GMSEC : Goddard Mission Services Evolution Center
The Goddard Mission Services Evolution Center (GMSEC) in Code 583 at GSFC/NASA is responsible for the creation and development of the GMSEC suite of software components. The suite leverages unique GMSEC architecture – a scalable, open, and extensible framework for mission operations centers and other mission-critical systems.
Location
Greenbelt, MD
Founded
2001
People
20+
Missions supported
100+
GMSEC Lab and Demonstration Facility
The GMSEC Development Lab provides a platform for prospective missions to evaluate and test GMSEC-compliant Government Off-The-Shelf (GOTS) and Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) solutions.
The GMSEC Reference Architecture is validated in the GMSEC Development Lab. It provides multiple operating systems, languages, and communications protocols. The lab’s activities include development, benchmarking, demonstrations, evaluations, system integration, functional testing, and what-if scenarios. A local area network enables connectivity of other campus labs facilitating development and testing. New components can be augmented with adapters and tested with other components in the lab. This capability enables thorough assessment of potential flight and ground system components prior to integration.
Request a flight or ground system component demo about GMSEC Lab and Demonstration Facility
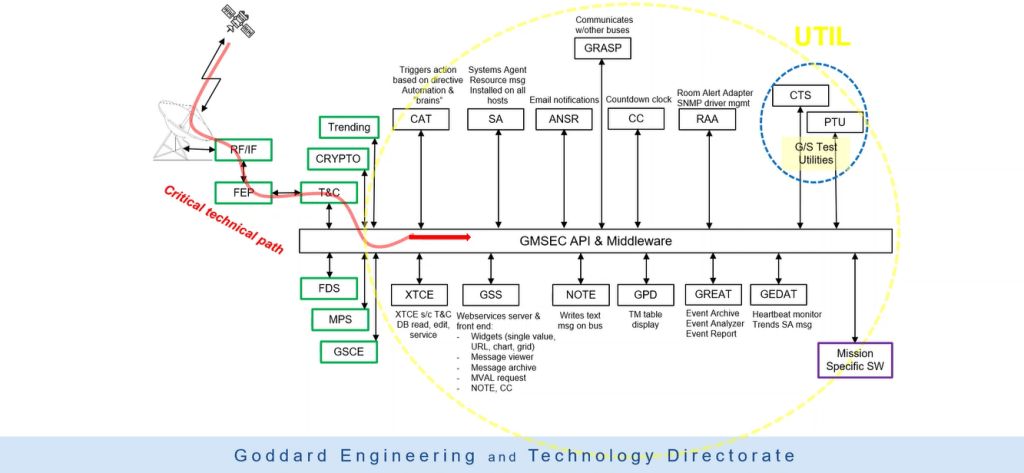
GMSEC Architecture
The core feature of the architecture is standardized messages and formats, defined by the GMSEC team with industry involvement.
By using standard messages, the event-driven architecture enables quick and easy integration of functional components, in a “plug and play” concept for current and future missions.
The system components are selected to meet the unique needs of a mission or user. Messages are passed between applications by an information software bus using the publish/subscribe paradigm. Application components maintain an interconnection to the information software bus that isolates most of the components’ complexity from other components.
About GMSEC
GMSEC was established in 2001 to coordinate ground systems development and services at GSFC.
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) originally conceived and defined GMSEC to support its satellite missions. However, the use of GMSEC has spread well beyond GSFC.
Most of the NASA operations Centers have had GMSEC labs and continue to evaluate or use GMSEC. Marshall Space Flight Center has used GMSEC operationally for event message processing. Ames Research Center employed GMSEC for the (LADEE) and the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) missions. Independent Verification and Validation Facility has created a software test suite based on GMSEC. Wallops Flight Facility has examined GMSEC for range operations at their launch site.
As of today, ESMO Earth Science Mission Operations (ESMO) and Space Science Mission Operations (SSMO) represent the primary GMSEC user-base at Goddard. ESMO is responsible for spacecraft maintenance and operations for Earth Science missions conducted by the Earth Science Projects Division and SSMO manages operations for heliophysics, astrophysics, and planetary science missions at the Goddard Space Flight Center.

API Goals
The GMSEC API provides a multi-language, cross-platform, standard communications interface, which is easily integrated with any application.
The goal for the GMSEC API is to simplify development, integration and testing of ground systems and to facilitate new technology infusion over time. The middleware abstraction layer built into the API allows different middleware products to run without changing the applications software. This abstraction helps prevent vendor lock-in and reduces risk.
Access GMSEC API Open Source
GMSEC Components
In addition to the GMSEC API, the Goddard Mission Services Evolution Center Development team develops and maintains a suite of GMSEC-API software components to aid in mission automation, ground equipment monitoring, event message reporting, performance monitoring, and Telemetry and Commanding support.
A major benefit of the GMSEC SW suite is that it enables significant automation within Mission Operations. This automation enables lights out operations (for example, operations staff on-site Monday-Friday, 8AM-5PM only, instead of operations staff on-site 24/7). Experience has shown that when a Mission transitions to GMSEC, it can lower operations costs by up to 50%.

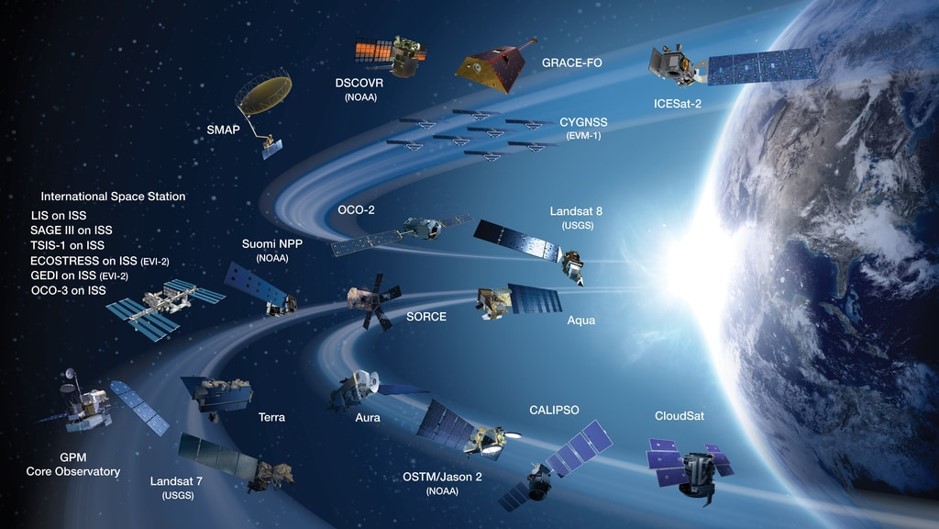
Missions and Facilities GMSEC Supports
The API as well as the suite of software components are used across various missions in ESMO and SSMO and the Flight Dynamics Facility at GSFC

Flight Dynamics Facility
The Flight Dynamics Facility is a provider of comprehensive flight dynamics services to space communications networks, science and exploration programs, and expendable launch vehicle providers.

PACE
Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) is a NASA Earth-observing satellite mission that will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
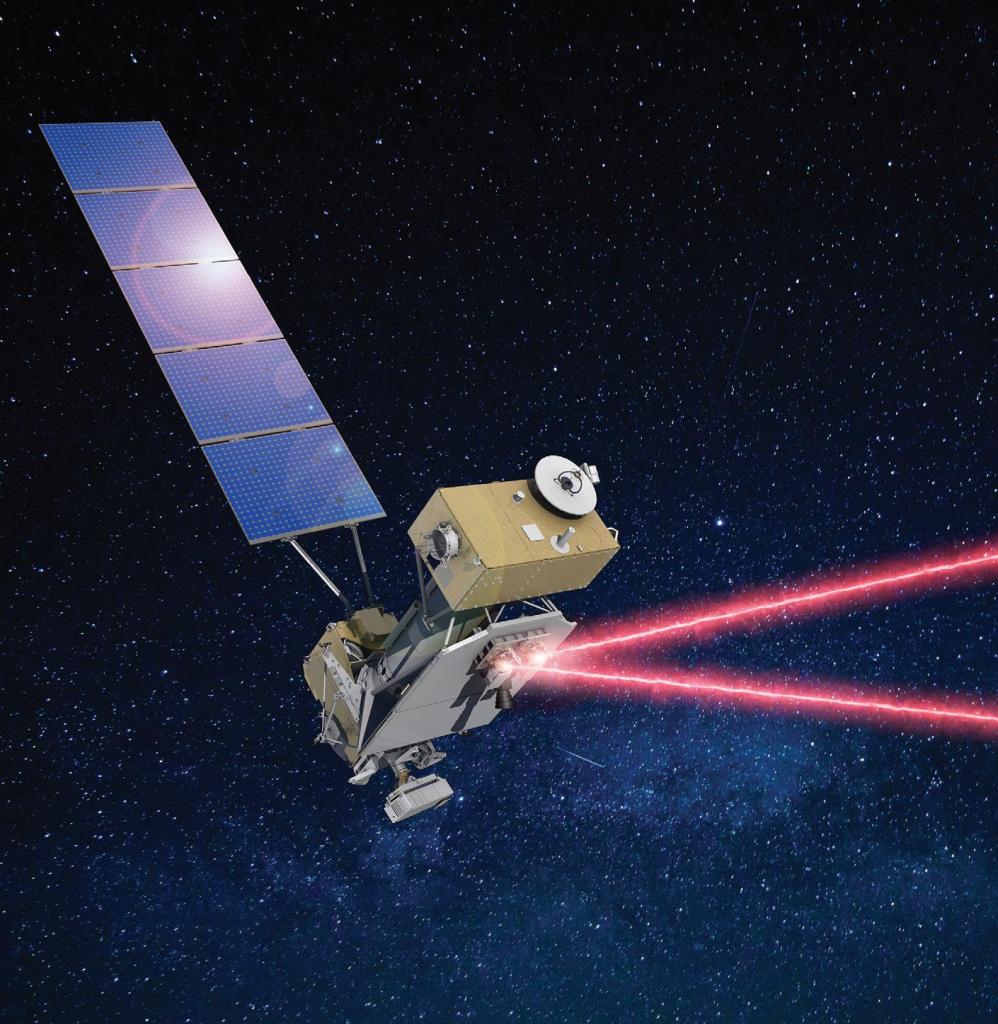

