Goddard Sustainability
Sustainability is an important aspect of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center from an institutional perspective, as well as within specific program areas. Goddard also supports sustainability goals on the center, agency, and national (Executive Order 14057, Executive Order on Catalyzing Clean Energy Industries and Jobs Through Federal Sustainability) levels.
What is sustainability?
At Goddard, sustainability means ensuring that our operations are compatible with the environmental systems that support us.
As a global leader in Earth Science, Goddard has a unique obligation to lead the way in identifying and implementing strategies to ensure continued human progress, productivity, and prosperity while sustaining natural species and systems.
What is Goddard’s Sustainability Plan?
The Goddard plan for sustainability includes five objectives:
- Reduce Energy Consumption
- Manage Water Impacts
- Reduce Waste
- Promote Transportation Alternatives
- Support Local Ecosystems
Information on projects that support these objectives can be found in the 2024 Goddard Sustainability Report and Implementation Plan .
What is Goddard doing to promote sustainability?
Goddard supports the sustainability goals listed above through several of its programs.
- Energy and Sustainability Management The Goddard Facilities Management Division (FMD) coordinates LEED certification and Guiding Principles for Sustainable Federal Facilities increasing renewable energy use, reducing energy and water consumption, promoting EnergyStar systems, and researching low carbon materials and construction methods. For more information contact David Katzenberg, Taylor Chandler, or Kelly Busquets.
- Air and Water Quality The Goddard Medical and Environmental Management Division (MEMD) monitors pollutant emissions, greenhouse gas emissions, emissions controls on equipment, water conservation and quality, and ozone-depleting substance management. For more information, please visit the MEMD Air Quality. Employees can find additional information on water quality on MEMD’s internal website.
- Pollution Prevention and Green Purchasing The Goddard MEMD collaborates with the NASA Headquarters Technology Evaluation for Environmental Risk Mitigation and Recycling and Sustainable Acquisition programs to identify, test, and evaluate environmentally preferable materials and chemicals (e.g., launch system coatings), including bio-based products. Employees can find additional information on MEMD’s internal website.
- Climate Change The Goddard MEMD, FMD and Airborne Science Program each use their unique skills and capabilities to support Goddard climate change goals. These include greenhouse gas emissions tracking; reduction of pollutant emissions through administrative controls and increased use of lower emission systems; ground-truthing of the Global Precipitation Measurement mission; airborne science efforts such as the Carbon in Arctic Reservoirs Vulnerability Experiment and Operation IceBridge missions.
How is Goddard using renewable energy?
Goddard uses a diverse array of renewables at the Greenbelt and Wallops sites. Goddard will explore all options to meet the 100% carbon pollution free electricity goal by 2030, as outlined in Executive Order 14057.
Goddard’s Greenbelt site receives 50% of its electricity through wind power generated offsite. Goddard validates its renewable electricity usage through the purchase of renewable energy credits (RECs) as part of the current electricity contract.
Additionally, Greenbelt has used landfill gas to supplement natural gas heating for the main campus since 2003. Landfill gas not only reduces carbon emissions by replacing natural gas consumption (accounting for roughly 40% of gas usage on site), but it also has saved Greenbelt ~$21.5M over the first 20 years of operation. NASA extended the existing landfill gas contract with Toro Energy in 2023. To learn more about this project, see: https://www.epa.gov/lmop/landfill-gas-energy-project-data#nasa.
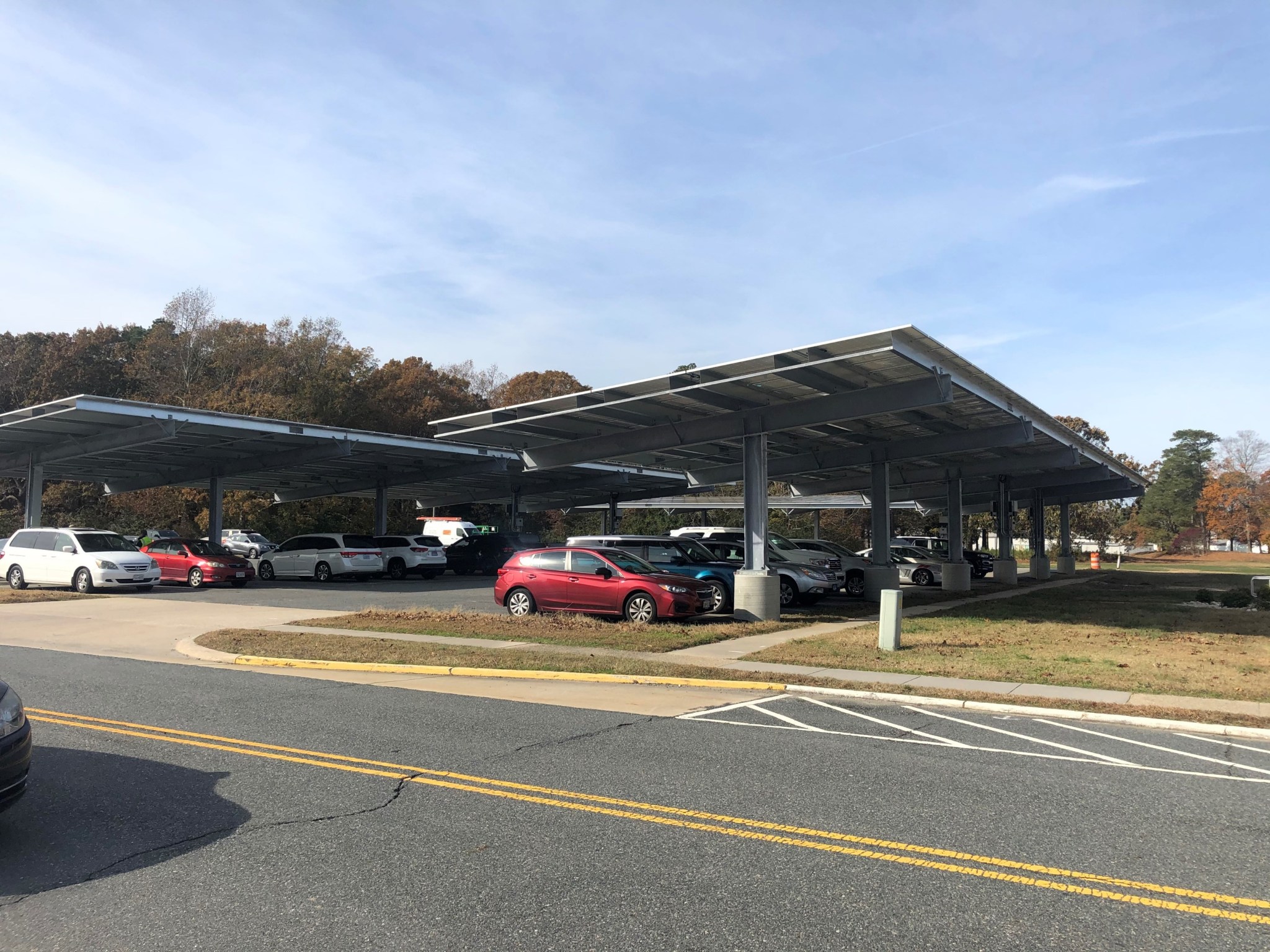
Wallops has two photovoltaic (PV) solar arrays to provide carbon-free electricity. Most of this production comes from a 4.3-Megawatt PV array located next to Wallops Airfield on the main base. The second PV array is a 270-Kilowatt Solar Carport next to F-006. Altogether, the solar arrays have provided about 27% of the Wallops main base power each year since installation in early 2020.
Goddard’s electric vehicle transition
In 2024, Goddard will install 8 level 2 electric vehicle charging stations at the Greenbelt site and 7 stations at Wallops with the goal of supporting 100% zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) acquisitions by 2035 and 100% ZEV light-duty vehicle acquisitions by 2027. Electrifying the Goddard fleet is just one way Goddard can reduce associated transportation carbon emissions.
Sustainability through energy efficiency improvements
Across its sites, Goddard is constantly seeking to retrofit old buildings with more efficient lighting, HVAC systems, building controls, and more. These are financed through energy contracts which incentivize the contractor to maximize energy savings through projects that will pay for themselves with efficiency gains. The Greenbelt site is currently engaged in a Utility Energy Service Contract (UESC) while Wallops is starting a new Energy Savings Performance Contract (ESPC). To learn more about how financed energy contracts (UESCs and ESPCs) can benefit federal facilities, see: https://www.energy.gov/femp/about-federal-energy-savings-performance-contracts.
