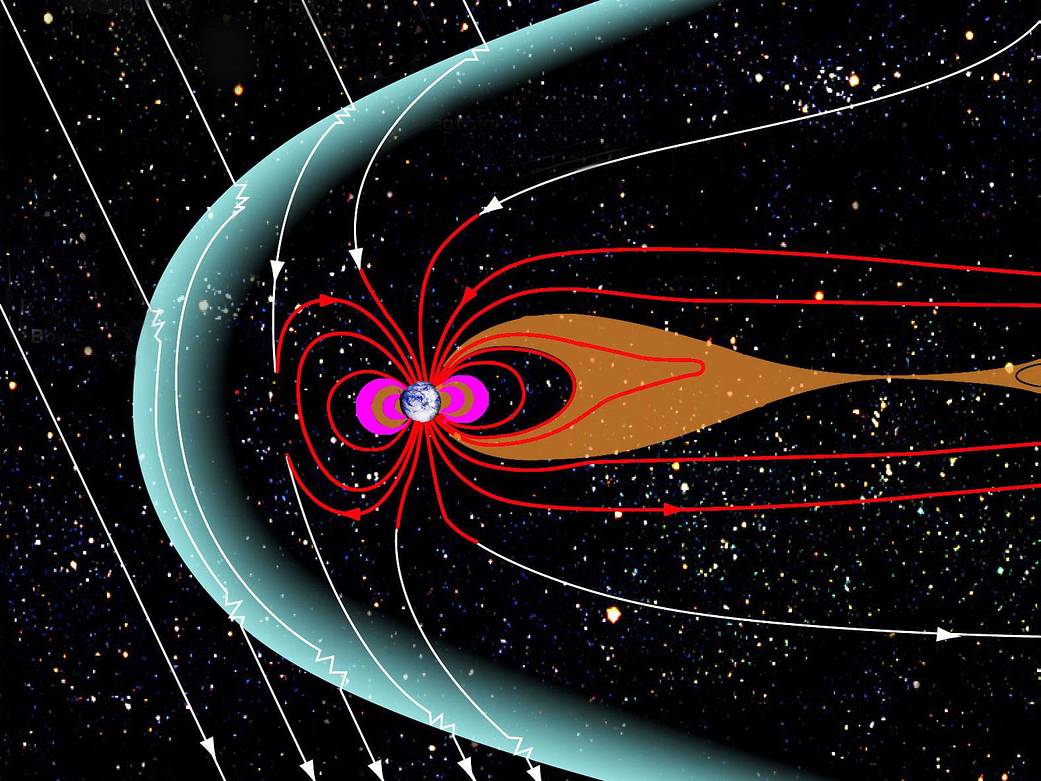
A magnetosphere is that area of space, around a planet, that is controlled by the planet’s magnetic field. The Earth’s magnetosphere is a highly dynamic structure that responds dramatically to solar variations. The shape of the Earth’s magnetosphere is the direct result of being blasted by solar wind. The solar wind compresses its sunward side to a distance of only 6 to 10 times the radius of the Earth. A supersonic shock wave is created sunward of Earth called the Bow Shock. Most of the solar wind particles are heated and slowed at the bow shock and detour around the Earth in the Magnetosheath. The solar wind drags out the night-side magnetosphere to possibly 1000 times Earth’s radius; its exact length is not known. Residing within the magnetosphere is the Van Allen Radiation Belts and the Plasmasphere.
Credit: NASA/Goddard/Aaron Kaase