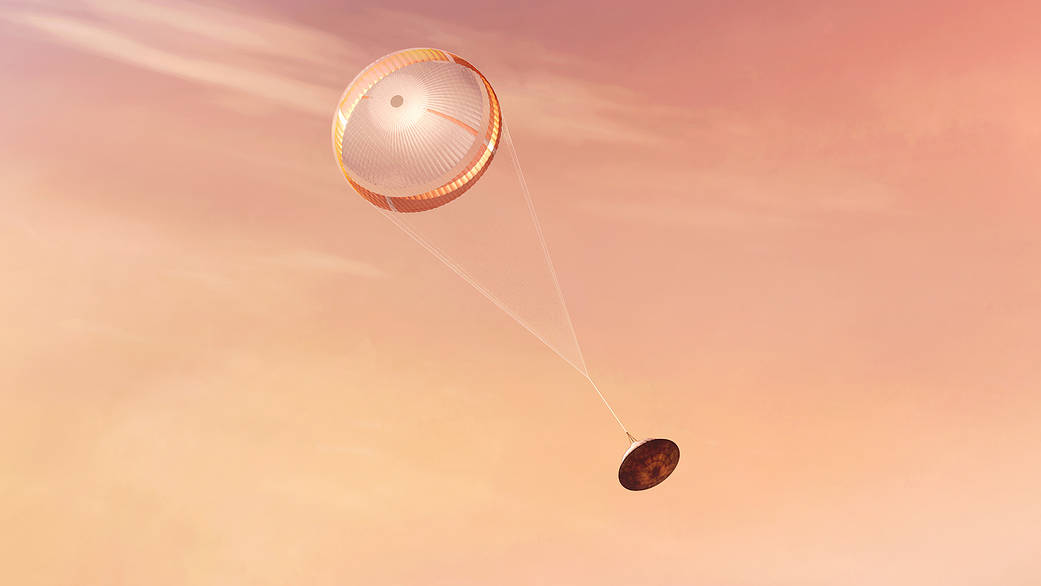
NASA’s Perseverance rover deploys a supersonic parachute from its aeroshell as it slows down before landing, in this artist’s illustration. Hundreds of critical events must execute perfectly and exactly on time for the rover to land safely on Feb. 18, 2021.
Entry, Descent, and Landing, or “EDL,” begins when the spacecraft reaches the top of the Martian atmosphere, travelling nearly 12,500 mph (20,000 kph). EDL ends about seven minutes after atmospheric entry, with Perseverance stationary on the Martian surface.
The parachute, 70.5 feet (21.5 meters) in diameter, deploys about 240 seconds after entry into the Martian atmosphere, at an altitude of about 7 miles (11 kilometers) and a velocity of about 940 mph (1,512 kph). The parachute slows the vehicle to about 200 mph (320 kph).
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California built and will manage operations of the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover for NASA.
For more information about the mission, go to: https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech