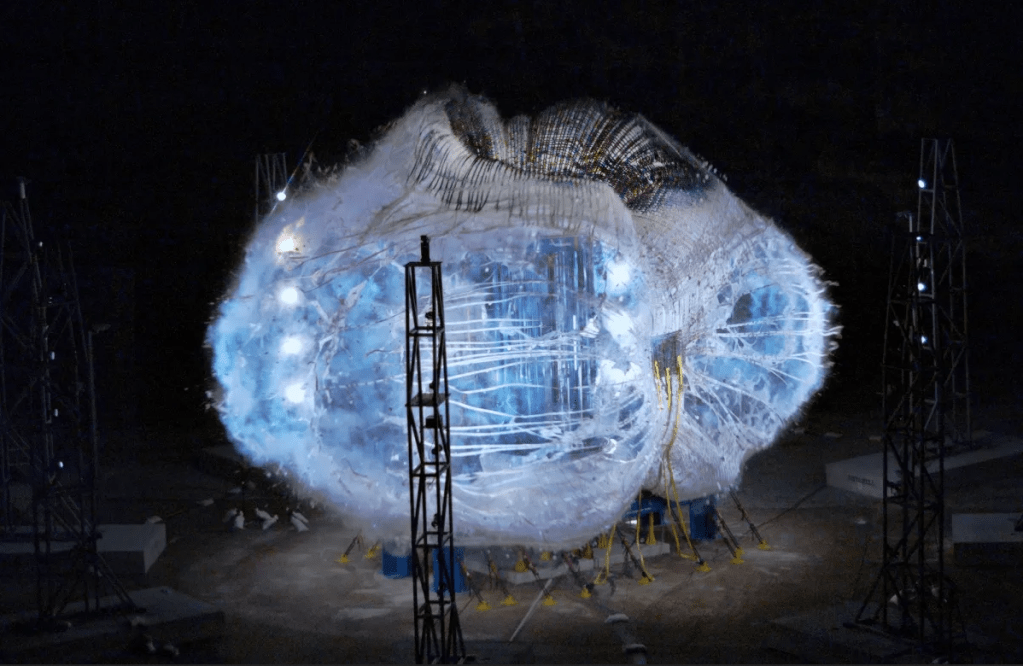
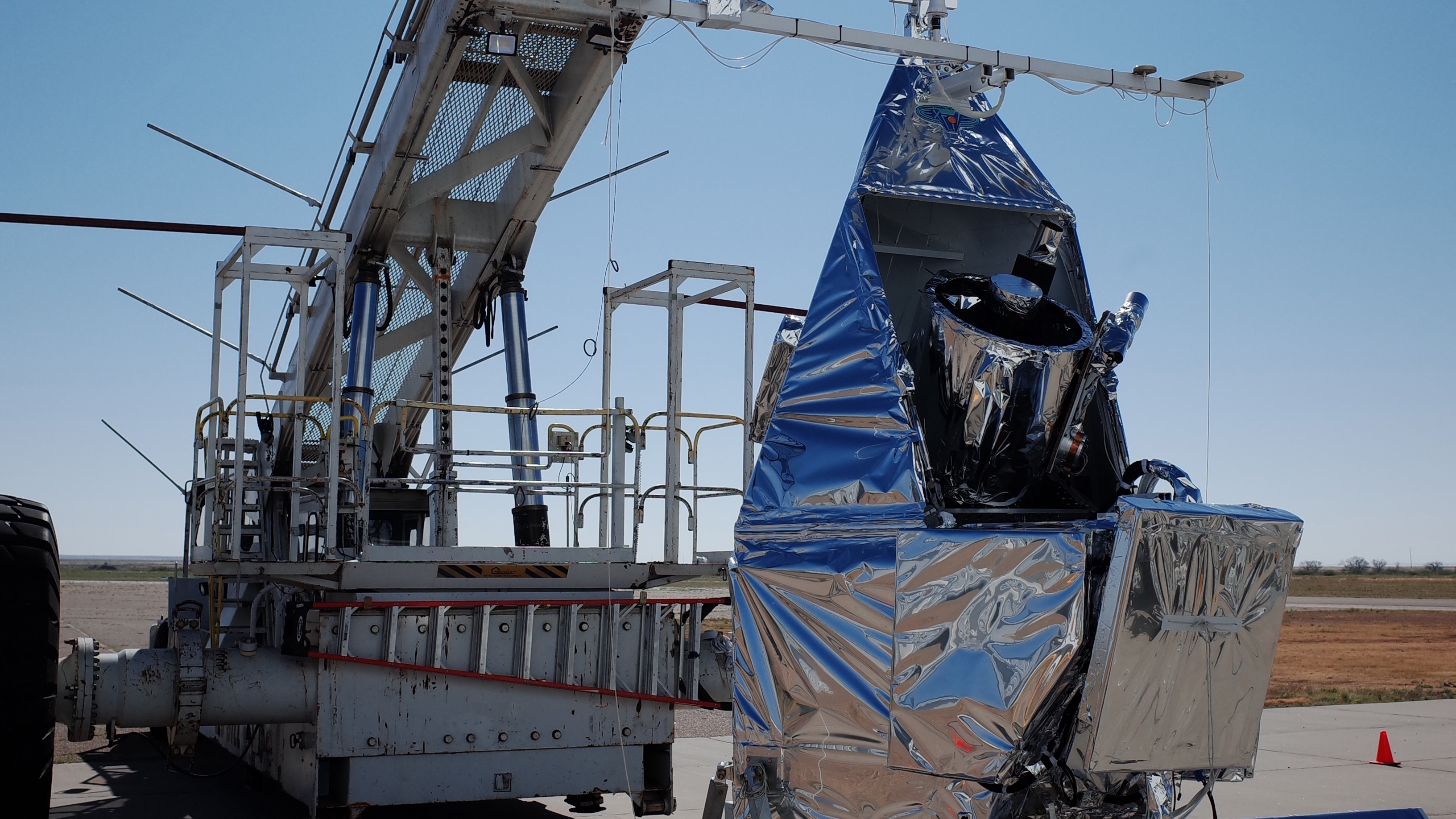
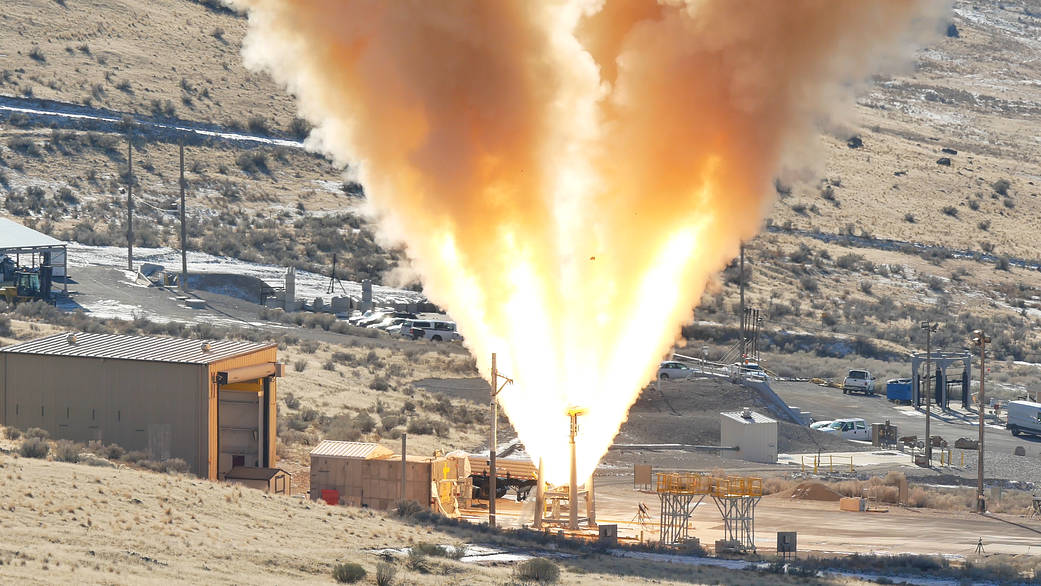
NASA, Northrop Grumman, and Lockheed Martin successfully performed a ground firing static test of the abort motor for NASA’s Orion spacecraft Launch Abort System (LAS) at Northrop’s facility in Promontory, Utah, Dec. 13.
The abort motor is a part of the LAS, which is designed to protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch and ascent by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket and positioning it for a safe landing. The LAS is comprised of three solid propellant rocket motors: the abort motor, an attitude control motor, and a jettison motor.
Data from the abort motor test will confirm the motor can activate within milliseconds and perform as designed under cold temperatures. The success of this milestone brings Orion one step closer to its first flight atop NASA’s Space Launch System enabling humans to explore the Moon and deep-space destinations.
The jettison motor was successfully tested in November by engineers in Huntsville, Alabama. The abort and jettison motors, along with the attitude control motor, will undergo a flight test of the LAS, known as Ascent Abort-2, at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in preparation for the first flight with crew.