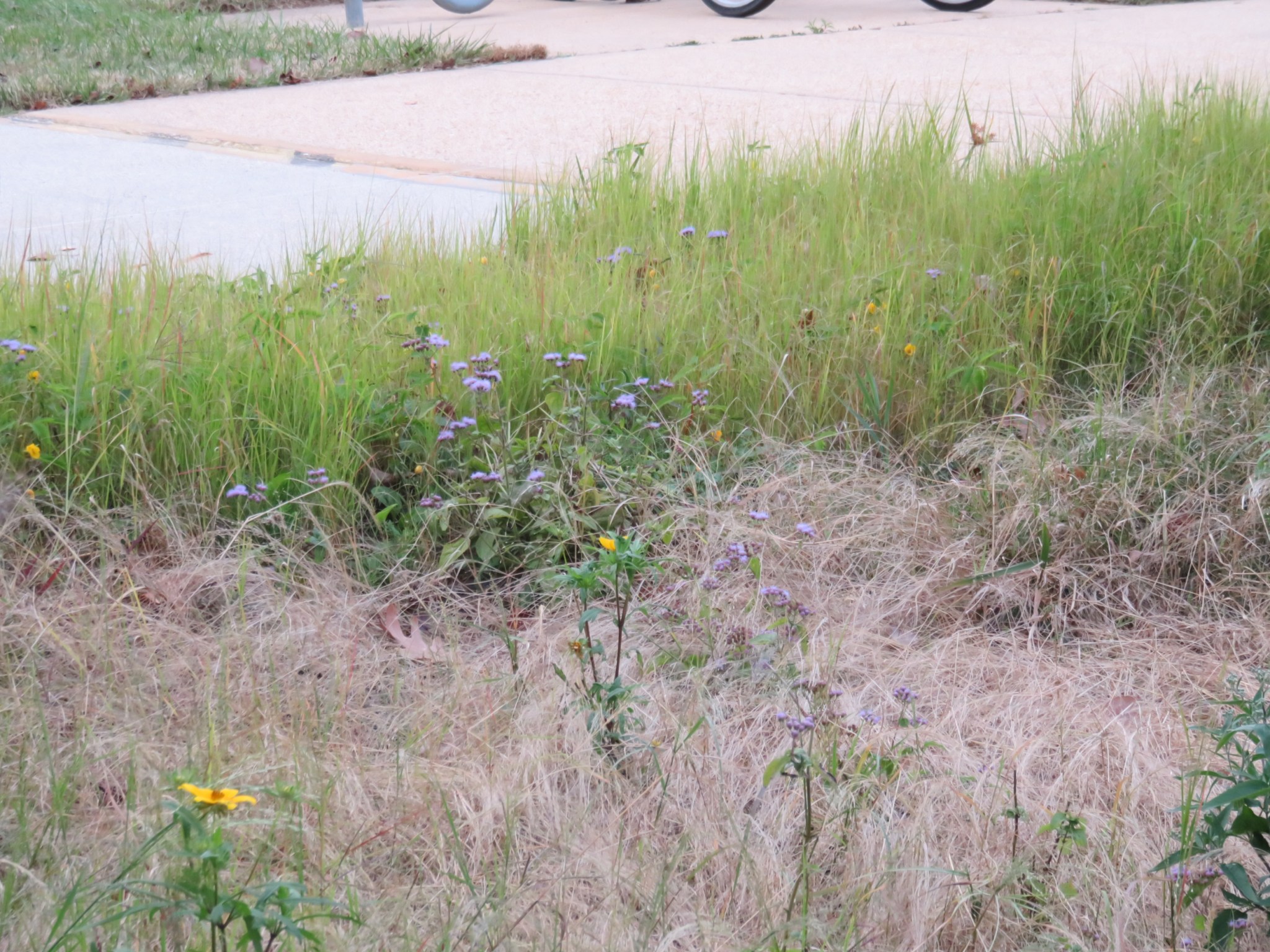
Greenbelt Meadows
Goddard’s sustainability team strives to increase the amount of sustainable, wildlife-friendly meadows across its campuses. To that end, Goddard has entered a partnership with the USDA/Natural Resources Conservation Service’s Plant Materials Center (Plant Materials | Natural Resources Conservation Service (usda.gov)) to search for effective methods for landowners to convert grass into meadows. From a small 0.1-acre testing plot, the project has evolved into several larger meadow areas.
For more information on Goddard meadows, please see Greenbelt Meadows – NASA
Sustainable Buildings – LEED Certification
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is the most ubiquitous green construction rating system in the world. LEED-certified buildings are recognized as a symbol of a low-carbon sustainable future.
Several Goddard buildings, both new constructions and retrofits, have been recognized with LEED certification.
Contact Us
If you have ideas. comments, or questions, please contact David Katzenberg, Taylor Chandler or Kelly Busquets.
Documents
| Title | Format | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 Sustainability Report and Implementation Plan | April 2024 | |
| 2021 Sustainability Plan | April 2022 | |
| 2020 Sustainability Report and Implementation Plan | July 2020 | |
| Evaluating the Performance of Stormwater Management Practices Using EPA’s Stormwater Model | February 2016 | |
| 2015 Sustainability Plan | July 2015 | |
| 2014 Sustainability Plan | July 2014 | |