At NASA, high-end computing is essential for many agency missions. This technology helps us advance our understanding of the universe – from our planet to the farthest reaches of the cosmos. Supercomputers enable projects across diverse research, such as making discoveries about the Sun’s activity that affects technologies in space and life on Earth, building artificial intelligence-based models for innovative weather and climate science, and helping redesign the launch pad that will send astronauts to space with Artemis II.
These projects are just a sample of the many on display in NASA’s exhibit during the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, or SC24. NASA’s Dr. Nicola “Nicky” Fox, associate administrator for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate, will deliver the keynote address, “NASA’s Vision for High Impact Science and Exploration,” on Tuesday, Nov. 19, where she’ll share more about the ways NASA uses supercomputing to explore the universe for the benefit of all. Here’s a little more about the work NASA will share at the conference:
1. Simulations Help in Redesign of the Artemis Launch Environment
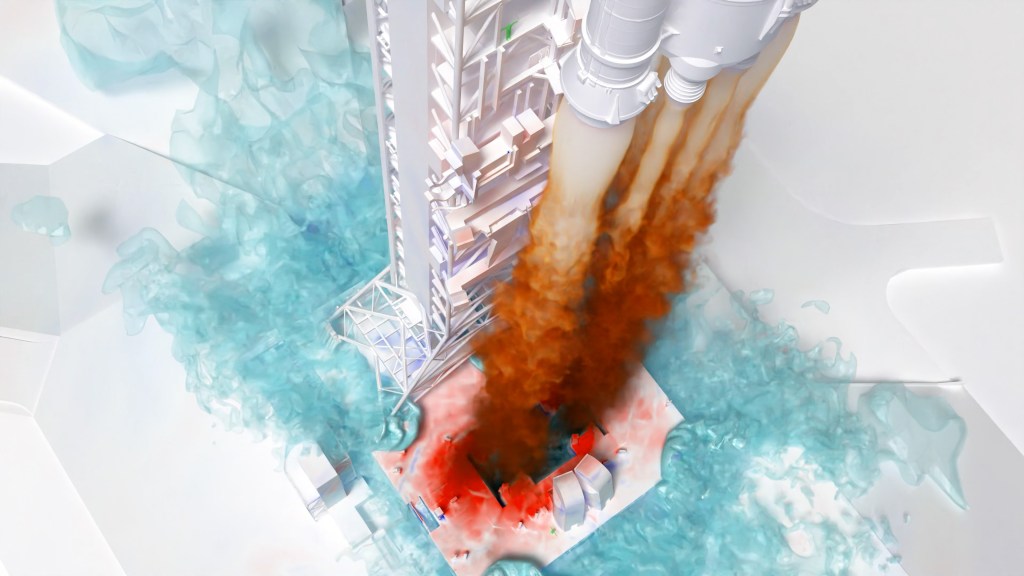
Researchers at NASA Ames are helping ensure astronauts launch safely on the Artemis II test flight, the first crewed mission of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft, scheduled for 2025. Using the Launch Ascent and Vehicle Aerodynamics software, they simulated the complex interactions between the rocket plume and the water-based sound suppression system used during the Artemis I launch, which resulted in damage to the mobile launcher platform that supported the rocket before liftoff.
Comparing simulations with and without the water systems activated revealed that the sound suppression system effectively reduces pressure waves, but exhaust gases can redirect water and cause significant pressure increases.
The simulations, run on the Aitken supercomputer at the NASA Advanced Supercomputing facility at Ames, generated about 400 terabytes of data. This data was provided to aerospace engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, who are redesigning the flame deflector and mobile launcher for the Artemis II launch.
