E-860
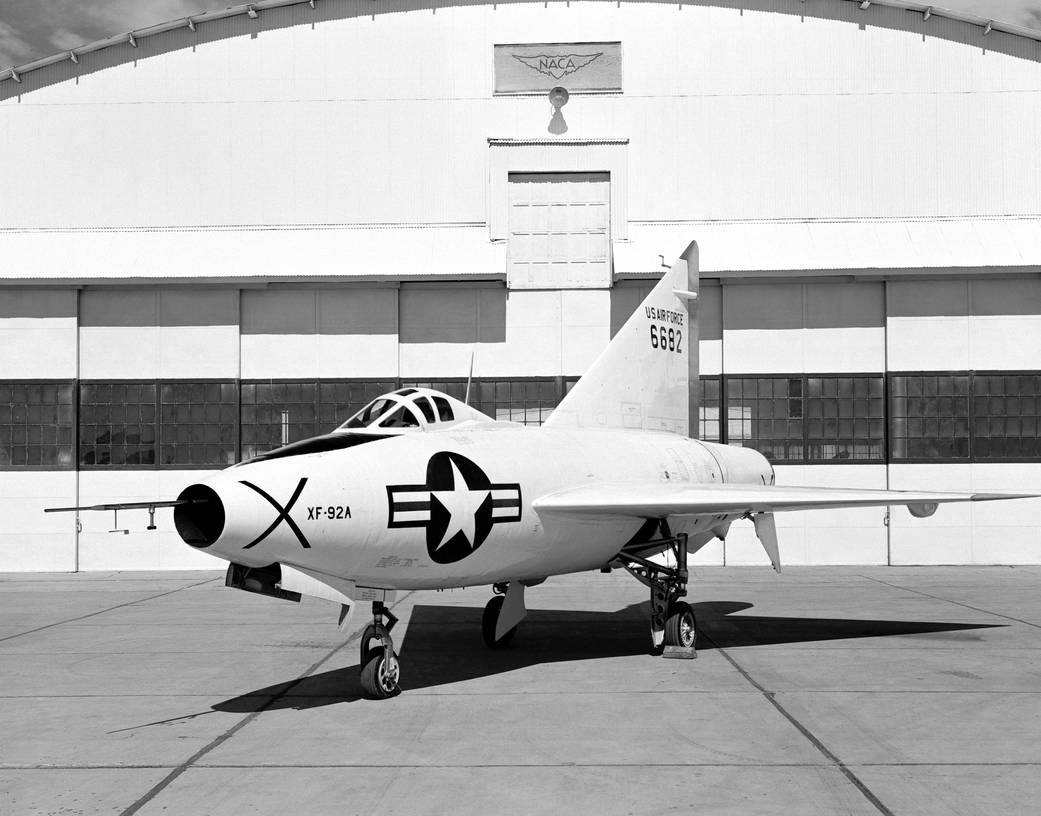
This NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station photograph of the XF-92A was taken at the South Base of Edwards Air Force Base. The photograph shows the pitot-static probe, used to measure airspeed, Mach number, and altitude mounted on a noseboom protruding from the aircraft’s nose engine inlet. Also attached to the pitot-static-probe portion of the noseboom are flow direction vanes for sensing the aircraft’s angles of attack and sideslip. The Convair XF-92A aircraft was powered by an Allison J33-A turbojet engine with an afterburner, and was unique in having America’s first delta wing. The delta wing’s large area, thin airfoil cross section, low weight, and structural strength made this design a promising combination for a supersonic airplane.January 1953NACA/NASA› XF-92A Project Description
1 min read