LCRD
NASA’s first two-way laser relay system, The Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), uses infrared light, or invisible lasers, to transmit and receive signals rather than radio wave systems conventionally used on spacecraft.
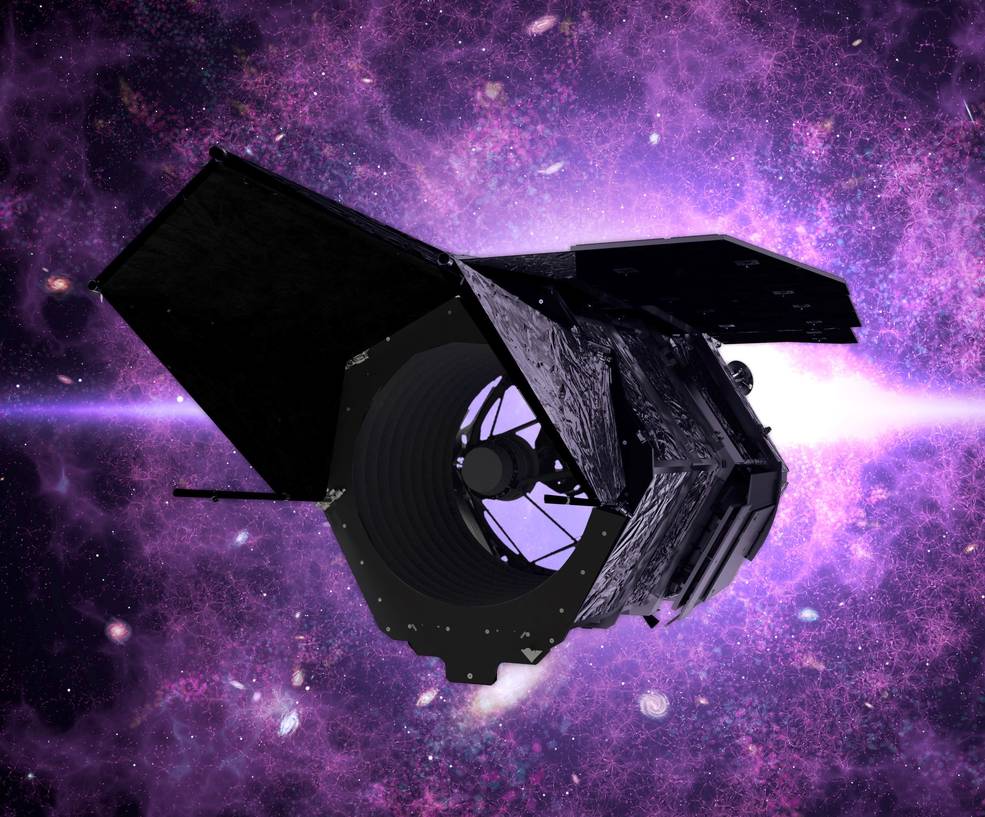

Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Roman Space Telescope is a NASA observatory designed to settle essential questions in the areas of dark energy, exoplanets and infrared astrophysics.

LRO
LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter) created a 3D map of the Moon, as part of a program to identify future landing sites and resources – including deposits of water ice shadowed in polar craters. LRO continues to orbit the Moon.

TESS
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is designed to discover thousands of exoplanets in orbit around the brightest dwarf stars in the sky.

ICESat-2
The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, measures the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a detail.
MMS
MMS investigates how the Sun’s and Earth’s magnetic fields connect and disconnect, explosively transferring energy from one to the other in a process that is important at the Sun, other planets, and everywhere in the universe, known as magnetic reconnection.