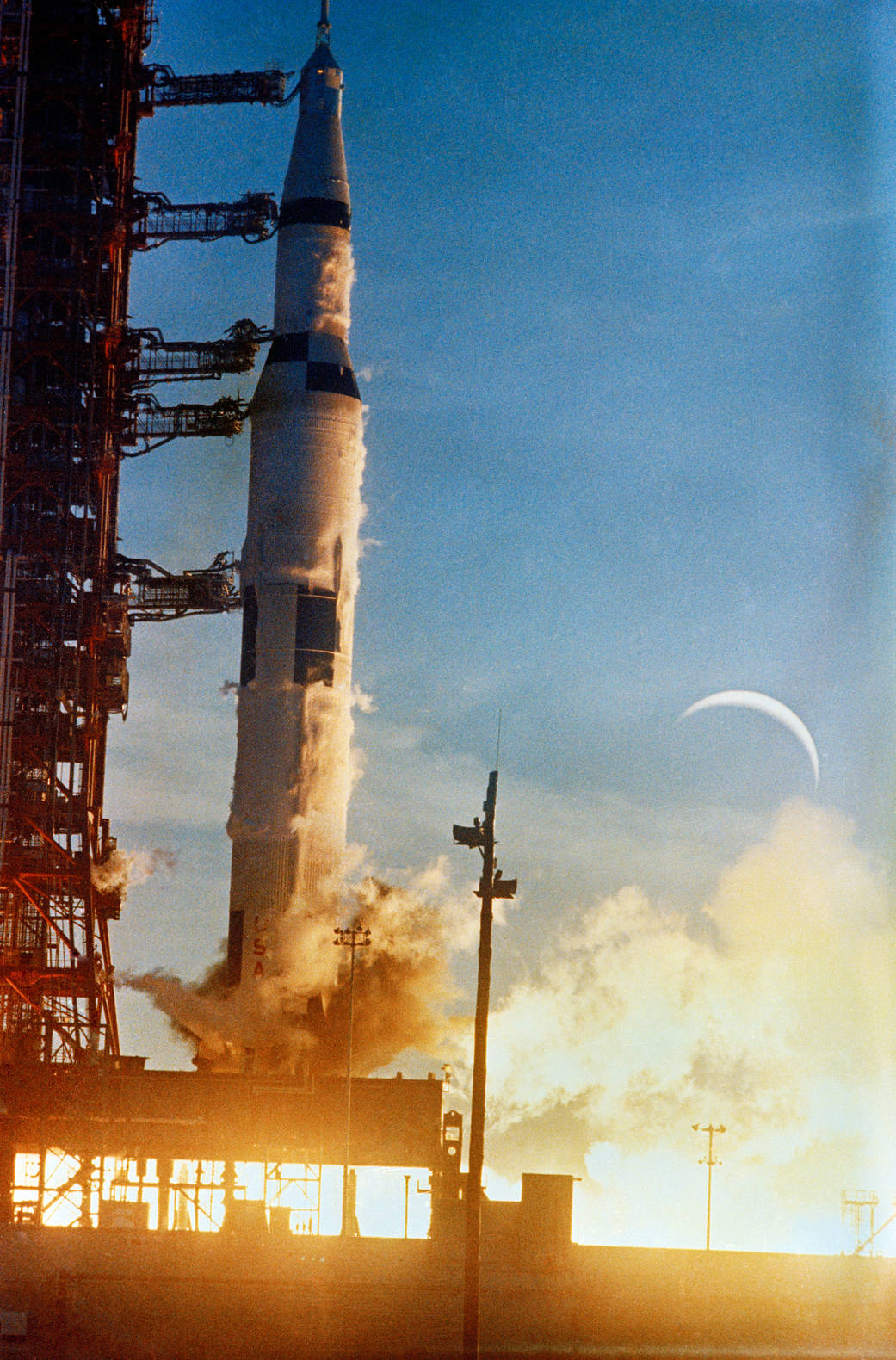
This week in 1968, Apollo 8 lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The primary mission objectives included a coordinated performance of the crew, the command and service module and the support facilities. The mission also demonstrated trans-lunar injection — a propulsive maneuver used to set a spacecraft on a trajectory that will cause it to arrive at the Moon. All primary mission objectives were met and detailed test objectives were achieved. The crew escaped Earth’s gravity, traveled to the lunar vicinity, and orbited the Moon before returning to Earth on Dec. 27. Apollo 8 was the first crewed flight of the Saturn V vehicle and the first crewed lunar orbit mission. Now through December 2022, NASA will mark the 50th anniversary of the Apollo Program that landed a dozen astronauts on the Moon between July 1969 and December 1972, and the first U.S. crewed mission — Apollo 8 — that circumnavigated the Moon in December 1968. The NASA History Program is responsible for generating, disseminating, and preserving NASA’s remarkable history and providing a comprehensive understanding of the institutional, cultural, social, political, economic, technological and scientific aspects of NASA’s activities in aeronautics and space. For more pictures like this one and to connect to NASA’s history, visit the Marshall History Program’s webpage. (NASA)
2 min read