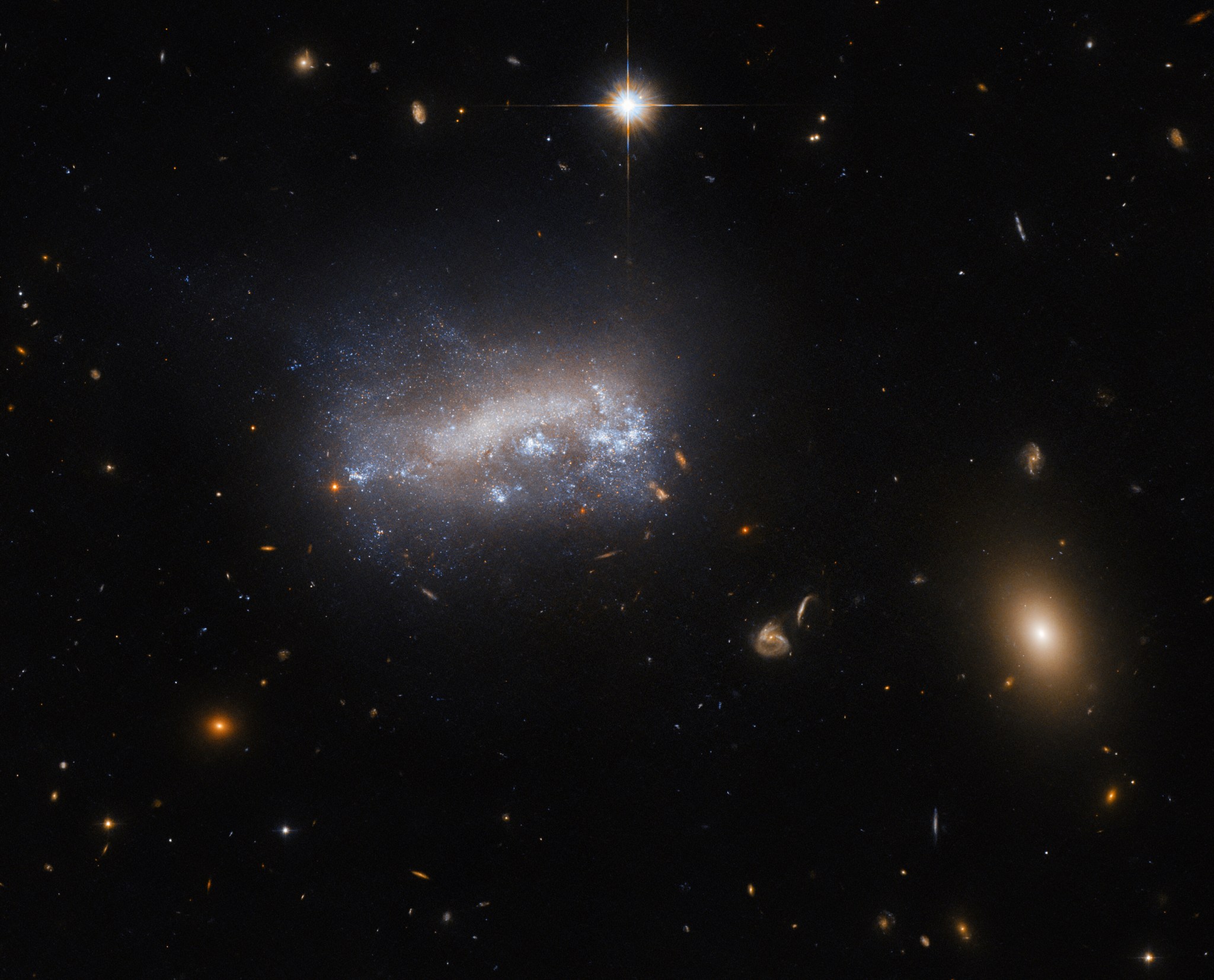
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows LEDA 42160, a galaxy about 52 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. The dwarf galaxy is one of many forcing its way through the comparatively dense gas in the massive Virgo cluster of galaxies. The pressure exerted by this intergalactic gas, known as ram pressure, has dramatic effects on star formation in LEDA 42160.
The gas and dust that permeates space exerts pressure on a galaxy as it moves. This resistance, called ram pressure, can strip a galaxy of its star-forming gas and dust, reducing or even stopping the creation of new stars. However, ram pressure can also compress gas in the galaxy, which can boost star formation.
The Hubble data used to create this image of LEDA 42160 is part of a project that studied dwarf galaxies undergoing ram pressure stripping that are part of large galaxy clusters, like the Virgo cluster. Studies show that ram pressure stripping can initially cause new stars to form in larger galaxies. The researchers wanted to see if the same holds true for smaller galaxies, like LEDA 42160. The bright patches on LEDA 42160’s lower-right flank may be star-forming regions spurred on by ram pressure stripping. Hubble’s observations of LEDA 42160 will help astronomers determine the processes that created the features we see in this small galaxy.
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov