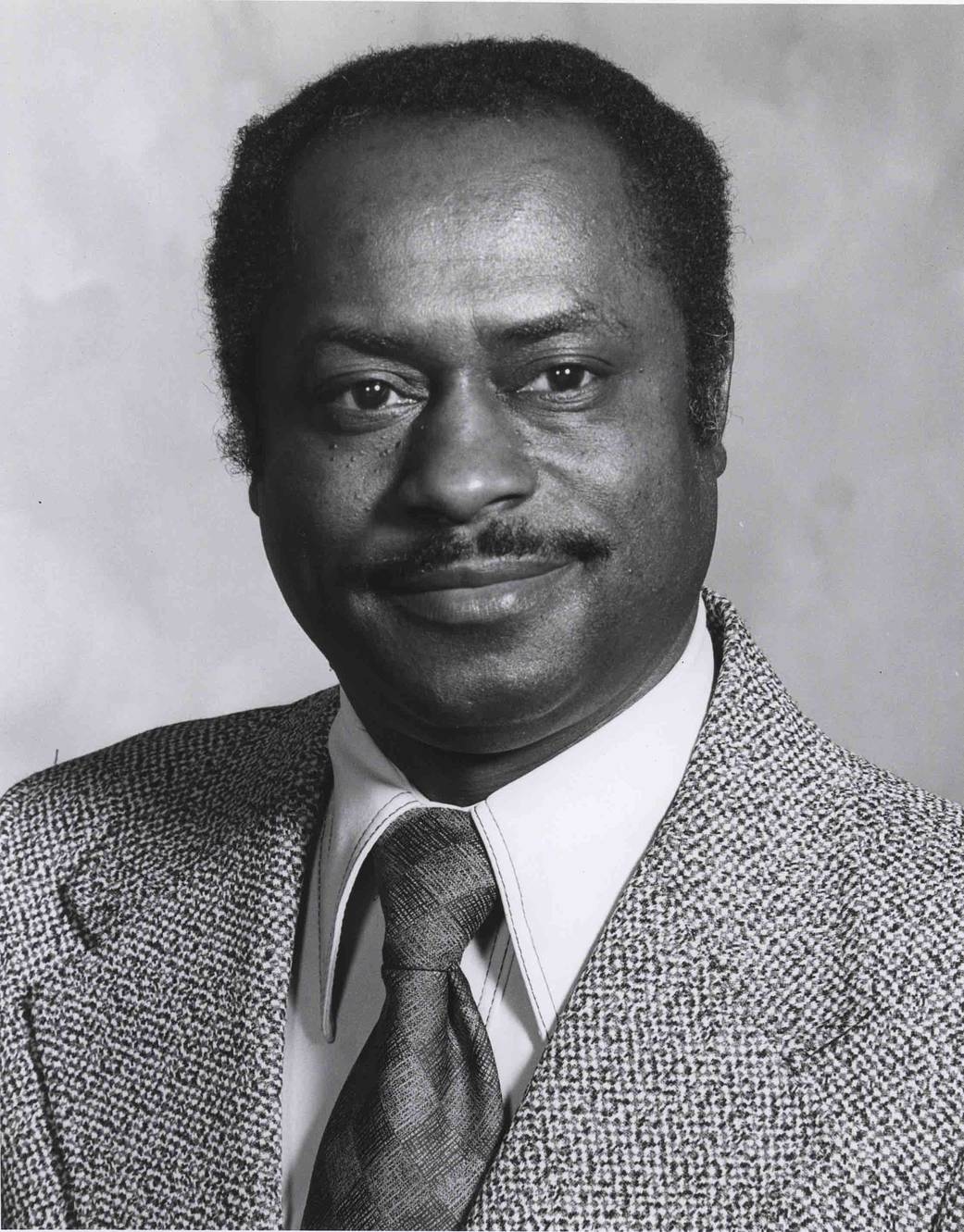
Earnest C. Smith was born in Pine Bluff, Arkansas on May 17, 1932 and graduated from Jefferson High School in Pine Bluff in 1950. After serving in the United States Army from January 1953 to January 1955, Smith earned a Bachelor’s of science degree in mathematics from the University of Arkansas in Pine Bluff in 1956. In 1963, Smith accepted a National Science Foundation Fellowship which he used to complete a Master’s of science degree in mathematics from the University of Arkansas in Fayetteville in 1964.