2. Airplane Design Optimization for Fuel Efficiency
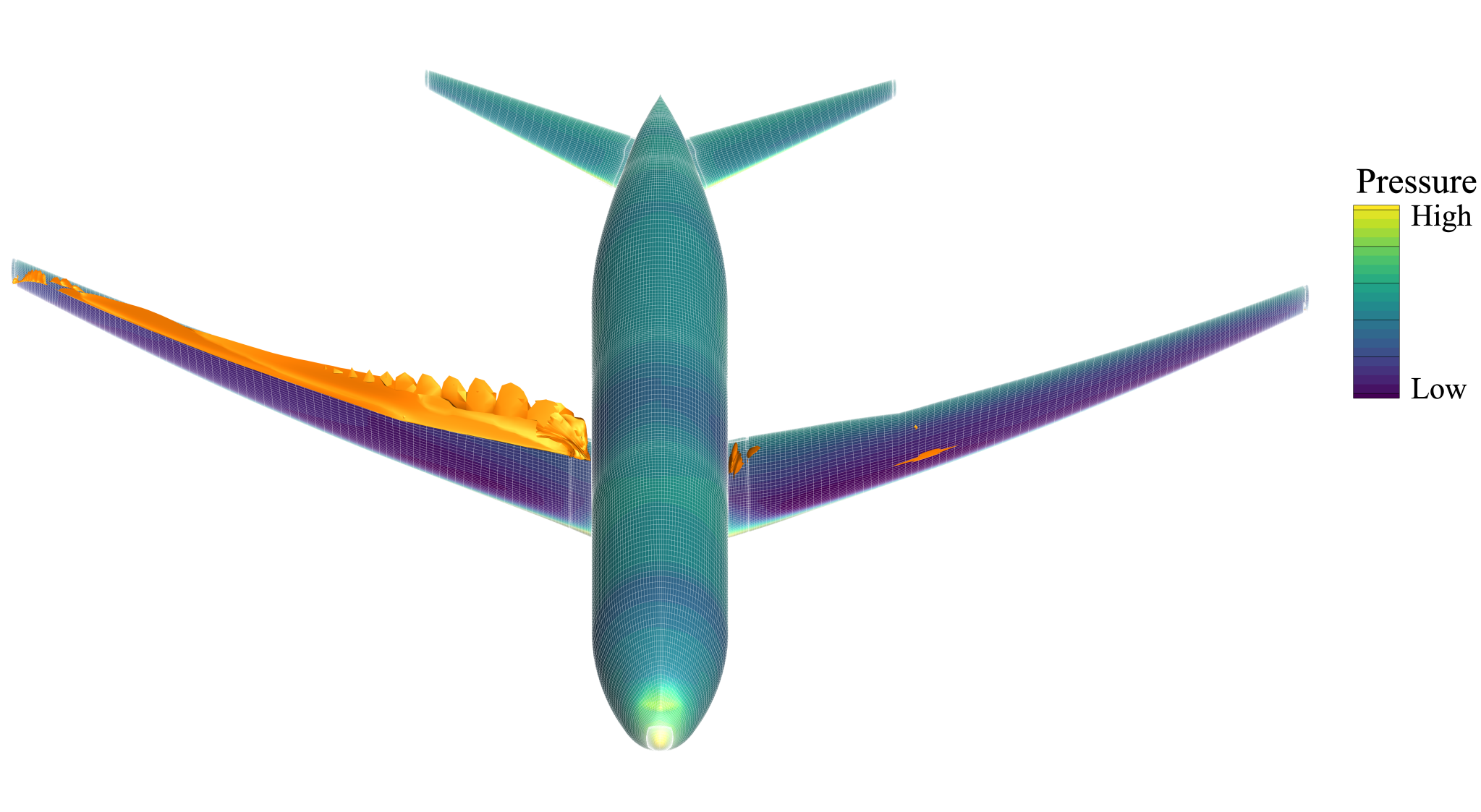
To help make commercial flight more efficient and sustainable, researchers and engineers at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley are working to refine aircraft designs to reduce air resistance, or drag, by fine-tuning the shape of wings, fuselages, and other aircraft structural components. These changes would lower the energy required for flight and reduce the amount of fuel needed, produce fewer emissions, enhance overall performance of aircraft, and could help reduce noise levels around airports.
Using NASA’s Launch, Ascent, and Vehicle Aerodynamics computational modeling software, developed at Ames, researchers are leveraging the power of agency supercomputers to run hundreds of simulations to explore a variety of design possibilities – on existing aircraft and future vehicle concepts. Their work has shown the potential to reduce drag on an existing commercial aircraft design by 4%, translating to significant fuel savings in real-world applications.
3. Applying AI to Weather and Climate
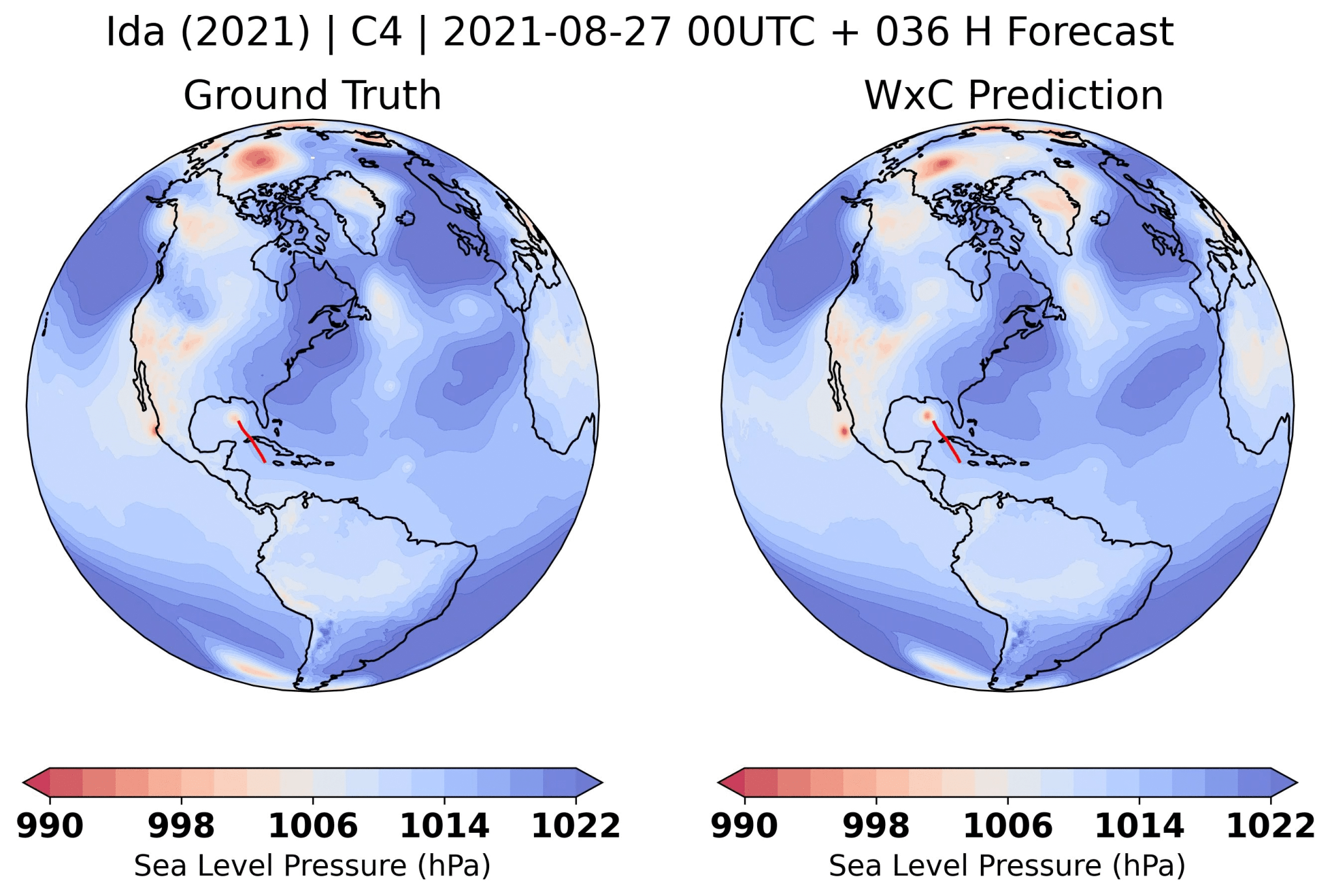
Traditional weather and climate models produce global and regional results by solving mathematical equations for millions of small areas (grid boxes) across Earth’s atmosphere and oceans. NASA and partners are now exploring newer approaches using artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to train a foundation model.
