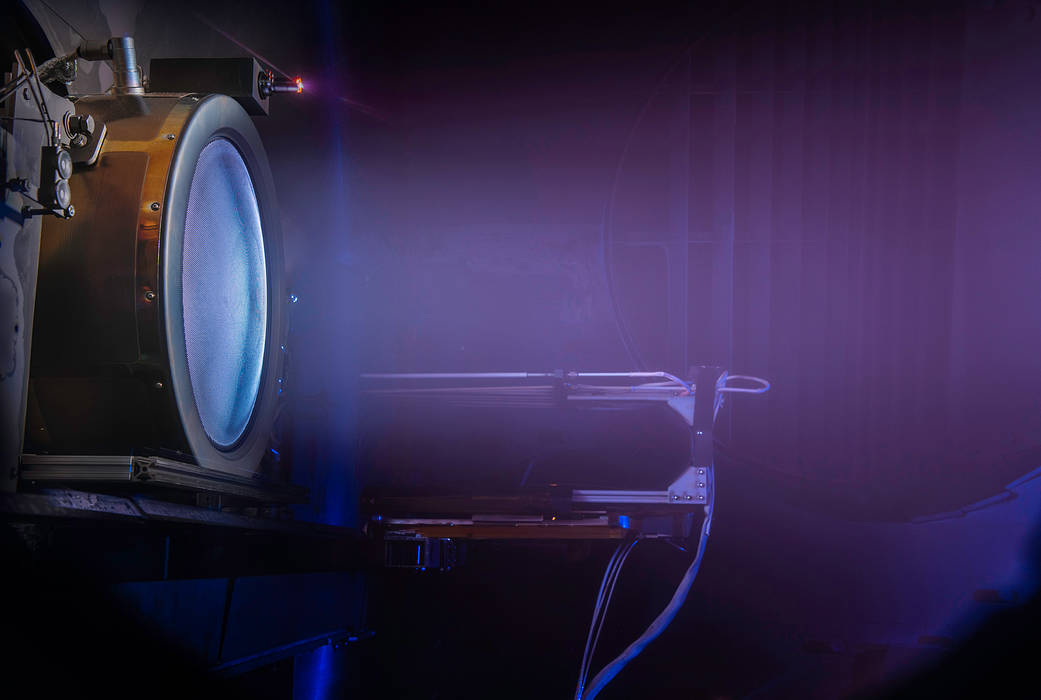
NASA’s Evolutionary Xenon Thruster – Commercial (NEXT-C) fired for the first time recently inside a vacuum chamber at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The thruster is undergoing performance testing to verify it can withstand the extreme launch vibrations and hot and cold temperatures of spaceflight. This photo shows an engineering model firing inside a Glenn vacuum chamber earlier this year.
NEXT-C is a powerful next-generation solar electric propulsion system that could propel future long-duration science missions. The technology was developed at Glenn, and the flight hardware was designed and built by Aerojet Rocketdyne. Over the next few months, the Glenn and Aerojet Rocketdyne team will conduct vibration, thermal vacuum and performance tests on the flight hardware. The test campaign will conclude this winter when engineers mate the thruster with its power processing unit for an integration test.
NEXT-C is scheduled for in-space testing on the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission in 2021. DART is a demonstration of technologies for preventing a hazardous asteroid from impacting Earth by changing the motion of the asteroid in space. The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) leads DART for NASA with support from several NASA centers.
Image Credit: NASA/Rami Daud, Alcyon Technical Services