EG-0024-01
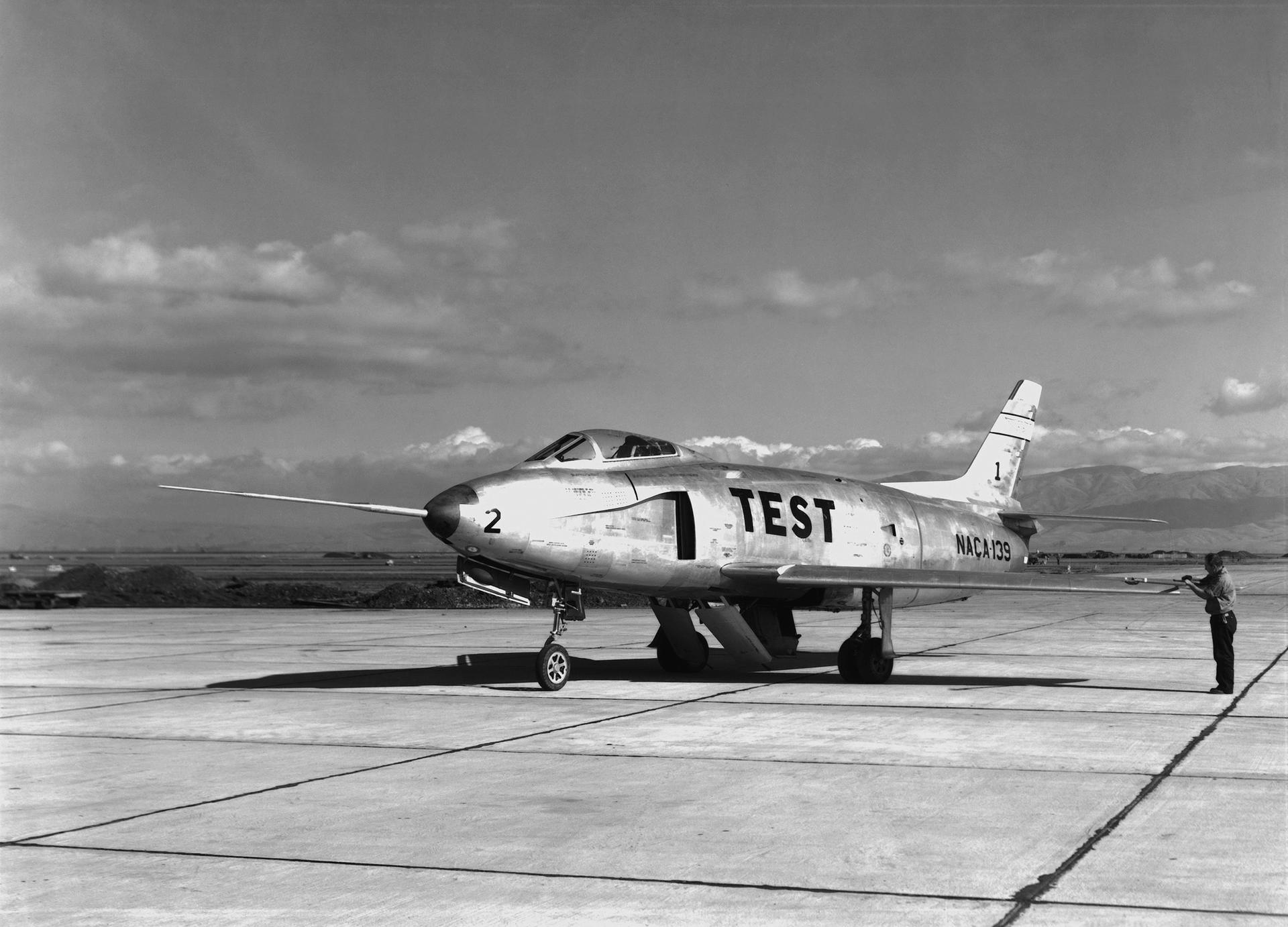
NASA operates two Lockheed ER-2 Earth resources aircraft as flying laboratories in the Airborne Science Program under the Agency’s Science Mission Directorate. The aircraft, based at NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, CA, collect information about Earth resources, celestial observations, atmospheric chemistry and dynamics, and oceanic processes. The aircraft also are used for electronic sensor research and development, satellite calibration, and satellite data validation.Program History
NASA acquired its first ER-2 aircraft in 1981 and a second in 1989. They replaced two Lockheed U-2 aircraft, which NASA had used to collect science data since 1971. The U-2s, and later the ER-2s, were based at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, CA, until 1997, when the ER-2s and their operations moved to NASA Dryden.
Since the Airborne Science Program’s inaugural flight on Aug. 31, 1971, NASA U-2s and ER-2s have flown more than 4,500 data missions and test flights in support of scientific research.
NASA’s ER-2 set a world-altitude record for the class of aircraft with a takeoff weight between 26,455 and 35,275 lb on Nov. 19, 1998, when the aircraft reached 68,700 feet…Learn more