Lee esta historia en español aquí.
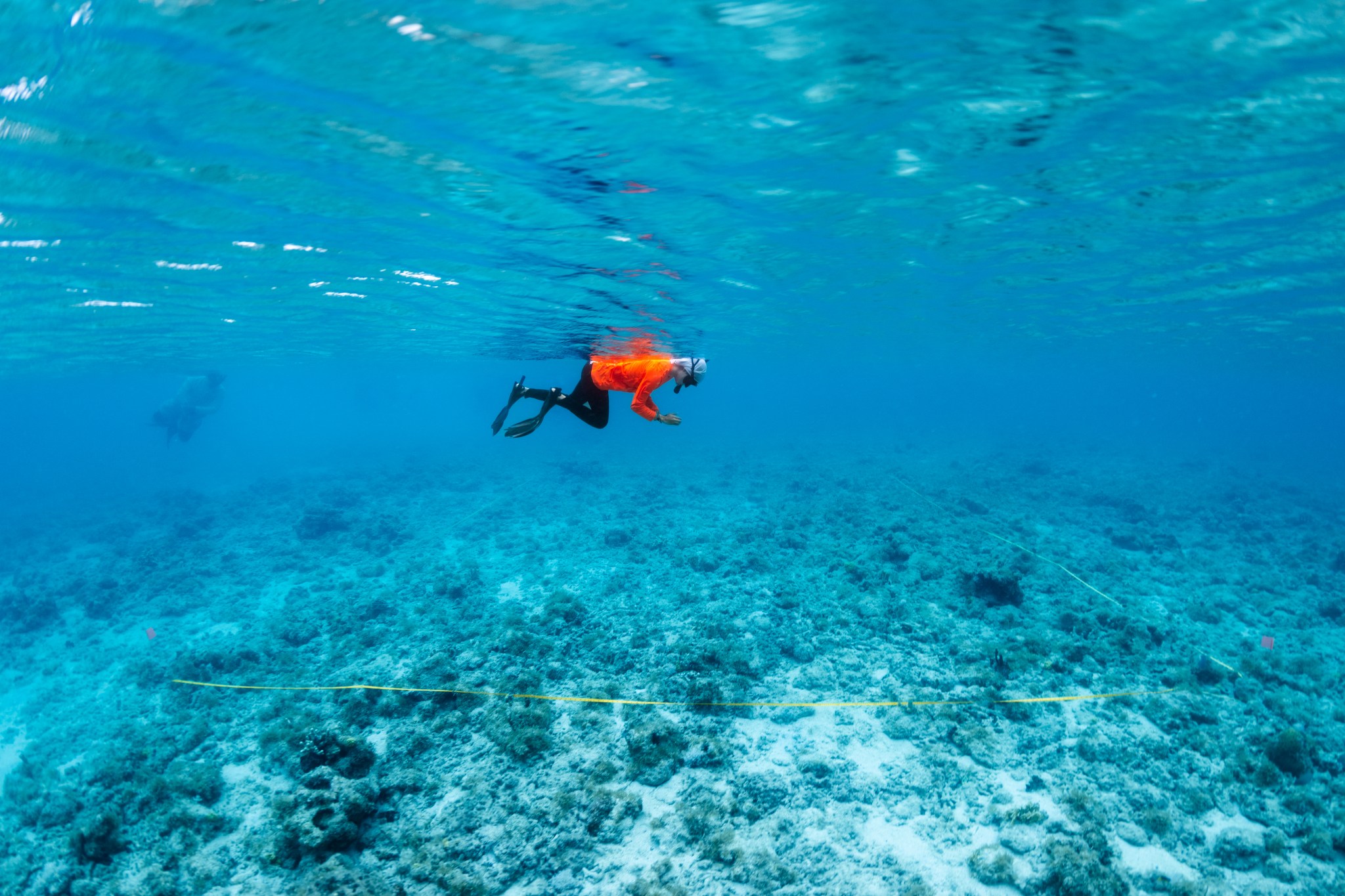
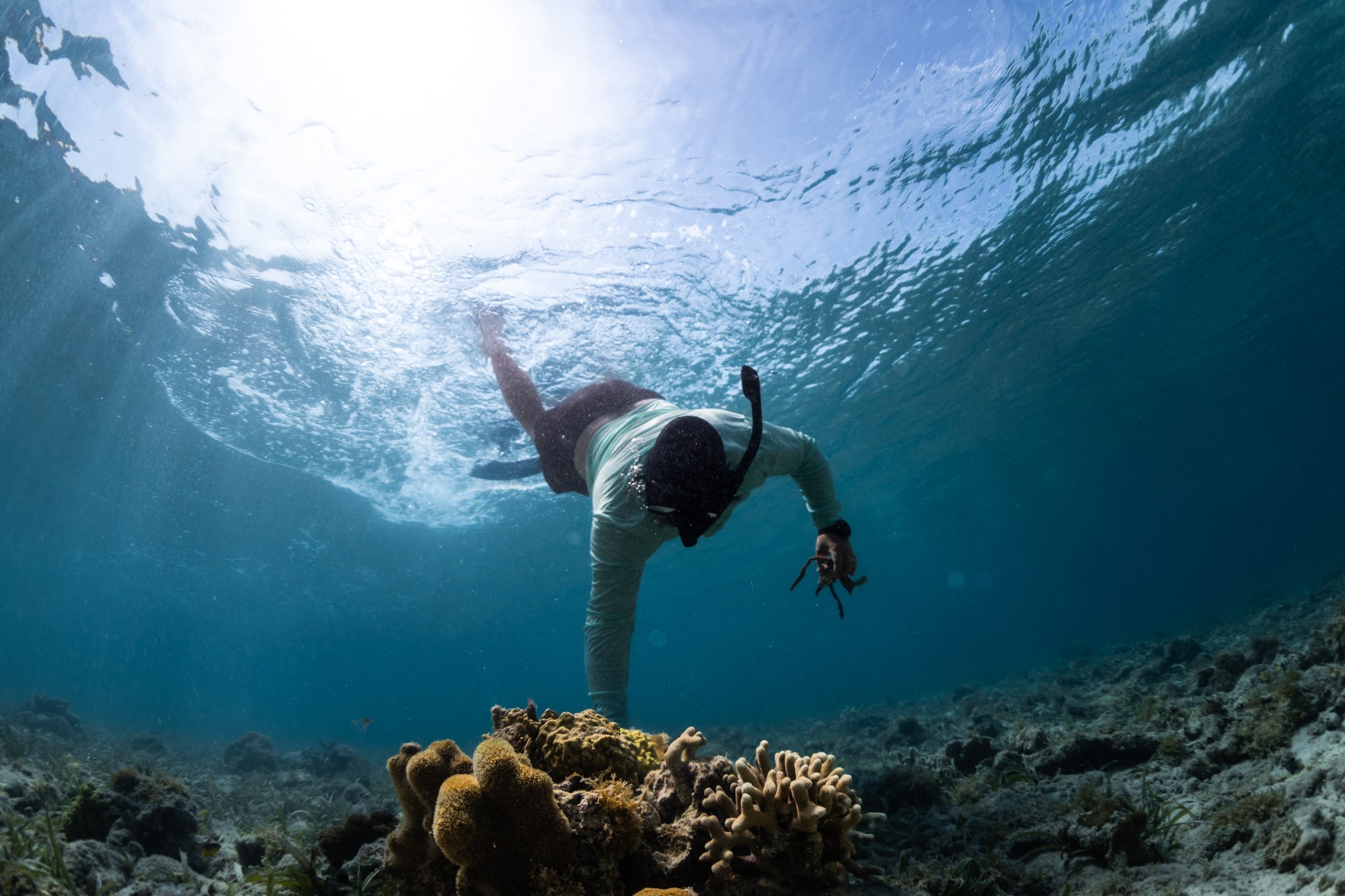
Tainaliz Marie Rodríguez Lugo took a deep breath, adjusted her snorkel mask, and plunged into the ocean, fins first. Three weeks earlier, Rodríguez Lugo couldn’t swim. Now the college student was gathering data on water quality and coral reefs for a NASA-led marine biology project in Puerto Rico, where she lives.
“There is so much life down there that I never knew about,” Rodríguez Lugo said. “And it’s beautiful.”
“There is so much life down there that I never knew about, and it’s beautiful.”