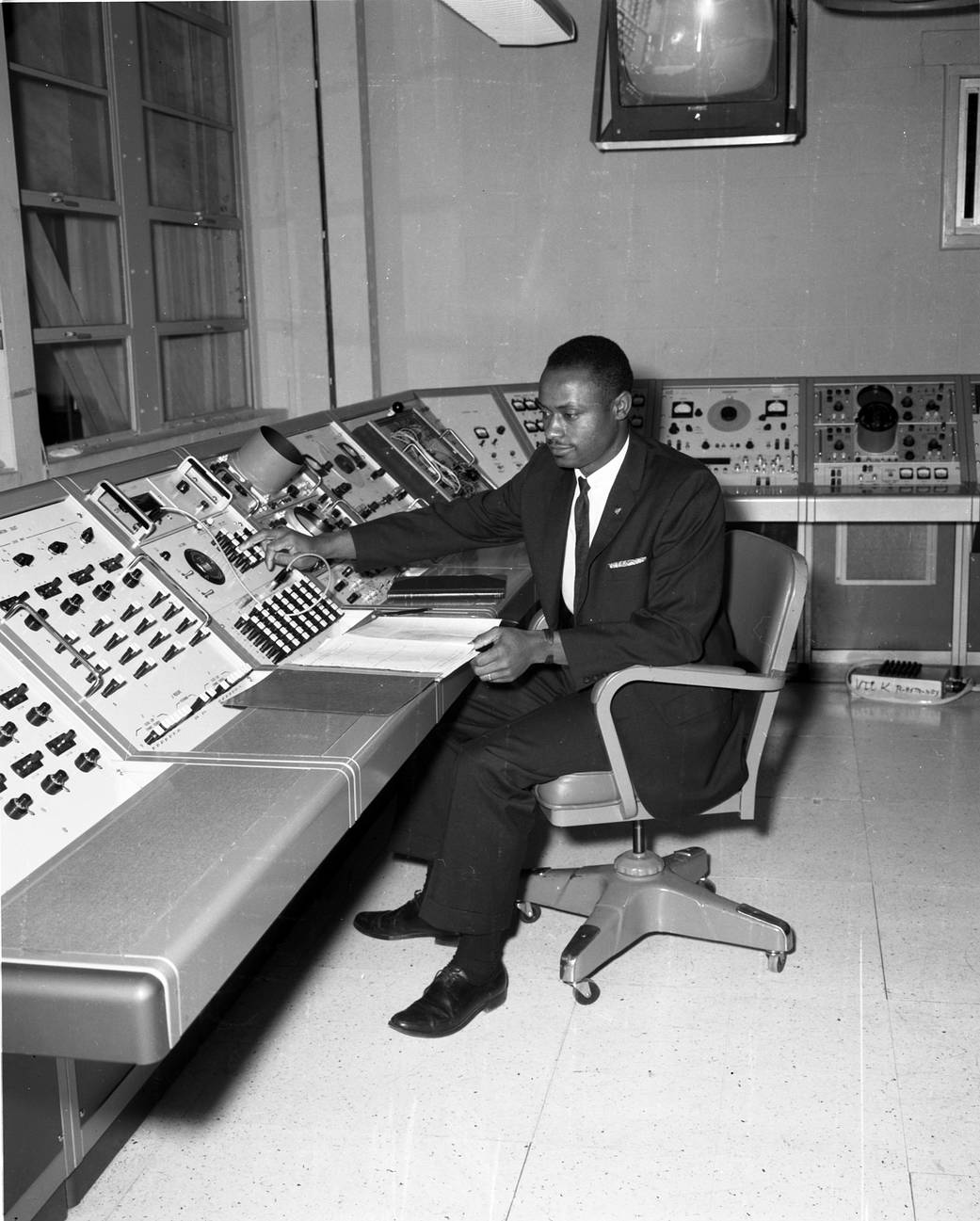
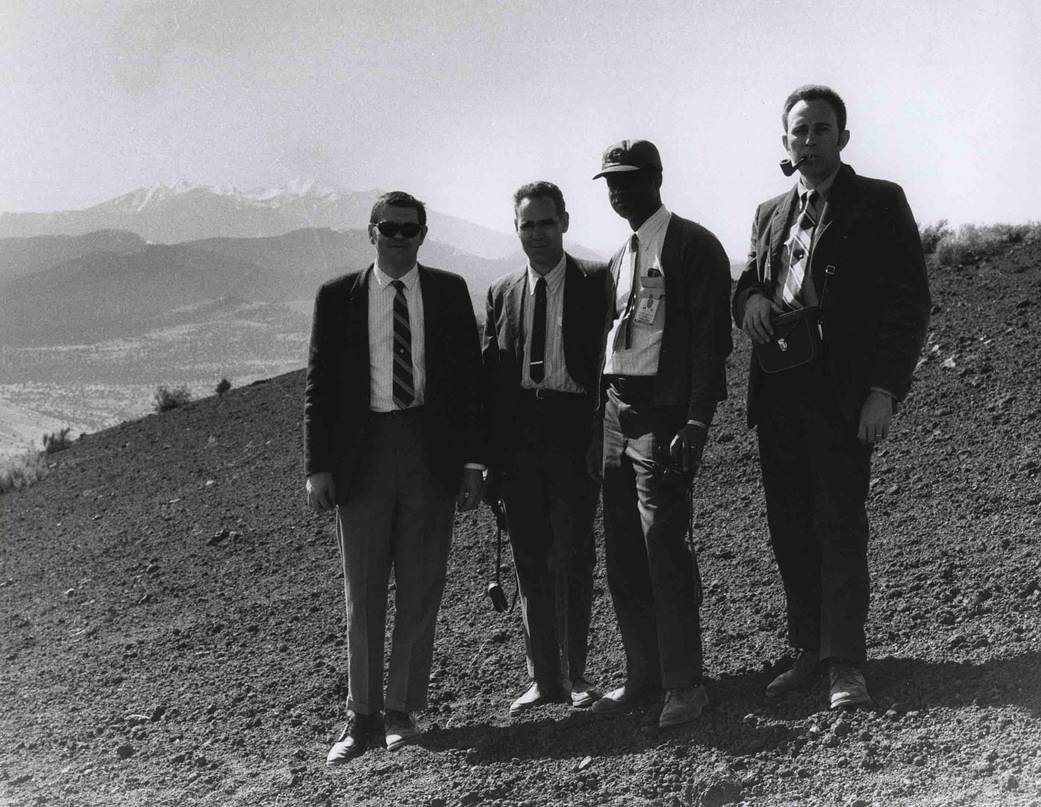
In 1964, Charles Smoot recruited Smith to Marshall Space Flight Center where he took a position as aerospace engineer in the Astrionics Laboratory. There, he performed analyses and evaluations of the guidance, control and navigations systems for the Saturn launch vehicles. For the Skylab Program, Smith carried out studies of the control subsystem, using digital and hybrid -more system simulations. He also was instrumental in the development and verification of the navigation system of the Lunar Roving Vehicle during which he travelled to Flagstaff, Arizona for testing. Smith later became director of the Astrionics Laboratory at Marshall.
Over his career, Smith received the NASA Exceptional Service Medal in 1972 for significant personal contributions to the theoretical development, practical implementation and operational support of the navigation systems for the Lunar Roving Vehicle on the Apollo 16 mission, as well as several commendations and the astronauts’ Snoopy Award.