Foundation models are developed using large, unlabeled datasets so researchers can fine-tune results for different applications, such as creating forecasts or predicting weather patterns or climate changes, independently with minimal additional training.
NASA developed the open source, publicly available Prithvi Weather-Climate foundation model (Prithvi WxC), in collaboration with IBM Research. Prithvi WxC was pretrained using 160 variables from NASA’s Modern-era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA-2) dataset on the newest NVIDIA A100 GPUs at the NASA Advanced Supercomputing facility.
Armed with 2.3 billion parameters, Prithvi WxC can model a variety of weather and climate phenomena – such as hurricane tracks – at fine resolutions. Applications include targeted weather prediction and climate projection, as well as representing physical processes like gravity waves.
4. Simulations and AI Reveal the Fascinating World of Neutron Stars

To explore the extreme conditions inside neutron stars, researchers at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, are using a blend of simulation, observation, and AI to unravel the mysteries of these extraordinary cosmic objects. Neutron stars are the dead cores of stars that have exploded and represent some of the densest objects in the universe.
Cutting-edge simulations, run on supercomputers at the NASA Advanced Supercomputing facility, help explain phenomena observed by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) observatory. These phenomena include the rapidly spinning, highly magnetized neutron stars known as pulsars, whose detailed physical mechanisms have remained mysterious since their discovery. By applying AI tools such as deep neural networks, the scientists can infer the stars’ mass, radius, magnetic field structure, and other properties from data obtained by the NICER and Fermi observatories.
The simulations’ unprecedented results will guide similar studies of black holes and other space environments, as well as play a pivotal role in shaping future scientific space missions and mission concepts.
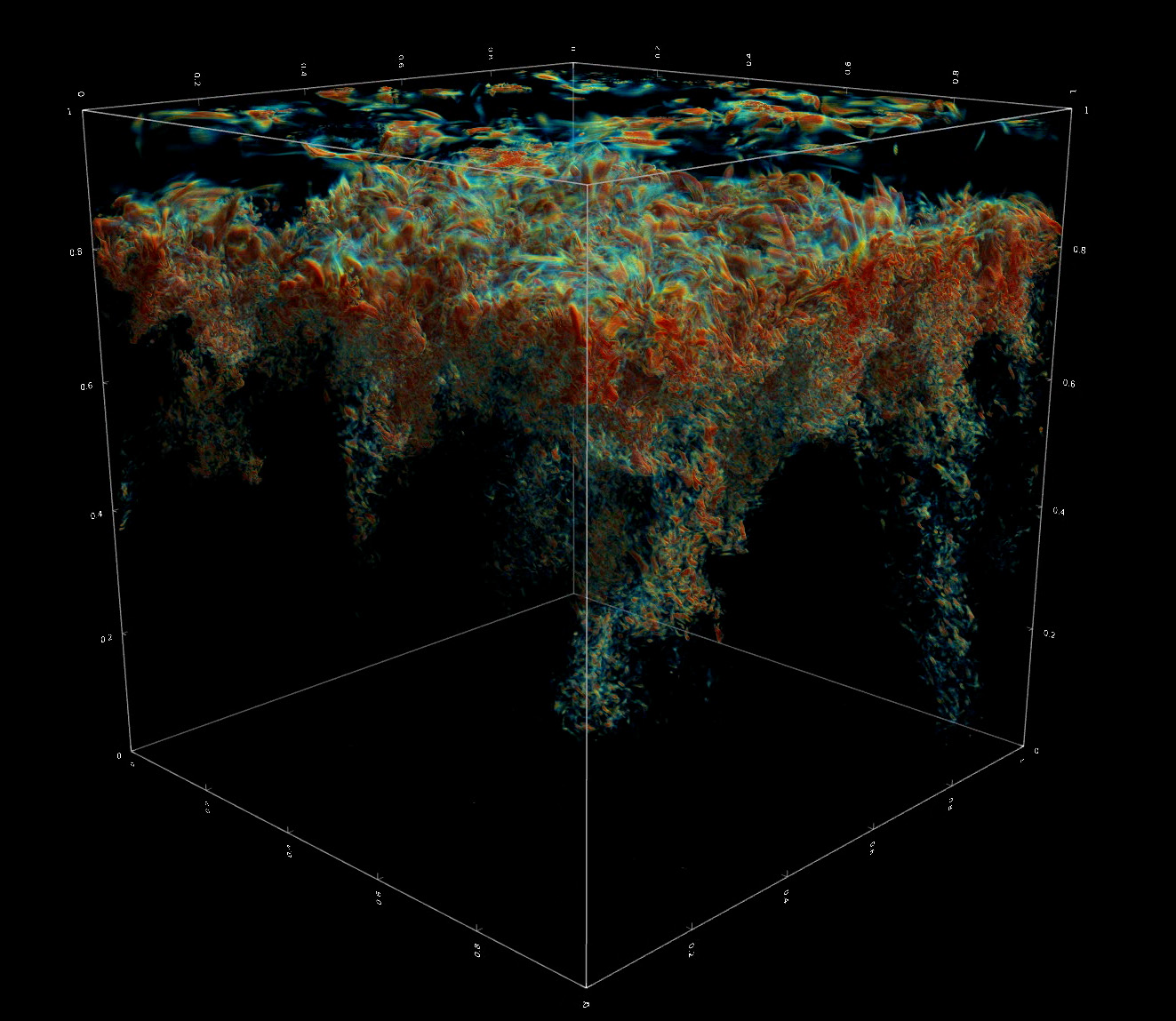
5. Modeling the Sun in Action – From Tiny to Large Scales
The Sun’s activity, producing events such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, influences the space environment and cause space weather disturbances that can interfere with satellite electronics, radio communications, GPS signals, and power grids on Earth. Scientists at NASA Ames produced highly realistic 3D models that – for the first time – allow them to examine the physics of solar plasma in action, from very small to very large scales. These models help interpret observations from NASA spacecraft like the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Using NASA’s StellarBox code on supercomputers at NASA’s Advanced Supercomputing facility, the scientists improved our understanding of the origins of solar jets and tornadoes – bursts of extremely hot, charged plasma in the solar atmosphere. These models allow the science community to address long-standing questions of solar magnetic activity and how it affects space weather.
6. Scientific Visualization Makes NASA Data Understandable
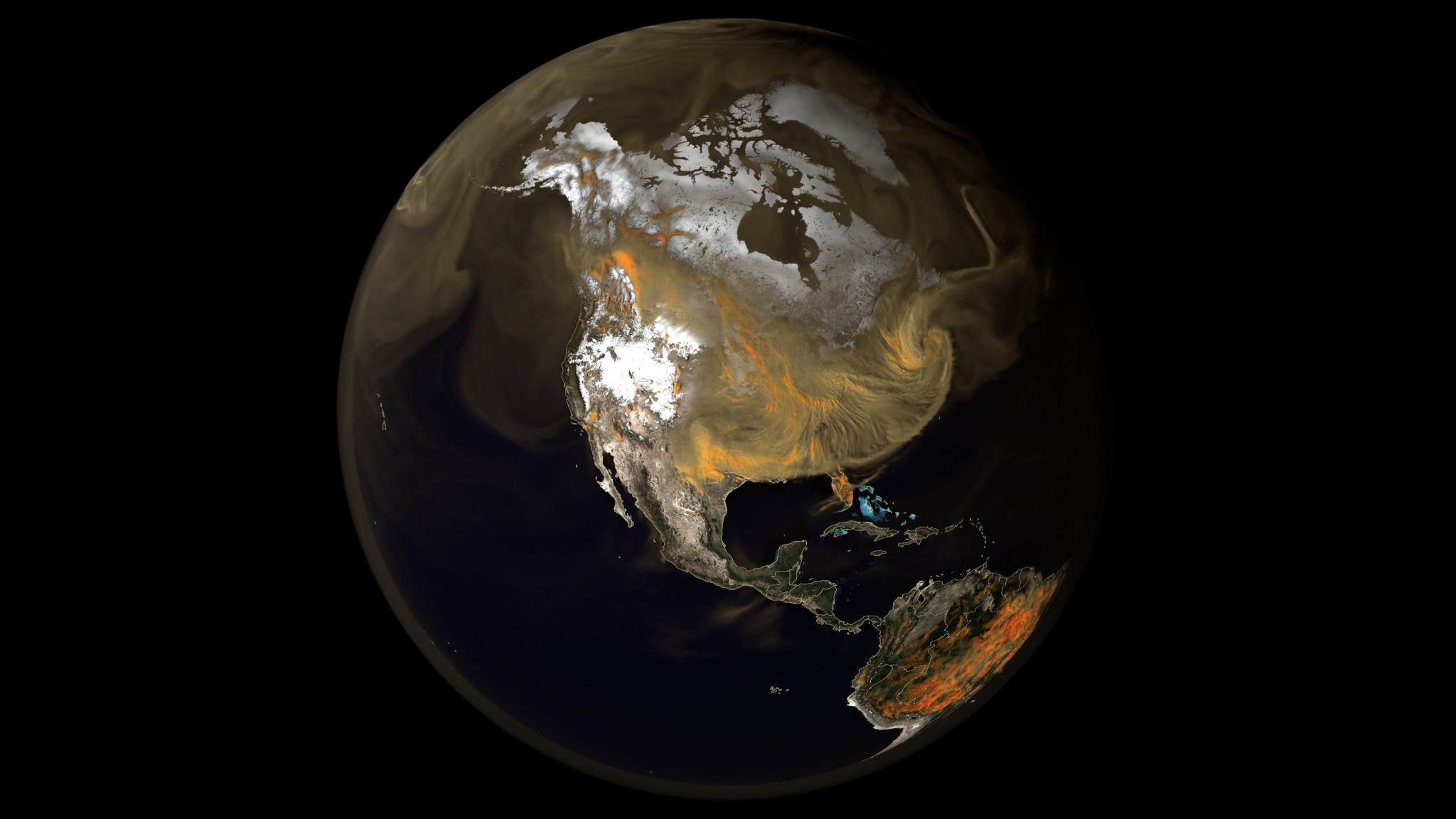
NASA simulations and observations can yield petabytes of data that are difficult to comprehend in their original form. The Scientific Visualization Studio (SVS), based at NASA Goddard, turns data into insight by collaborating closely with scientists to create cinematic, high-fidelity visualizations.
Key infrastructure for these SVS creations includes the NASA Center for Climate Simulation’s Discover supercomputer at Goddard, which hosts a variety of simulations and provides data analysis and image-rendering capabilities. Recent data-driven visualizations show a coronal mass ejection from the Sun hitting Earth’s magnetosphere using the Multiscale Atmosphere-Geospace Environment (MAGE) model; global carbon dioxide emissions circling the planet in the DYnamics of the Atmospheric general circulation Modeled On Non-hydrostatic Domains (DYAMOND) model; and representations of La Niña and El Niño weather patterns using the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) model.
For more information about NASA’s virtual exhibit at the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, being held in Atlanta, Nov. 17-22, 2024, visit:
For more information about supercomputers run by NASA High-End Computing, visit:
For news media:
Members of the news media interested in covering this topic should reach out to the NASA Ames newsroom.
Authors: Jill Dunbar, Michelle Moyer, and Katie Pitta, NASA’s Ames Research Center; and Jarrett Cohen, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center