Tainaliz Marie Rodríguez Lugo
OCEANOS 2024 Intern
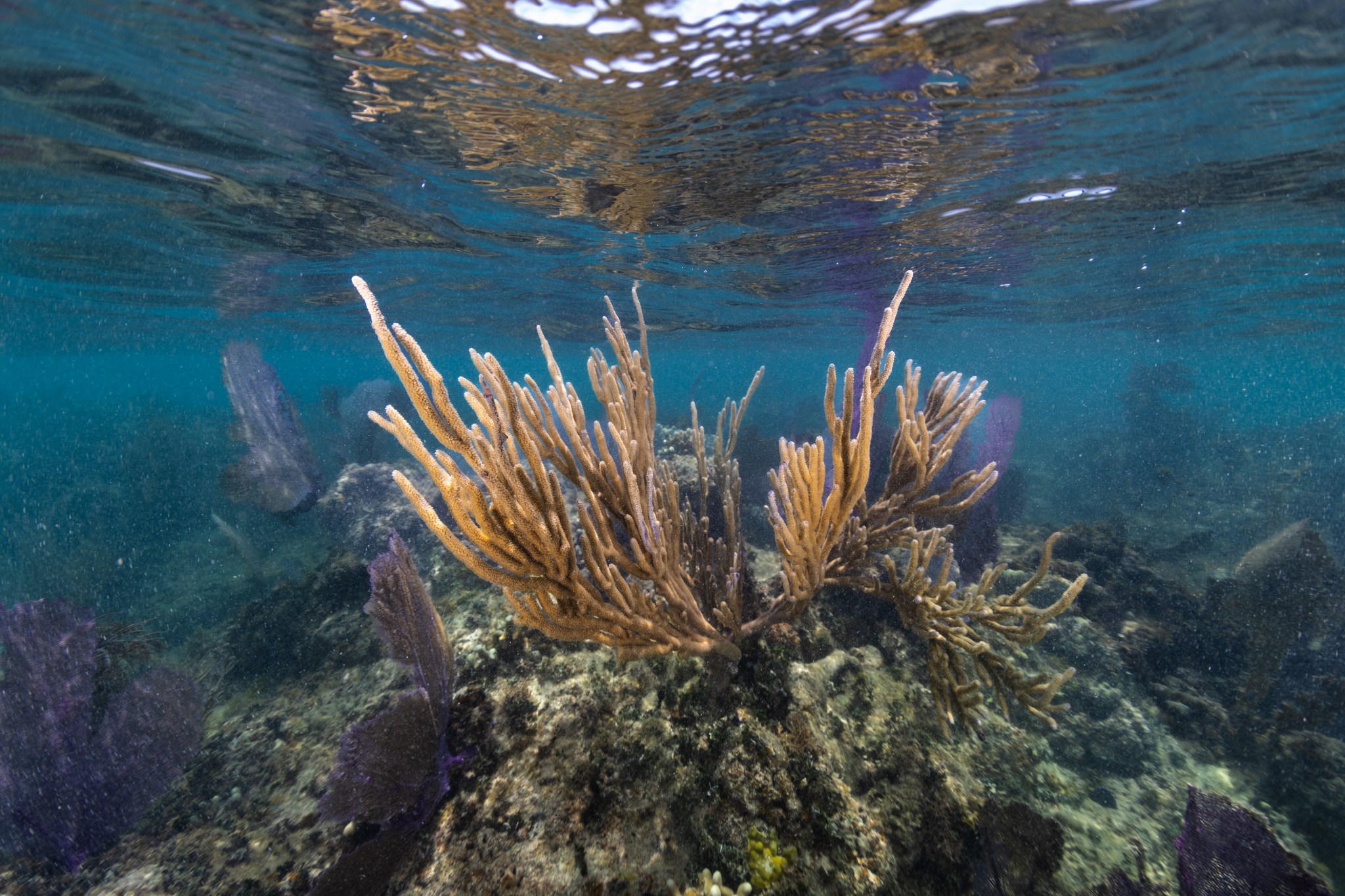
The sea whip and purple sea fans in the photo above are found off the coast of Playa Melones, Culebra, a small island off the east cost of Puerto Rico and a popular destination for snorkelers.
Puerto Rico is home to more than 1,300 square miles of coral reefs, which play a vital role in protecting the island from storms, waves, and hurricanes. Reef-related tourism provides nearly $2 billion in annual income for the island.
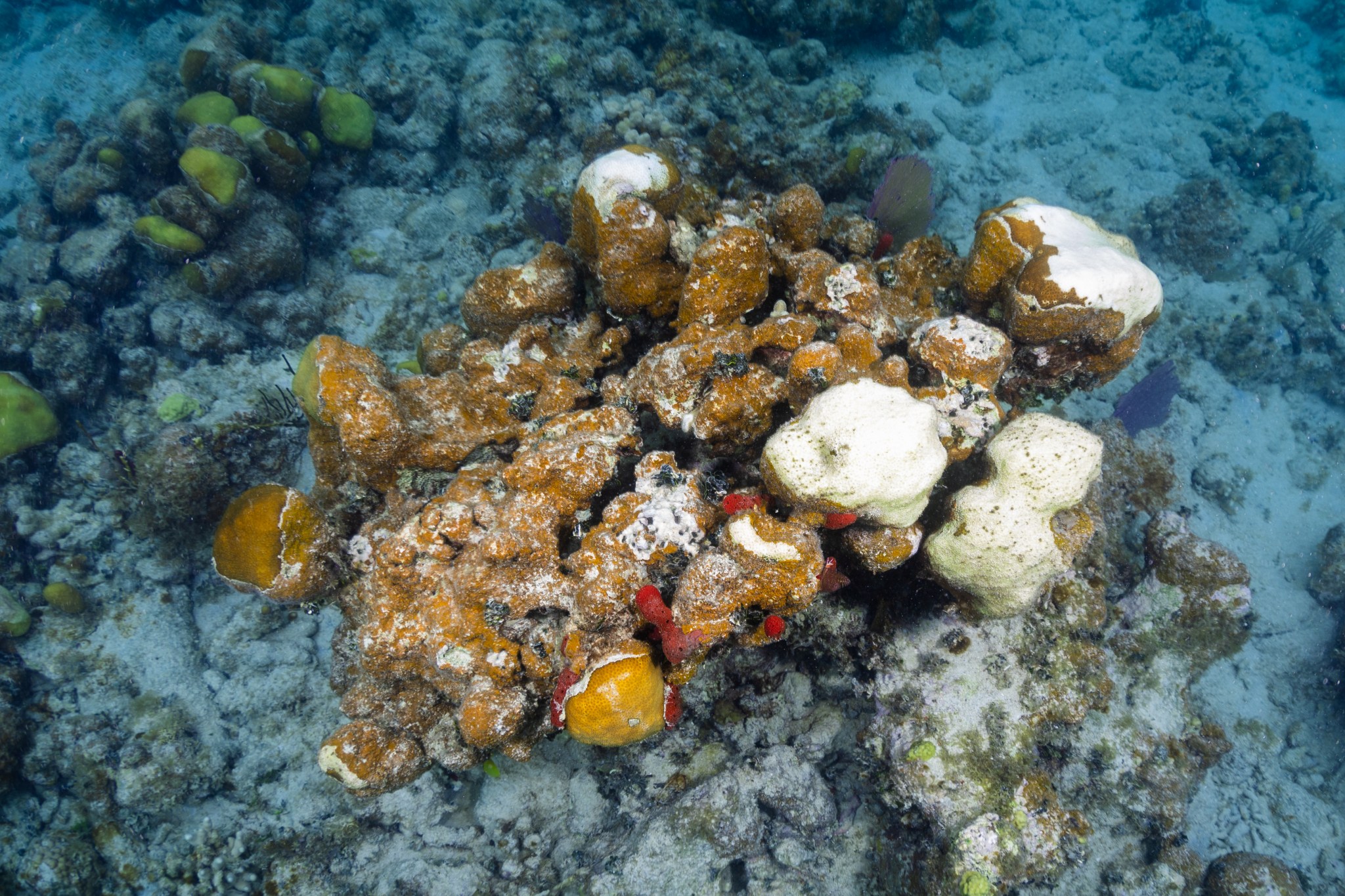
