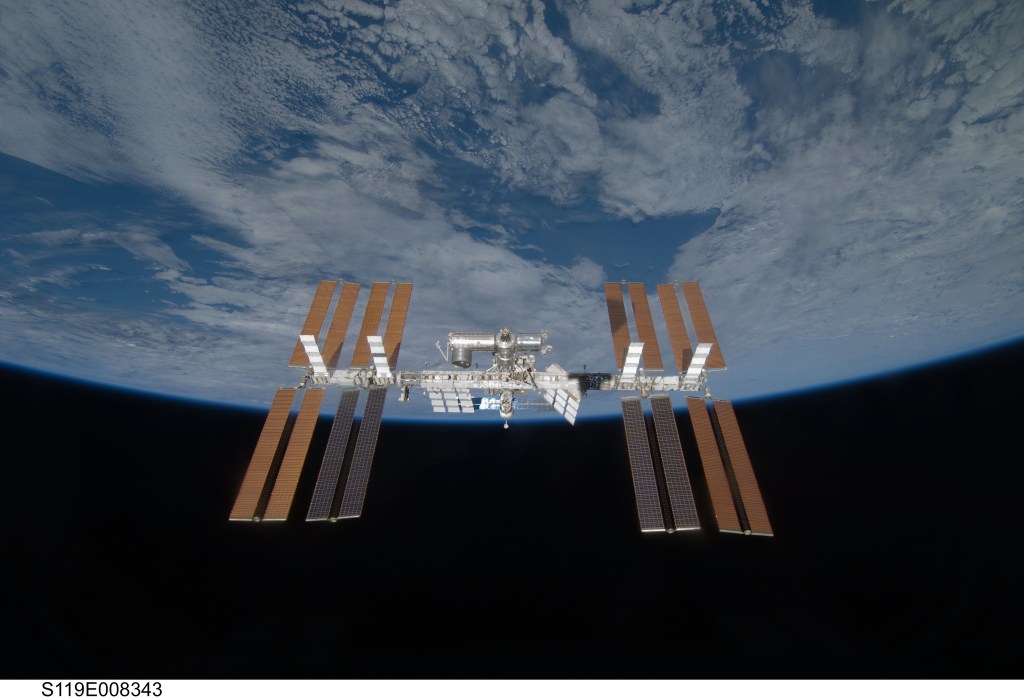
1. Why is the International Space Station up there?
The International Space Station is a convergence of science, technology, and human innovation that enables research not possible on Earth for the benefit of humanity. For more than 25 years, NASA has supported a continuous U.S. human presence aboard the station, through which astronauts have learned to live and work in space for extended periods of time.
The space station – which involves the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the ESA (European Space Agency) participating countries – is one of the most complex, interdependent international collaborations ever attempted. It brings together international flight crews and multiple space transportation providers, as well as globally distributed support teams, facilities, communications networks, and the worldwide scientific community.
Over the past 25 years, the space station has transformed into an orbiting laboratory with research capabilities that enable scientists from over 109 nations to conduct over 4,400 groundbreaking experiments in an extreme and unique spaceflight environment.
The space station serves as a springboard for developing a low Earth economy and NASA’s next great leaps in exploration, including missions to the Moon under Artemis and, ultimately, human exploration of Mars.
Learn more about the International Space Station, its research, and its crew, at:
2. How fast is the International Space Station traveling?
The International Space Station orbits the Earth once every 90 minutes. It travels at about 17,500 mph (28,000 kilometers per hour), which allows the crew onboard to see 16 sunrises and sunsets every day. Crews have occupied the space station continuously since November 2000. In that time, 280 people from 23 countries have visited the orbital outpost, and the station has circumnavigated the Earth hundreds of thousands of times.
3. How often can I expect to see the International Space Station?
The International Space Station is visible because it reflects sunlight – the same reason we can see the Moon. However, unlike the Moon, the space station is not bright enough to see during the day. Viewing opportunities can range from one a month to several a week as the light from the Sun reflects off station as it passes overhead at dawn and dusk at the user’s preferred location.
4. What is the Spot the Station mobile app?
The Spot the Station mobile app is an official NASA app that helps users track and receive notifications for International Space Station viewings as it passes over their respective location. It also provides real-time tracking, flyover schedules, and alerts.
5. How do I download the Spot the Station mobile app?
The Spot the Station mobile app is available on iOS and Android mobile and tablet devices.
6. How does the Spot the Station mobile app notify me of upcoming International Space Station viewing opportunities?
The Spot the Station mobile app sends push notifications to alert users of upcoming International Space Station passes, including the date, time, duration, and visibility conditions specific to a user’s preferred location. Users should ensure app notification permissions are enabled on their device’s settings.
7. Can I customize notifications in the Spot the Station mobile app?
The Spot the Station mobile app has the capability for personalized alert settings in order to receive push notifications specific to a user’s preferred location and timing of alerts.
8. What should I do if I am not receiving notifications?
Users should check the notification preferences on the Spot the Station mobile app to confirm the device is set up for alerts on a preferred location and timing. If users are still not receiving alerts, they should ensure notifications are enabled on their device’s settings.
