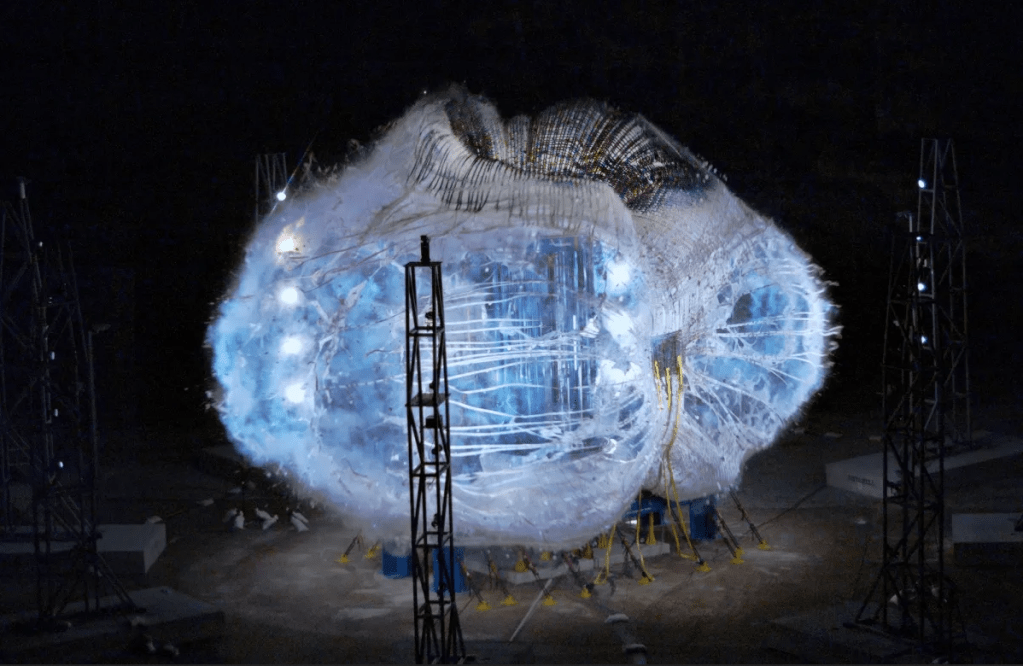
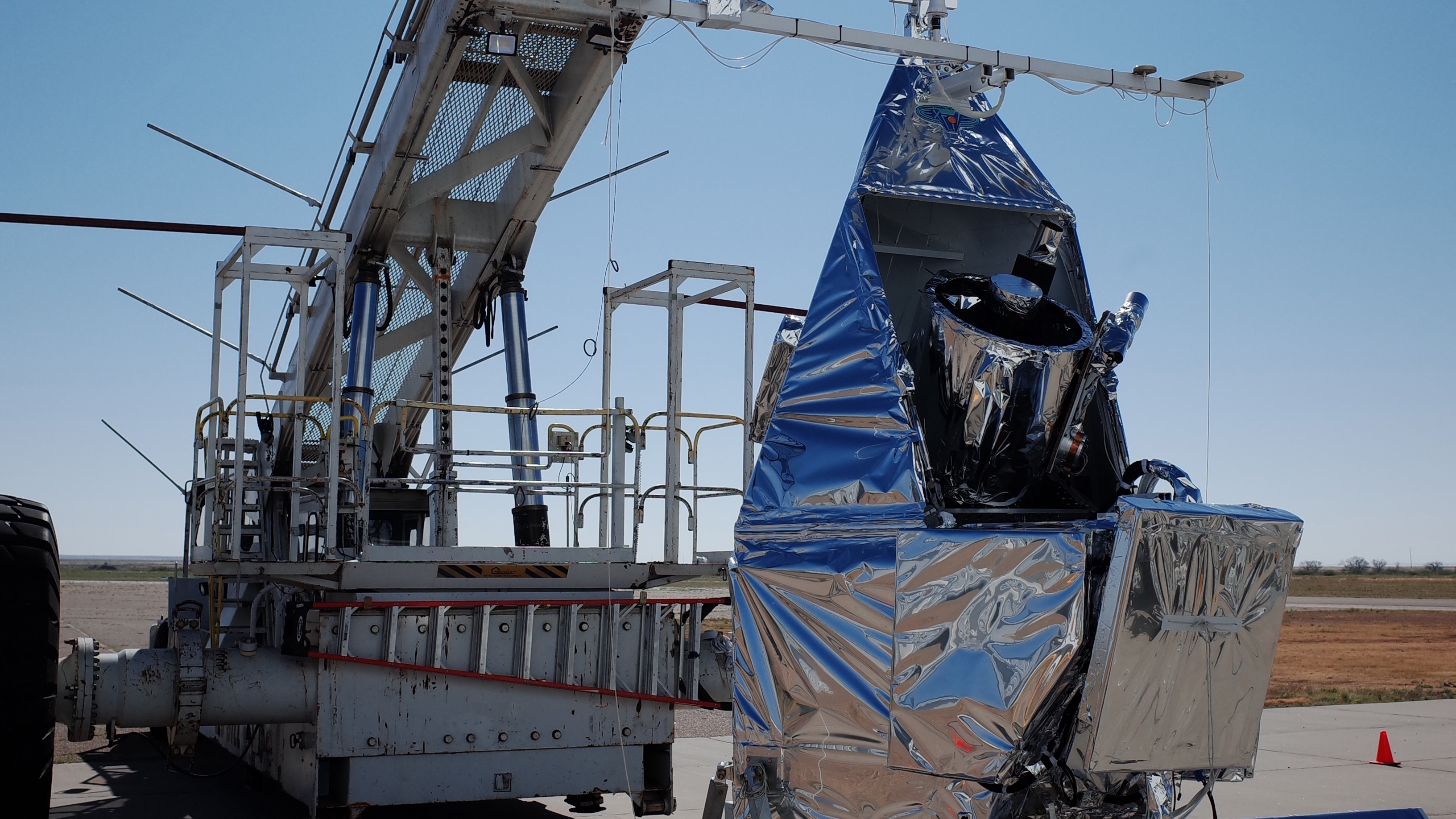
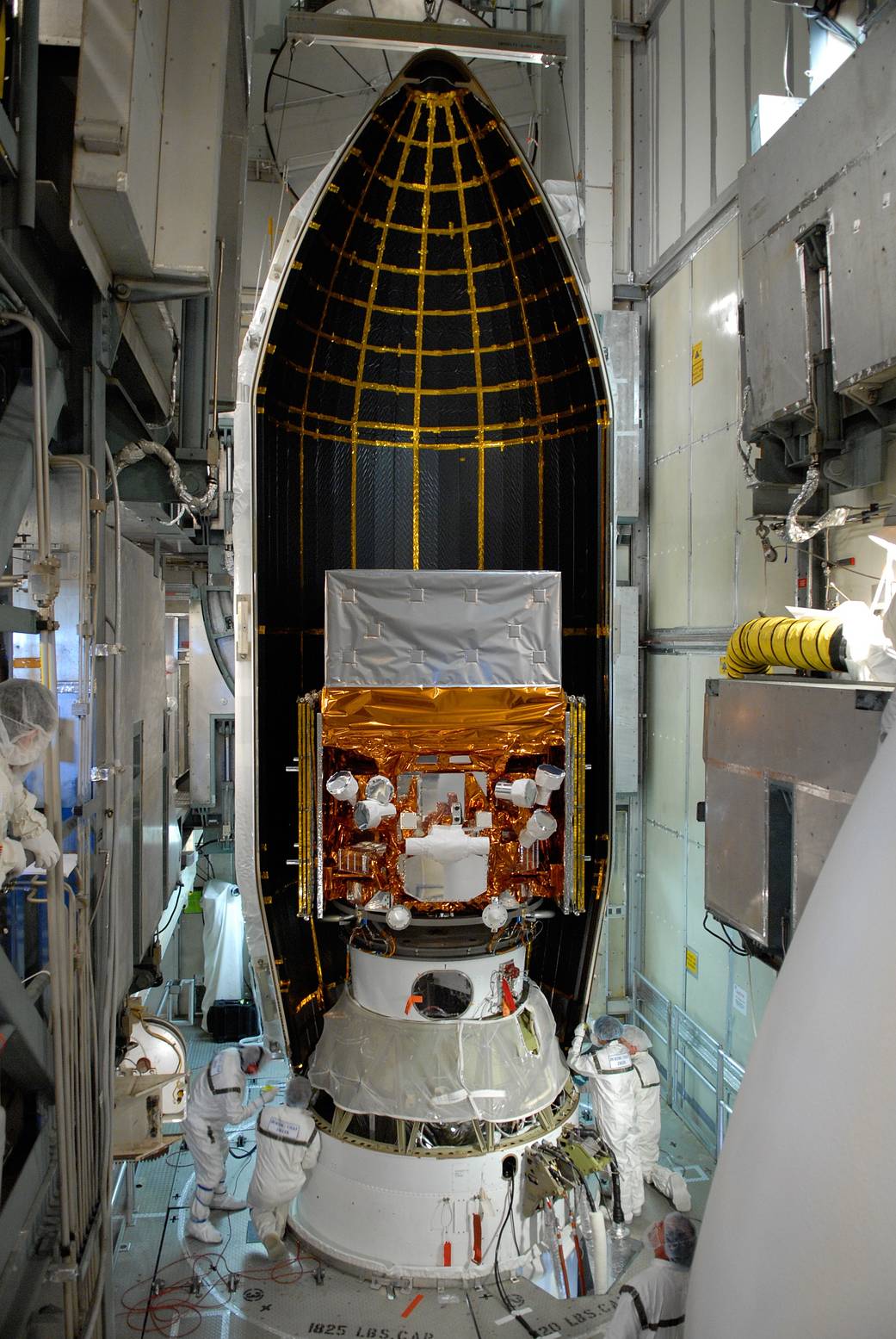
This week in 2008, the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, formerly known as the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST, was launched aboard a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Fermi has two instruments, the Large Area Telescope and the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor. The Gamma-ray Burst Monitor, a collaboration between the National Space Science and Technology Center and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany, complements the Large Area Telescope with its observations of transient sources and is sensitive to X-rays and gamma rays with energies between 8,000 and 40 million electron volts. Here, the first half of the payload fairing is prepared to move around the telescope. The Gamma-ray Burst Monitor is managed at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. The NASA History Program is responsible for generating, disseminating, and preserving NASA’s remarkable history and providing a comprehensive understanding of the institutional, cultural, social, political, economic, technological and scientific aspects of NASA’s activities in aeronautics and space. For more pictures like this one and to connect to NASA’s history, visit the Marshall History Program’s webpage. (NASA)
1 min read