But coral reefs in Puerto Rico and around the world are experiencing more frequent and severe bleaching events. High ocean temperatures in regions around the globe have led to coral bleaching, which is when corals expel zooxanthellae – the colorful, symbiotic microscopic algae that live inside coral tissues and provide 80-90% of its nutrients. When stressors persist, the corals eventually starve and turn bone-white.
In April 2024, NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) announced that the world was experiencing a global bleaching event, the fourth on record. You can see bleached spots in the lobed star coral pictured above, which is also colonized by Ramicrusta, an invasive, burnt orange algae that poses an additional threat to reefs.
Students Are Given Ocean Research Tools
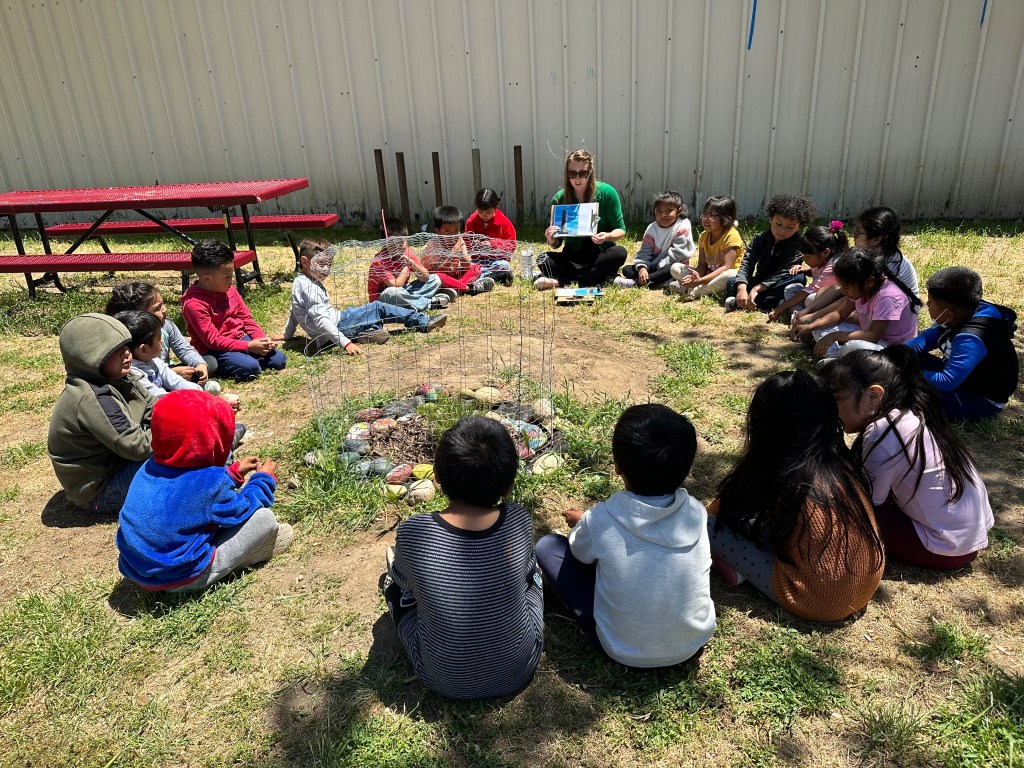
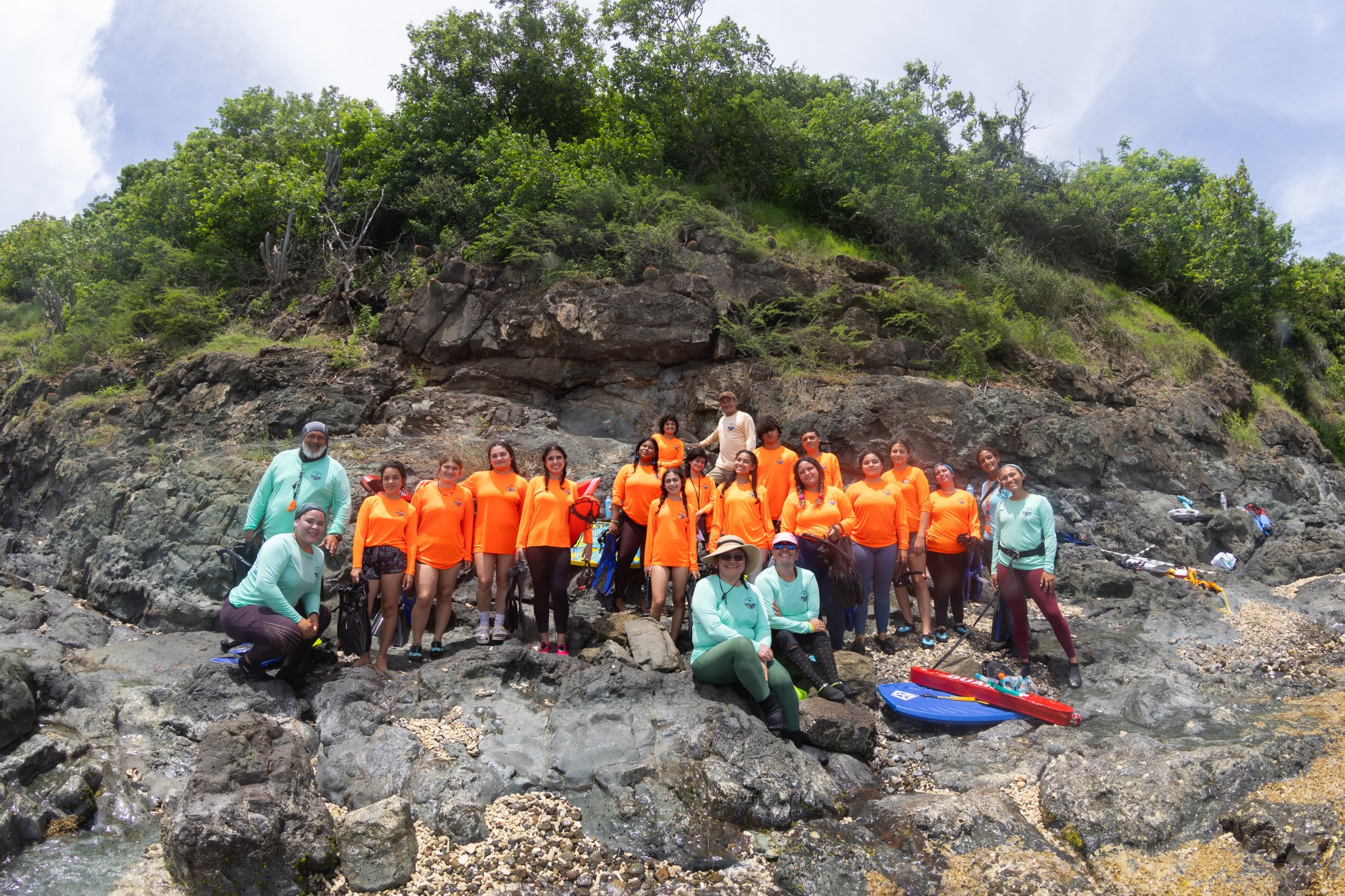
Beginning in June, the month-long program that Rodriguez and 29 other local students participated in is called the Ocean Community Engagement and Awareness using NASA Earth Observations and Science for Hispanic/Latino Students (OCEANOS). The goal of OCEANOS is twofold: to teach Puerto Rican students about marine ecology and conservation, and to train students through hands-on fieldwork how to use marine science tools to monitor the health of coral reefs.
The course included classroom instruction, scientific fieldwork, collecting and analyzing ocean data from La Parguera and Culebra Island, and a final presentation.
In the photo, OCEANOS instructor Samuel Suleiman shows a 3D-printed clump of staghorn coral to a group of students off the coast of Culebra. In areas where coral habitats have been damaged, conservationists use 3D-printed corals to attract and protect fish, algae, and other wildlife.