9. Does the Spot the Station app work internationally?
The Spot the Station mobile app is available worldwide and in multiple languages. The app provides viewing information for most inhabited locations.
10. Why are there not viewing opportunities for my location?
The Spot the Station mobile app will only send push notifications for visible viewing opportunities in a user’s preferred location, but not every time the International Space Station is overhead. The best viewing experience for station is typically during twilight or nighttime.
11. Do I need a telescope to see the International Space Station?
No, users can view the International Space Station with their bare eyes, no additional equipment is required.
12. Does the International Space Station appear and then disappear because of the light of the Moon?
The International Space Station is visible because it is reflecting sunlight. This is the same reason that the Moon appears to shine. Even when the Moon hasn’t risen, users can see the station.
13. What time zone is used for alert notifications?
All content within the Spot the Station mobile app is listed in the local time zone for the user’s selected location. The app automatically adjusts for daylight savings time.
14. What information does the Spot the Station app provide for each sighting?
For each sighting, the Spot the Station mobile app displays the time, visibility duration, maximum height above horizon, and directions where the International Space Station will appear and disappear, helping users locate it accurately in the sky.
15. The flyover schedule indicates the International Space Station is both appearing and disappearing from the same direction, how is that possible?
The Spot the Station mobile app software rounds off directions to the nearest cardinal and intracardial directions. This can result in it seeming as though the International Space Station will be appearing and disappearing in the same direction even though it is traveling across the sky. This typically happens on flyovers with a short window of visibility because the station is quickly moving into (or out of) the Earth’s dark shadow where, from the user’s location on the ground, a full pass across the sky cannot be observed.
16. Can I view a live map of the International Space Station’s location?
Yes, the Spot the Station mobile app includes a real-time map showing the current position of the International Space Station as it orbits Earth, giving users a visual reference to track its progress.
17. What is the augmented reality feature in the Spot the Station mobile app?
The augmented reality feature in the Spot the Station mobile app allows users to view a virtual overlay of the International Space Station’s path in the sky. This feature helps users locate the station more accurately by aligning their device with the real-time position of the station.
18. How do I access the augmented reality feature in the Spot the Station app?
To access the augmented reality feature, open the Spot the Station mobile app and navigate to the “AR View” option in the bottom menu. Follow on-screen prompts to align the device’s camera with the sky, where the app will display a virtual overlay indicating the International Space Station’s position and trajectory.
19. Do I need a specific device or software to use the augmented reality feature?
The Spot the Station mobile app augmented reality feature requires a device that can determine its orientation in 3D space. It requires specific hardware support, such as a gyroscope or motion co-processor. Older or budget devices may not support this functionality.
20. How does the augmented reality feature work?
Using the device’s camera and sensors, the Spot the Station mobile app augmented reality feature superimposes the location of the International Space Station in the sky onto the screen, adjusting in real time as the user moves the device. The app guides users to point the device’s camera in the correct direction and shows where the station will appear and disappear.
21. Can I use the augmented reality feature during both day and night?
Yes, the augmented reality feature within the Spot the Station mobile app is available during both day and night; however, the best viewing experience is typically during twilight or nighttime when the International Space Station is visible to the naked eye. The augmented reality overlay will work regardless of the light conditions, but actual viewing opportunities depend on visibility.
22. Is the augmented reality overlay accurate for all locations?
Yes, the augmented reality feature within the Spot the Station mobile app is designed to provide accurate position information based on the device’s GPS location. However, accuracy may vary slightly depending on the device’s compass and sensor calibration. If users notice discrepancies, recalibrate the device’s compass through settings.
23. Can the augmented reality feature help with exact sighting times?
The augmented reality feature within the Spot the Station mobile app visually guides users to locate the International Space Station at the precise time it appears in the sky. Coupled with the app’s alerts, it enhances the ability to see the station by providing a live, visual direction and height indicator to precisely track it.
24. Are there tips for optimizing my augmented reality experience?
For the best augmented reality experience in the Spot the Station mobile app, use the feature in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Avoid obstructions like tall buildings or trees, as these can block visibility. Calibrate the device’s compass and ensure location services and camera permissions are enabled for smooth functioning.
25. Is the augmented reality feature available on both iOS and Android devices?
Yes, the Spot the Station mobile app augmented reality feature is available on both iOS and Android mobile and tablet devices, as long as the device meets the AR platform requirements (ARKit for iOS, ARCore for Android).
26. Does the Spot the Station mobile app work offline?
Some basic functionality, like accessing previously downloaded viewing opportunity schedules or receiving scheduled notifications, may work offline. However, features requiring real-time data, such as tracking, require cellular service or an internet connection.
27. Are there any special requirements for using the Spot the Station mobile app?
The Spot the Station mobile app requires active cellular service or an internet connection for real-time tracking and alerts. Additionally, for location-specific information, ensure the device’s location services are enabled for the app.
28. Is the Spot the Station mobile app free to use?
Yes, the Spot the Station mobile app is free to download and use, with no in-app purchases or subscriptions.
29. Who can I contact for Spot the Station mobile app support?
For support with the Spot the Station mobile app, reach out through the app’s feedback option or email the team at: hq-spotthestation@mail.nasa.gov.