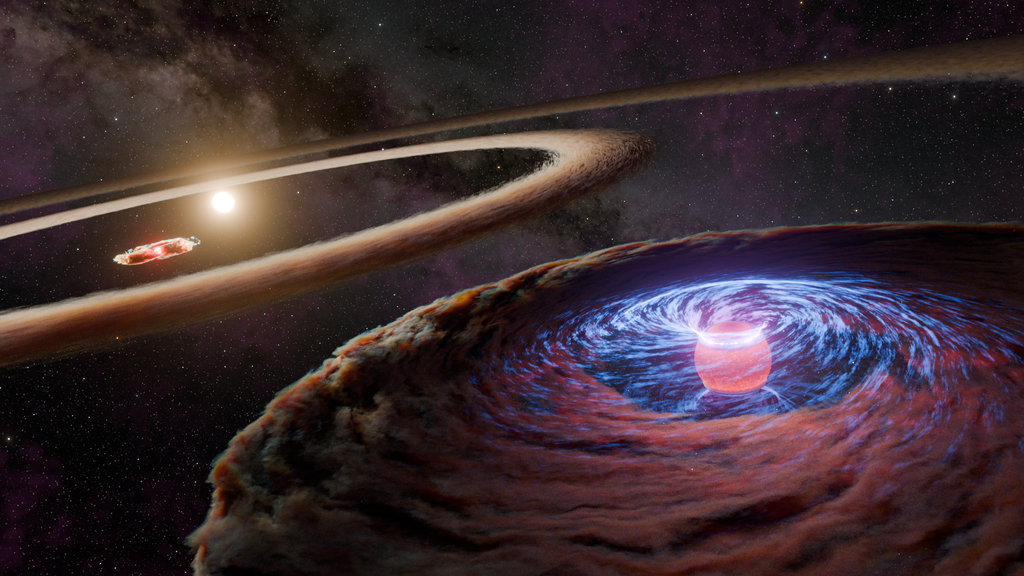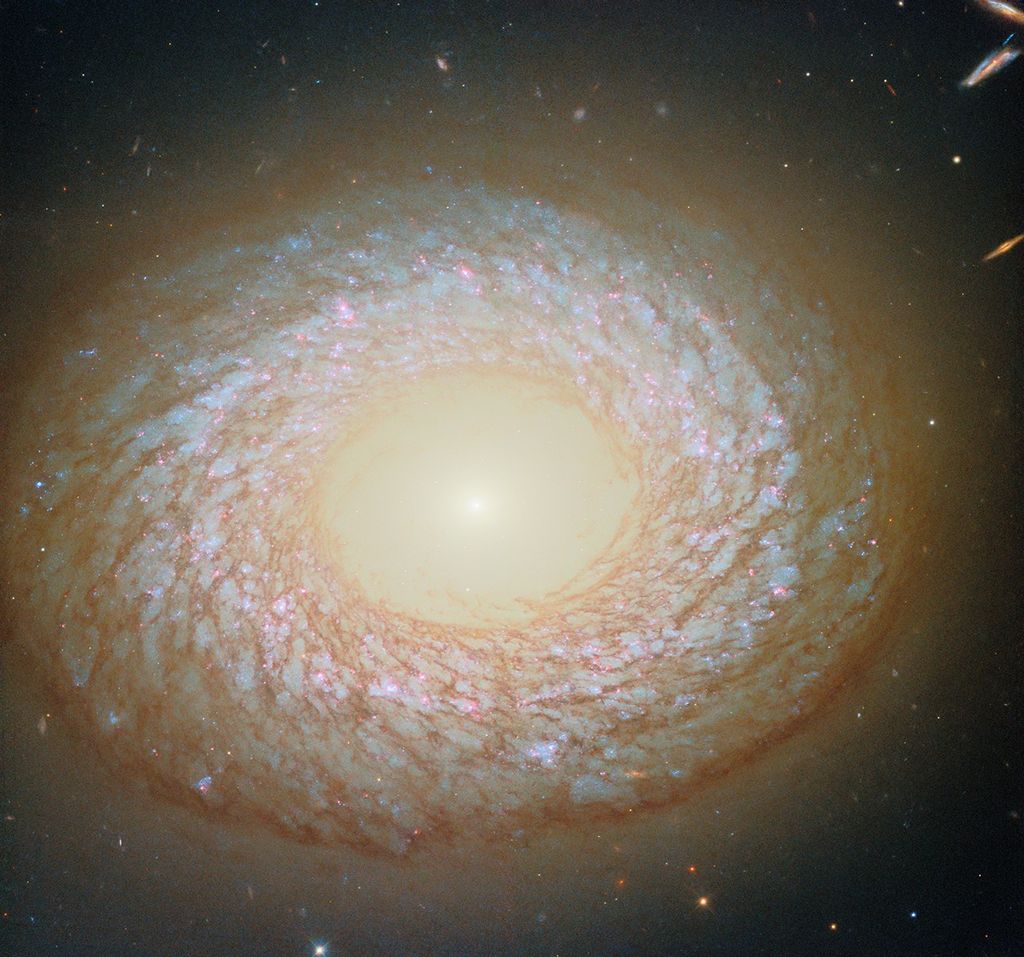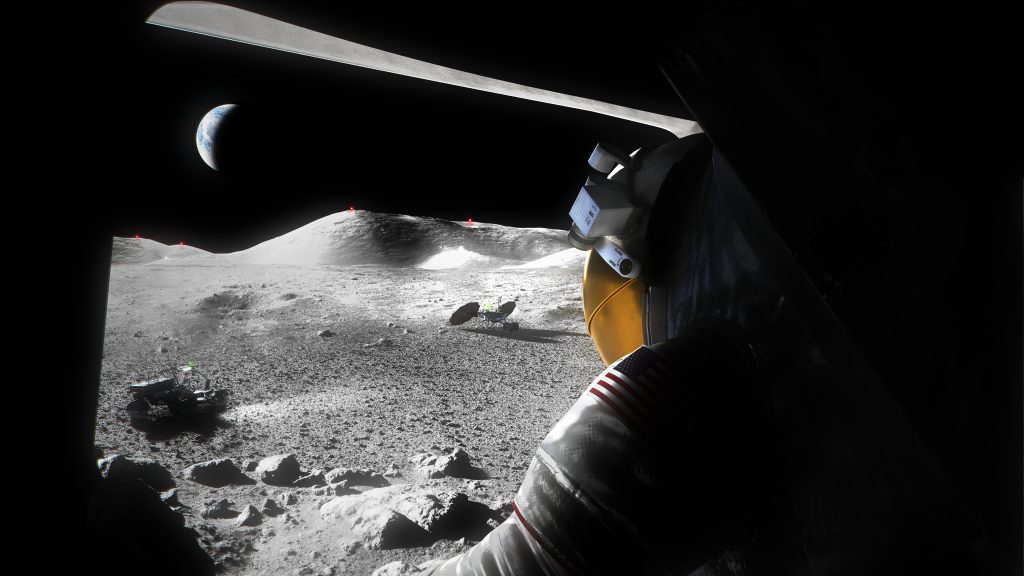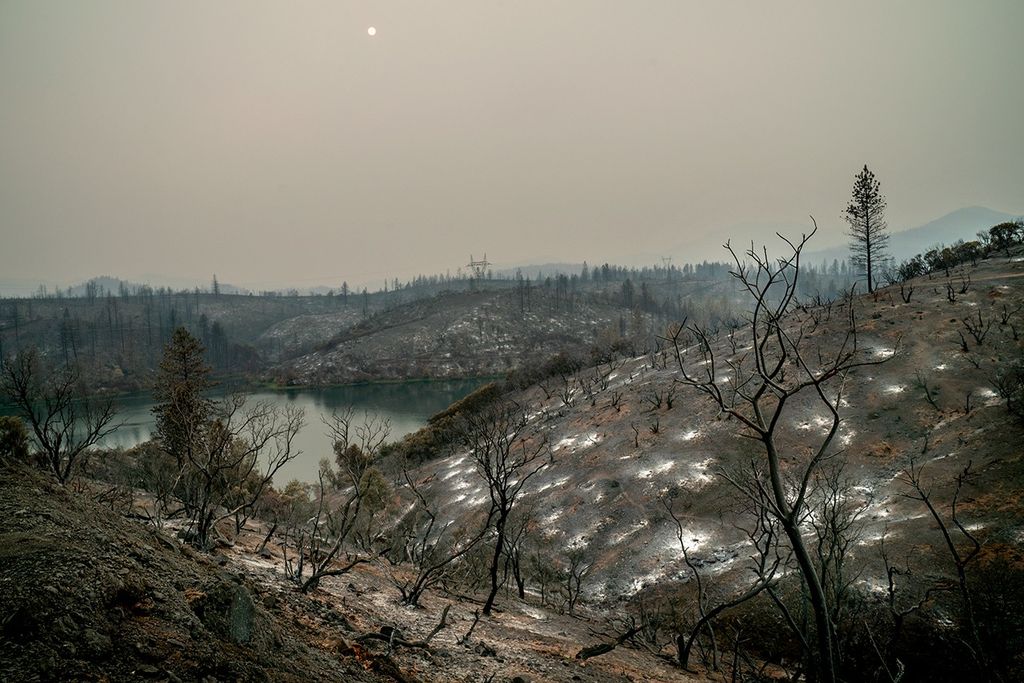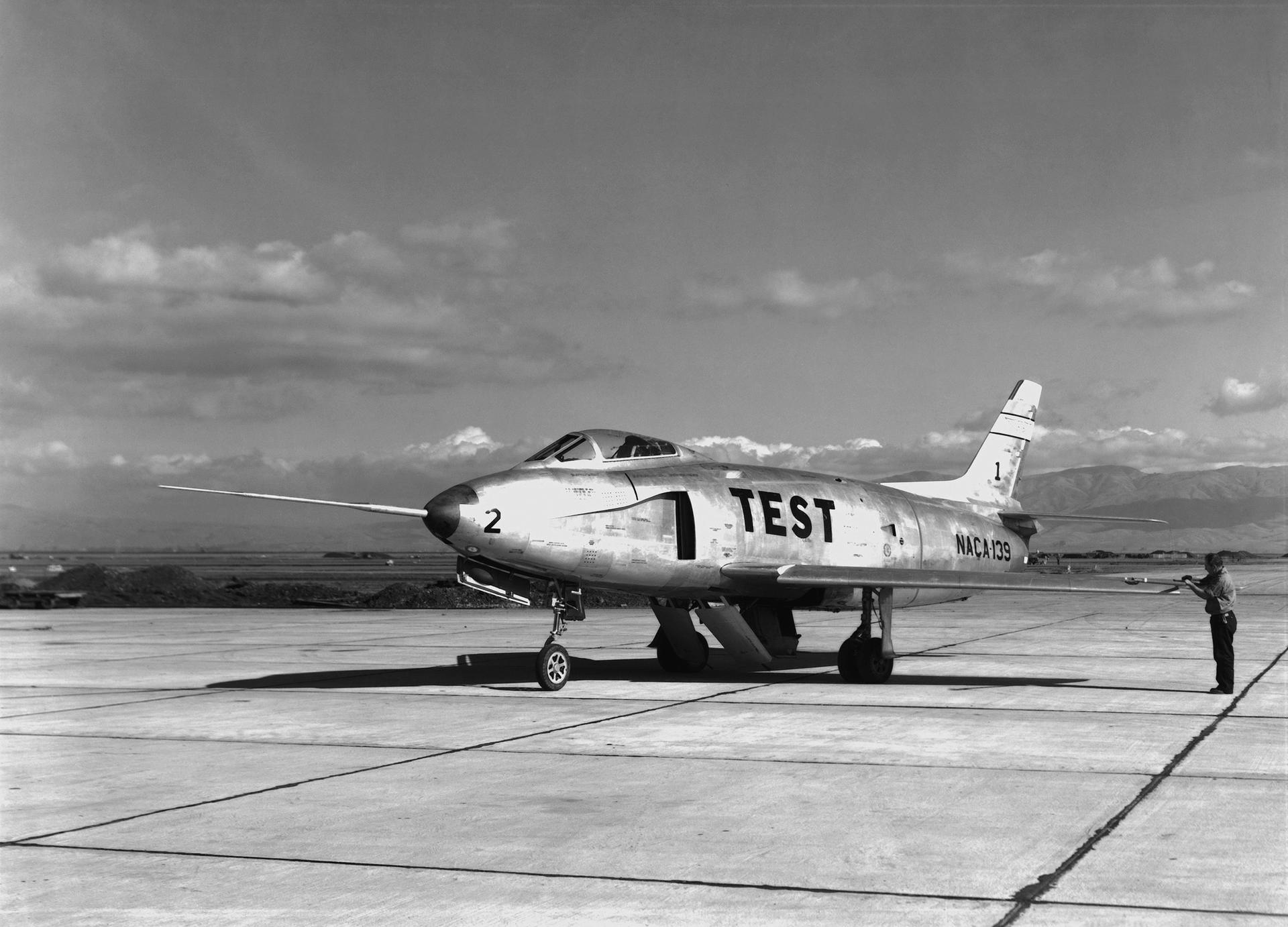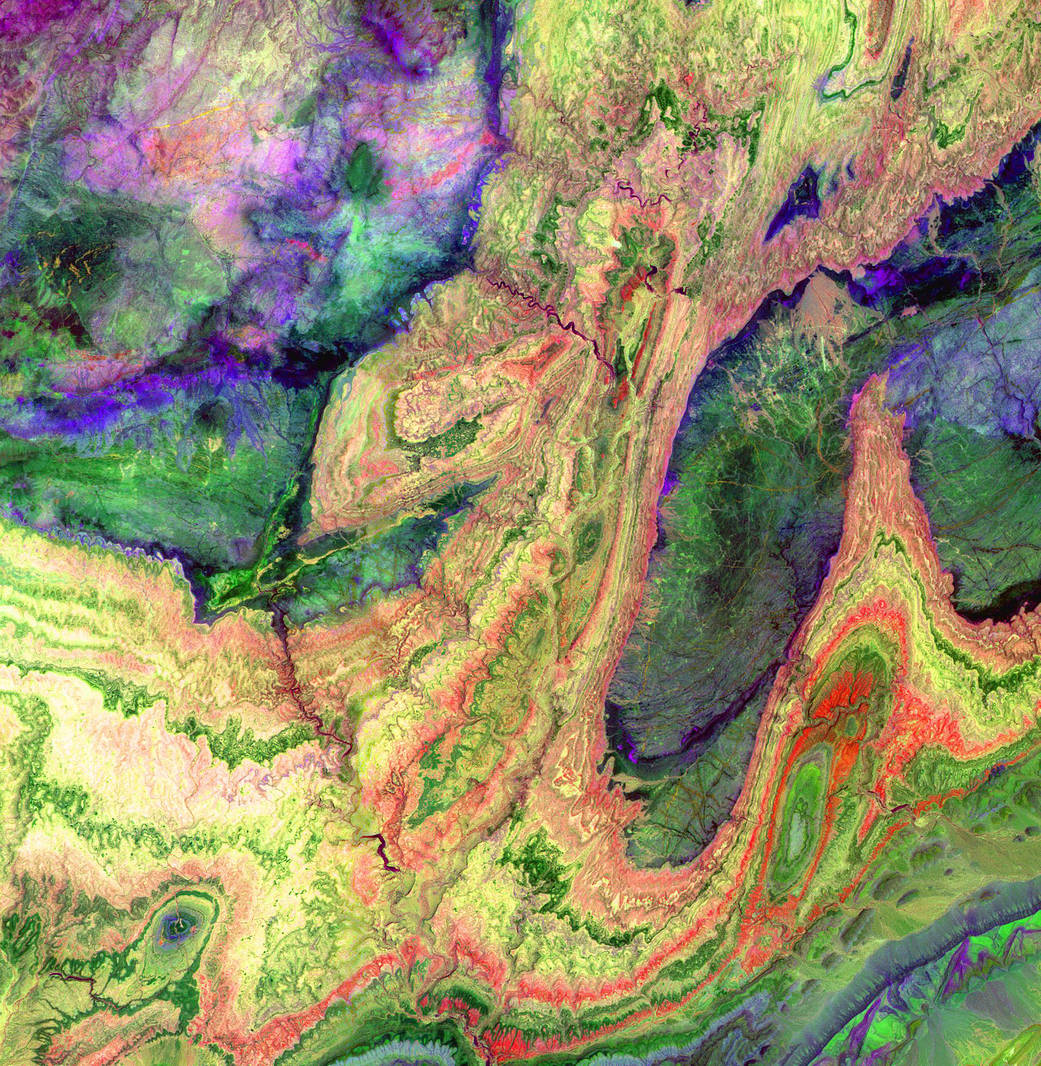
The Anti-Atlas Mountains of Morocco formed as a result of the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates about 80 million years ago, resulting in the destruction of the Tethys Ocean. The limestone, sandstone, claystone and gypsum layers that formed the ocean bed were folded and crumpled to create the Atlas and Anti-Atlas Mountains.
The Anti-Atlas Mountains of Morocco formed as a result of the collision of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates about 80 million years ago, resulting in the destruction of the Tethys Ocean. The limestone, sandstone, claystone and gypsum layers that formed the ocean bed were folded and crumpled to create the Atlas and Anti-Atlas Mountains. In this ASTER image, short wavelength infrared bands were combined to dramatically highlight the different rock types and illustrate the complex folding. The yellowish, orange and green areas are limestones, sandstones and gypsum; the dark blue and green areas are underlying granitic rocks.Image credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team


























