
Cabin Relief and Dump Valves
Adapted from 1969 Grumman Apollo LM News Release
Last revised 22 November 2005.

A bacteria filter could mounted on the cabin side of the forward cabin relief and dump valve. This was done only on Apollo 11. If used, the filter was mounted on the cabin side and removed 95% of all bacteria larger than 0.5 micron from the dumped cabin oxygen. The filter could be removed - or installed - by an astronaut in the cabin.
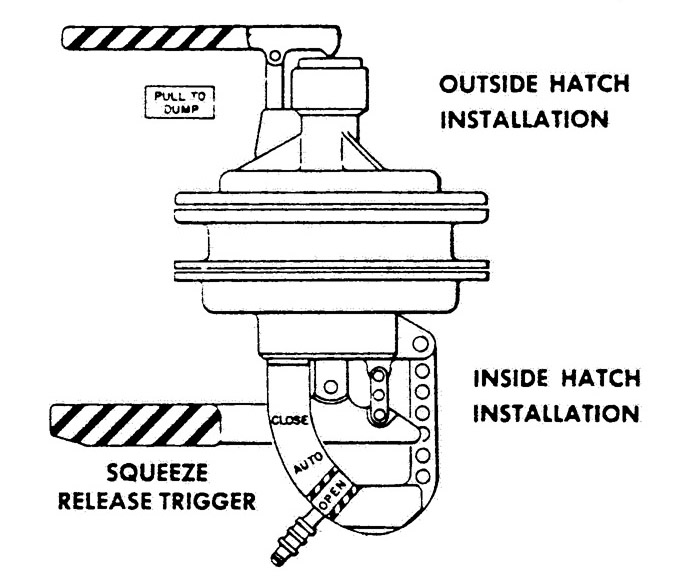
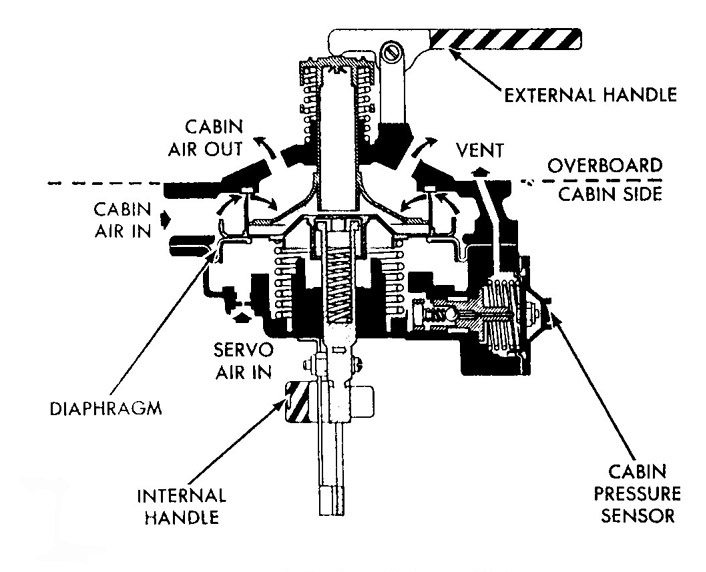
Normally, the cabin relief and dump valves were set to the automatic position. In this position, the valves were operated by the servo valve. When the cabin-to-ambient pressure differential reached approximately 5.4 psi, oxygen was vented overboard and cabin pressure was reduced to an acceptable value. When the pressure differential was 5.8 psi, one fully open dump valve could dump 11.1 pounds of oxygen per minute overboard. When the valve handle inside the cabin was set to the automatic position, the valve could be opened manually from the outside.
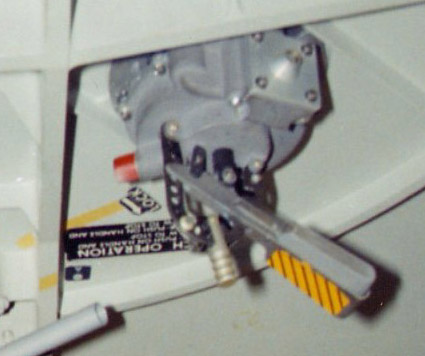
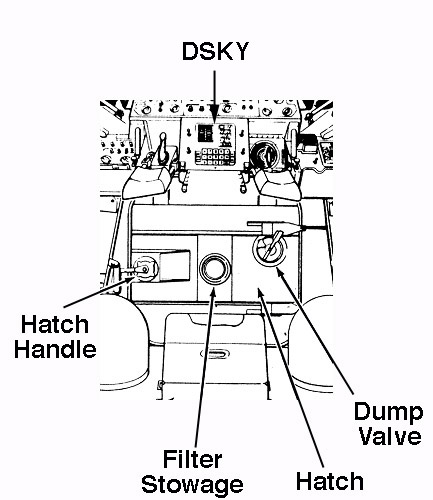
Setting the internal handle to the dump position unseated the poppet. With a bacterial filter installed, the forward hatch valve could dump pressure from 5.0 to 0.08 psia in 310 seconds without cabin oxygen inflow; without a filter in place, either valve could dump cabin pressure to 0.08 psia in 180 seconds; and, with both open and no filter in use, the time was 90 seconds. Setting the handle to the closed position prevented the valve from opening at normal pressures, if the servo valve failed.