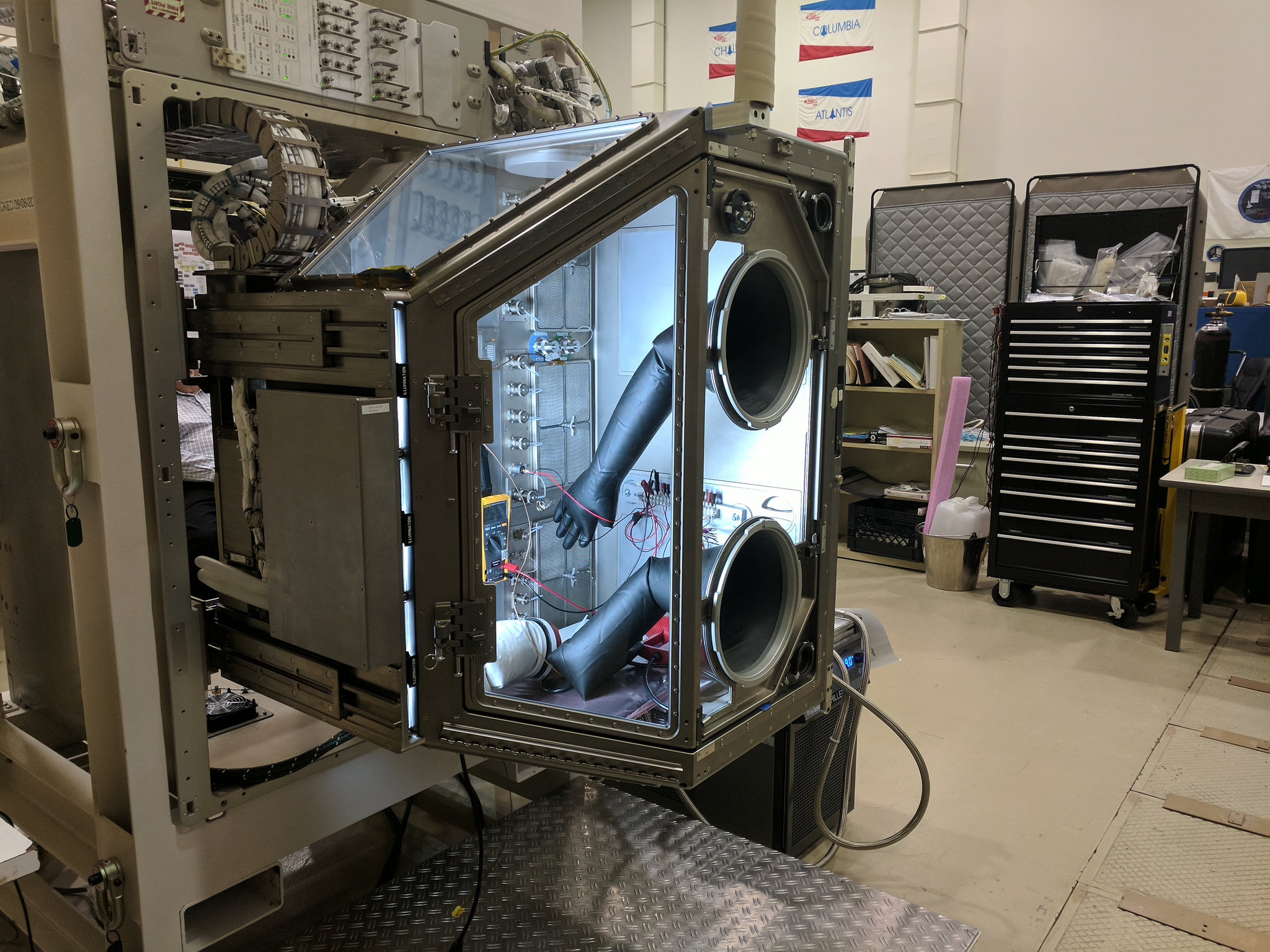
As the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency‘s H-IIB rocket carries NASA’s Life Sciences Glovebox toward its berth on the International Space Station, hardware specialists at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and their partners around the world are eager to initiate new, high-value biological research in Earth orbit.
The JAXA H-IIB rocket, hauling the state-of-the-art microgravity research facility and other cargo via the H-II Transport Vehicle-7 (HTV-7), successfully lifted off at 1:52 p.m. EDT on Sept. 22 from Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan.
“The teamwork and global partnership that delivered this hardware have been simply amazing,” said Bobby Watkins, director of Marshall’s Human Exploration Development and Operations Office. “We can’t wait to see it installed on the space station to enable more high-value biological and physical science experiments, with untold benefits on- and off-world.”
Its launch, previously delayed by inclement weather and technical issues, marks a first for hauling bulky equipment to space. Roughly the size of a large fish tank, the Life Sciences Glovebox — 26 inches high, 35 inches wide and 24 inches deep, with 15 cubic feet of available workspace — is officially the largest flight hardware ever launched in a “soft-stowed” configuration in which the equipment is packed securely in protective foam.
The HTV-7 is expected to dock with the space station on Sept. 27. It will be installed on the Harmony module, where it will remain for several weeks. NASA TV coverage of the rendezvous is scheduled to begin at 6:30 a.m. EDT. Capture of the transport vehicle is scheduled for approximately 8 a.m. To learn more, visit:
https://blogs.nasa.gov/spacestation
“The Life Sciences Glovebox is on its way to the space station to enable a host of biological and physiological studies, including new research into microgravity’s long-term impact on the human body,” said Yancy Young, project manager of the glovebox at Marshall. “This versatile facility not only will help us better protect human explorers on long voyages into deep space but it also could aid medical and scientific advances benefiting the whole world.”

Boeing engineers at Marshall modified a refrigerator-freezer rack to house the core facility, even using state-of-the-art, 3D-printing technology to custom design key pieces of the rack to secure the unit in its protective foam clamshell. Soft-stowing offers an efficient, low-cost alternative to conventional, hard-mounted cargo stowage, said Chris Butler, payload integration manager for the glovebox at Marshall — and could “open up new possibilities for other oversized flight hardware.”
The Life Sciences Glovebox will be transferred to a zero-gravity stowage rack in the station’s Kibo module, where up to two crew members can conduct one or more experiments simultaneously, overseen in real-time by project researchers on Earth.
Originally built by JAXA and the Dutch firm Bradford Engineering, the glovebox was redesigned and upgraded in 2017. Engineers at Marshall contributed its secondary support structure and thermal control and power control systems and designed the facility’s power supply, air filtration, lighting, video and data recording and real-time downlink capability.
NASA is now determining the roster of science investigations lined up to make use of the facility, beginning as early as late 2018. “We’ve already got more than a dozen glovebox experiments scheduled in 2019, with many more to follow,” Butler said. “That’s OK with all of us. We love to be busy.”
Marshall manages the Life Sciences Glovebox for NASA and monitors space station science and communications from its Payload Operations Integration Center, supporting the ISS Research Integration Office at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Learn more about scientific advances on the International Space Station at:
https://www.nasa.gov/station/research
See more images of the Life Sciences Glovebox undergoing testing at Marshall: