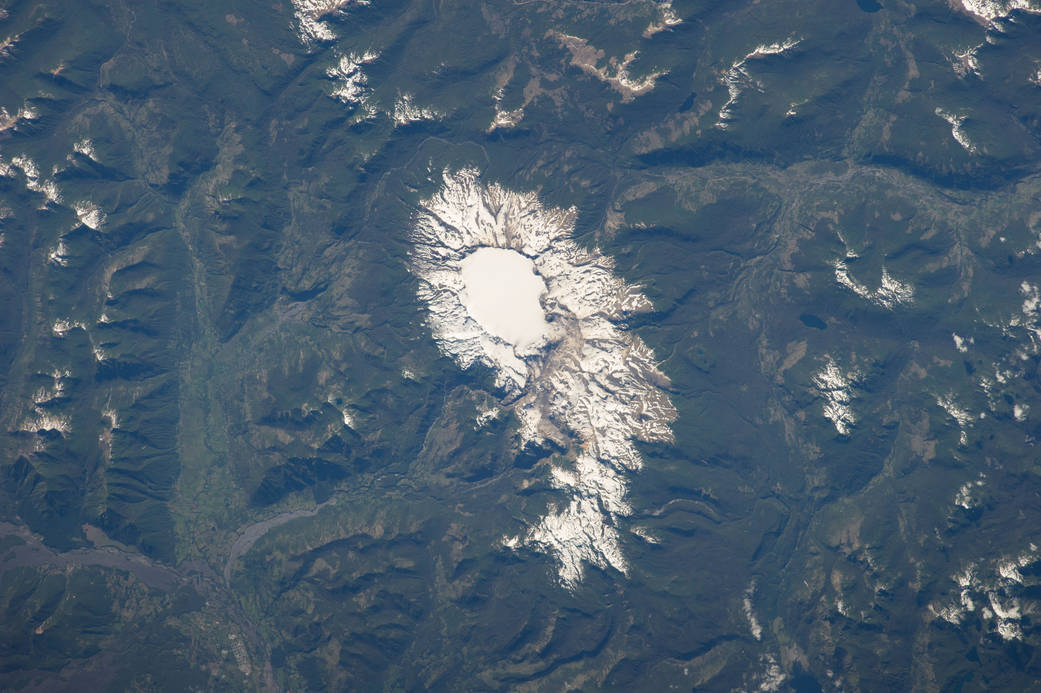
ISS038-E-012569 (6 Dec. 2013) — Sollipulli Caldera is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 38 crew member on the International Space Station. While active volcanoes are obvious targets of interest from the standpoint of natural hazards, there are some dormant volcanoes that nevertheless warrant concern due to their geologic history of activity. One such volcano is Sollipulli, located in central Chile near the border with Argentina in the southern Andes Mountains of South America. The volcano is located within the Parque Nacional Villarica of Chile. This photograph highlights the summit (2,282 meters above sea level) of the volcano and the bare slopes above the tree line. Lower elevations are covered with the green forests indicative of Southern Hemisphere summer. The summit of the volcano is occupied by a four-kilometer-wide caldera, currently filled with a snow-covered glacier (center). While most calderas form following violent explosive eruptions, the types of volcanic rock and deposits associated with such an event have not been found at Sollipulli. The geologic evidence does indicate explosive activity 2,900 years before present, and production of lava flows approximately 700 years before present. Together with craters and scoria cones located along the outer flanks of the caldera, scientists say this history suggests that Sollipulli could experience violent eruptions again, presenting an immediate potential hazard to such towns as Melipeuco in addition to the greater region.
2 min read