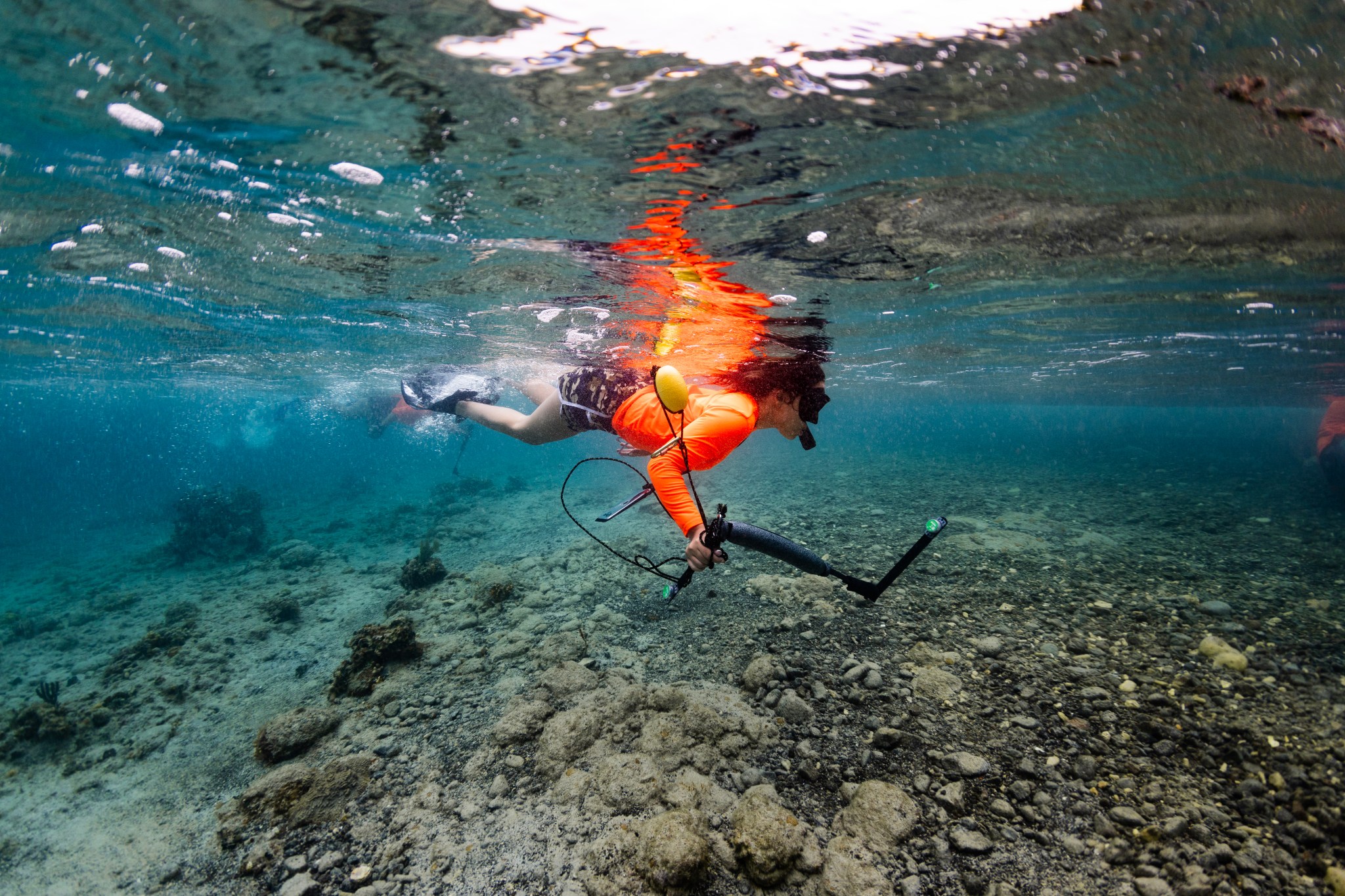
To practice coral surveying techniques and evaluate biodiversity,students used compact cameras to snap a photo every half second, recording seven-meter by seven-meter quadrants of the ocean floor. Back on land, the students stitched these images – roughly 600 images per quadrant – into high-resolution mosaics, which they then used to catalog the types and distributions of various coral species.
Low Light, Poor Water Quality, and Invasive Species Threaten Coral Reefs
Students also built their own low-cost instruments, with sensors on each end to measure temperature and light, to help assess water quality and characteristics.
The ideal temperature range for coral falls between 77- 82 degrees Fahrenheit (25-28 degrees Celsius). Water above or below this range is considered a potential stressor for coral and can impair growth. It can also increase the risk of disease, bleaching, and reproductive issues.
Coral relies on light for growth. Less light means less photosynthesis for the zooxanthellae that live inside the coral, which in turn means less food for the coral itself. Cloudy water due to excessive sediment or phytoplankton can dim or block sunlight.
Additional threats to coral include fishing equipment, boat groundings, chemical runoff, and invasive species.
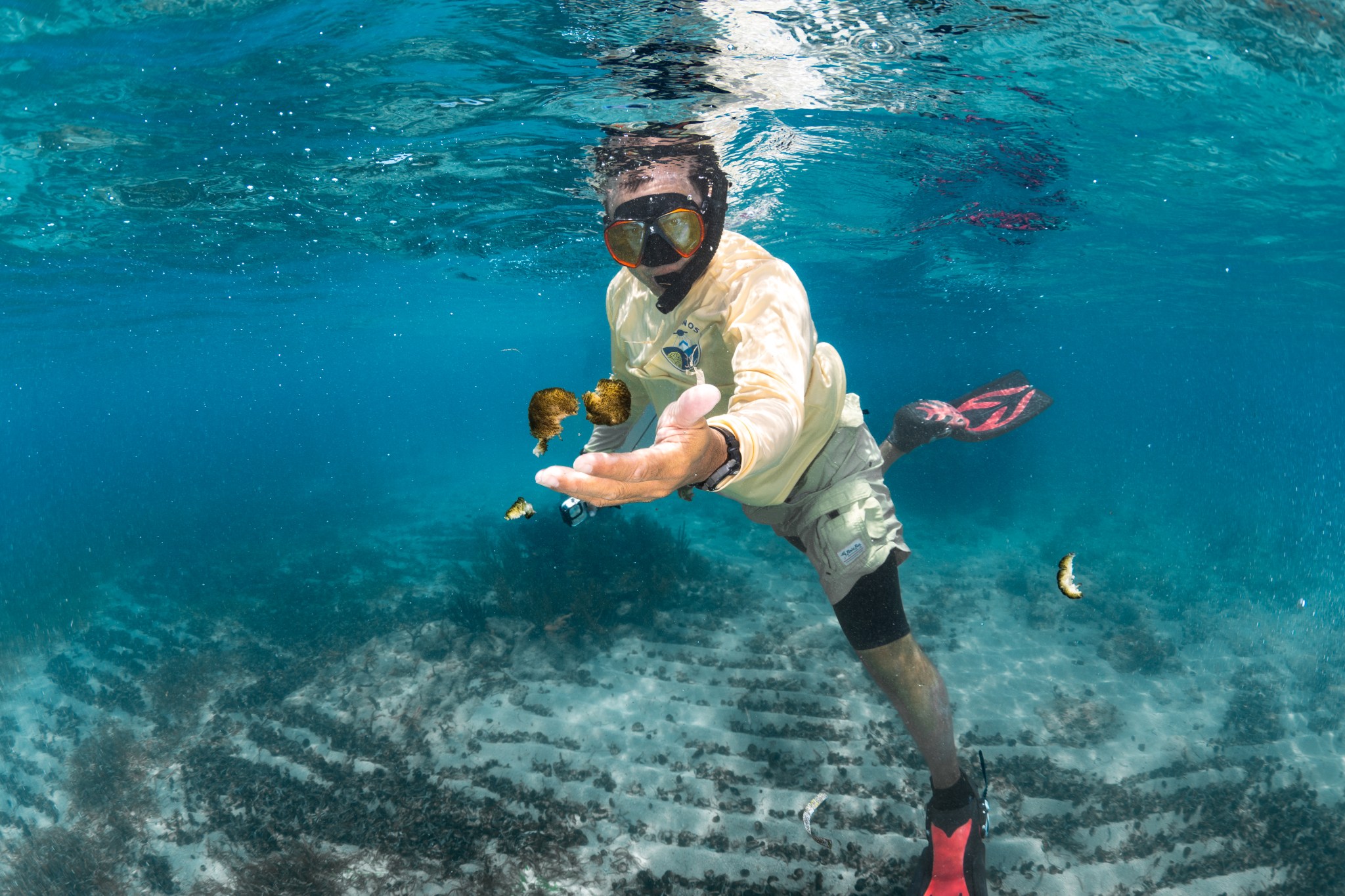
In the photo above, OCEANOS instructor Juan Torres-Pérez holds two clumps of cyanobacteria, a type of bacteria that has choked a section of reef near Playa Melones. The exact cause of this excessive cyanobacteria growth is unclear, but it is likely due to land-based pollution leaching into nearby waters, he said. In the background, dark brown piles of cyanobacteria littering the ocean floor are visible.
Students Help Grow and Plant New Coral
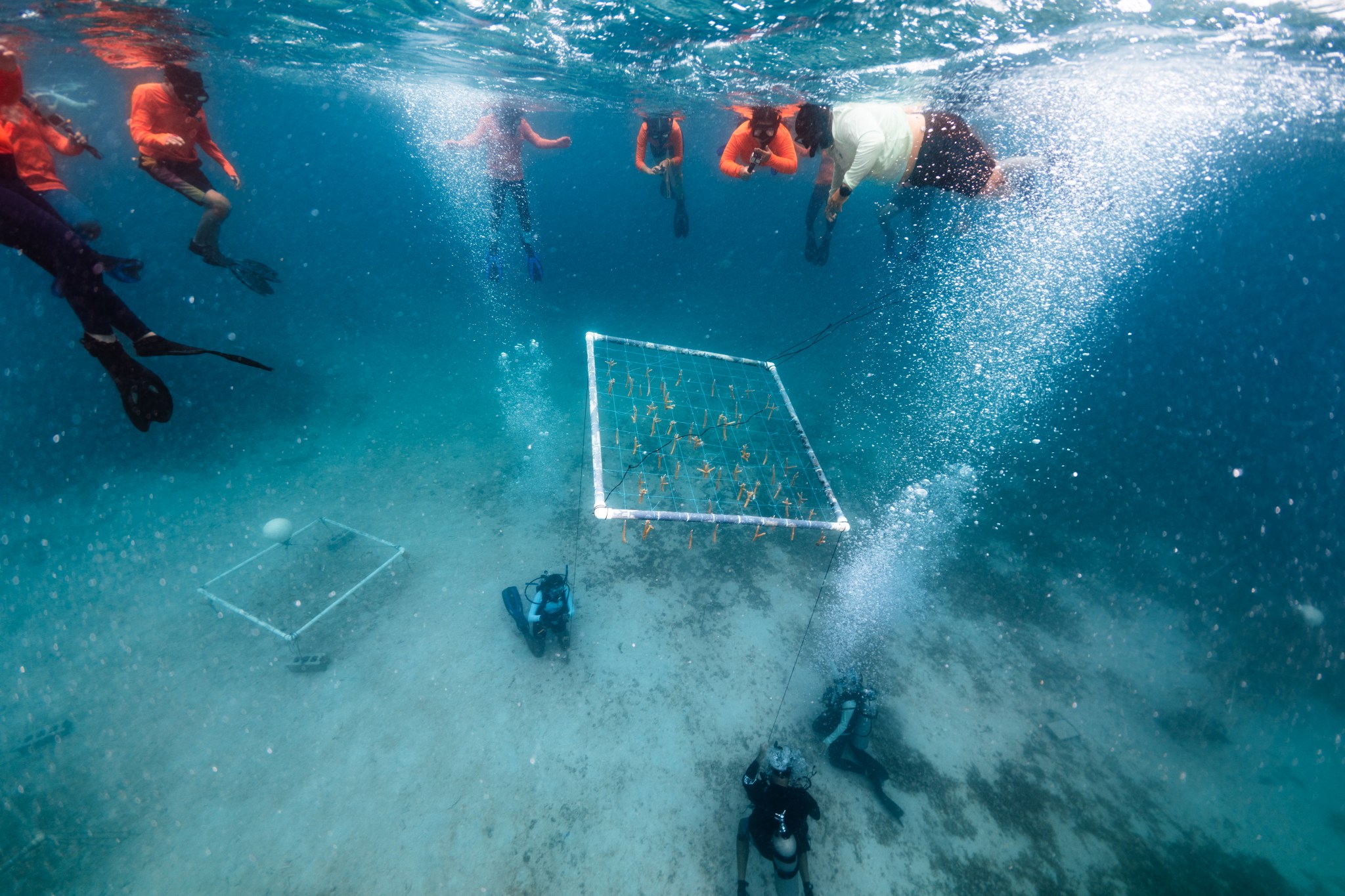
Suleiman walked students through the process of planting new coral, which involved tying loose staghorn and elkhorn corals into a square frame. Each frame holds about 100 individual pieces of coral. Suleiman leads a group called Sociedad Ambiente Marino (SAM), which has been working for more than 20 years to cultivate and plant more than 160,000 corals around Puerto Rico.
Divers anchored these frames to the ocean floor. Under ideal conditions, branching species like elkhorn and staghorn coral grow one centimeter per month, or about 12-13 centimeters per year, making them ideal candidates for coral reef restoration. By comparison, mountainous and boulder coral, also prevalent in the Caribbean Sea, grow an average of just one centimeter per year.
The frames will remain on the ocean floor for 10 to 14 months, until the corals have quadrupled in size. At any given time, SAM has about 45 of these frames in coral ‘farms’ around Culebra, totaling almost 4,500 corals.
Once the corals are ready to be planted, they will be added to various reefs to replace damaged or bleached corals, and shore up vulnerable habitats.
In the photo above, Suleiman gathers loose corals to place around an endangered coral species Dendrogyra cylindrus, more commonly referred to as Pillar Coral (front left). This underwater “garden,” as he called it, should attract fish and wildlife such as sea urchins, which will give the endangered coral — and the other species in this small reef — a better chance of survival.
A New Generation of Marine Scientists
From the 2023 OCEANOS class, roughly half of the undergraduate students went on to pursue marine science degrees, and many hope to continue with a post-graduate program. For a scientific field historically lacking diverse voices, this is a promising step.
Among the high school students in the 2023 class, three went on to change their degree plans to oceanography after participating in the OCEANOS program, while others are finding ways to incorporate marine science into their studies.
Francisco Méndez Negrón, a 2023 OCEANOS graduate, is now a computer science student at the University of Puerto Rico at Rio Piedras and wants to apply robotics to marine ecology. “My goal is to integrate computer science and oceanography to make something that can contribute to the problems marine ecosystems are facing, mostly originated by us humans,” Méndez Negrón said. He returned to the OCEANOS program to serve as a mentor for the 2024 class.
As for Tainaliz Marie Rodriguez Lugo, she managed to overcome her swim anxiety while discovering a love of the ocean. She credited the instructors who were patient, encouraging, and never left her side in the water.
“I was really scared going into this internship,” Rodríguez Lugo said. “I didn’t know how to swim, and I was starting a program literally called ‘Oceans.’ But now I love it: I could spend all day in the ocean.”
I was really scared going into this internship. I didn’t know how to swim, and I was starting a program literally called ‘Oceans.’ But now I love it: I could spend all day in the ocean.

Tainaliz Marie Rodríguez Lugo
OCEANOS 2024 Intern
When asked how she would describe coral to someone who has never seen one, Rodríguez Lugo just laughed. “I can’t. There are no words for it. I would just take them to the reefs.”
For more information about OCEANOS, visit:
The OCEANOS program’s final session will take place next year. Applications for the 2025 OCEANOS program will open in March. To apply, visit:
https://nasa.gov/oceanos-application
Photographs and story by Milan Loiacono, NASA’s Ames Research Center